3943
PET/MR in tumor differentiation of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a Preliminary Study of Multi-modality Imaging including PET, DWI, DCE and the combination1Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China
Synopsis
The purpose of our study was to evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of multiple parameters and the combination with PET/MR in tumor differentiation of HNSCC. The patients with clinical suspicion or diagnosis of HNSCC were included and had the PET/MR examination with 18F-FDG PET and multiple MR sequences. The results showed that there was no significant correlation among different parameters. The differences among groups of tumor differentiation were obvious with ADCmean and SUVmean. Finally, our study suggested that the multiple parameters of PET / MR could be complementary in diagnosis of tumor differentiation and the combination can further improve the performance.
Introduction
Recent studies have shown that the tumor differentiation of Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) was related to the tumor prognosis, which was helpful for optimal decision of treatment [1-2]. Therefore, for HNSCC patients, the current clinic needs to find a noninvasive means to predict the grading of pathological tumor differentiation for effective prognosis and assist of individualized treatment. The purpose of our study was to preoperatively evaluate the diagnostic efficiency of pathological differentiation with Positron emission tomography/Magnetic resonance imaging (PET/MR) by both independence and combination.Methods
patients with clinical suspicion or diagnosis by biopsy of HNSCC were included and had undergone PET/MR with multi parameters. All the patients had obtained the pathologic diagnosis subsequently. The PET/MR examination included 18F-FDG PET and MR sequences with T2WI, T1WI, diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and dynamic contrast enhanced imaging (DWI). The multi parameters of PET/MR including values of Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), standardize uptake value (SUV) and the mean values of parameters with DCE were calculated and measured. The parameters of DCE included the values of IAUGC(initial area under the concentration curve in 60 seconds), Ktrans(volume transfer coefficient), Kep (rate constant)and Ve (extracellular extravascular volume fraction). Pearson's correlation analysis was calculated between each parameter including values of ADCmean, SUVmax, SUVmean and the parameters of DCE. Box-plots and ANOVA were used to evaluate the distribution of parameters among the different groups of differentiation that were corresponded to the histo-pathological findings. Logistic regression was used to combine multi-parameters of PET/MR for diagnosis of tumors differentiation. The Cross-validation was calculated for combination. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.Results
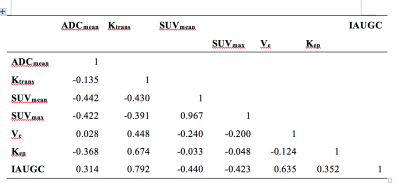
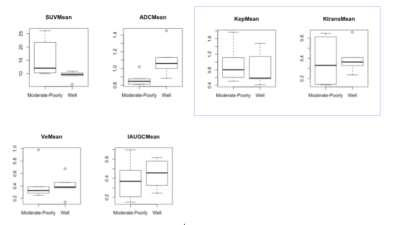
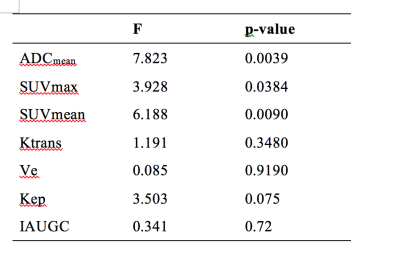
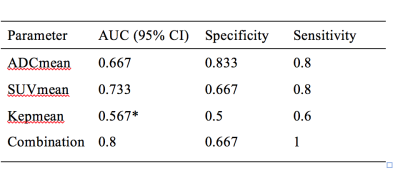
1) The study included 23 cases in all. 11 cases had received DCE examinations. 2) There were significant correlations between SUVmax and SUVmean. The other pairs of each parameter including ADCmean, SUVmax , SUVmean and the parameters of DCE were no statistical correlations. 3) The statistical differences among each group of tumor differentiation were obviously with ADCmean and SUVmean, while a slight difference with DCE parameters. 4) Kep was considered as the optimal parameters of DCE by variance analysis. We selected SUVmean, ADCmean and Kep to calculate the combined parameter of PET/MR by Logistic regression for the prognosis of the tumors’ differentiation. The combination had better predictive efficacy of tumor differentiation compared to the independent parameters with an area under curve(AUC) of 0.800.Discussion
This study showed that the values of SUV and ADC had a weak negative correlation in the PET / MR correlation analysis, which was similar to the previous report in separated PET and MR scanning [3-4]. It was accordant with the view that the tumor cells had an active proliferation lead to both the intensive cell density and increased metabolism [5]. According to the correlation analysis of each parameter, we believed that the combination of PET / MR parameters could complement each other to better describe the characteristics of tumor differentiation. We selected the three parameters including SUVmean, ADCmean and Kep, which had better discrimination between different pathological differentiated groups. The cross-validation showed that the combined model was more accurate for the pathological tumor differentiated with the area under the curve of 0.800. The combination significantly improved the predictive performance of tumor differentiation and helpful for prognosis and clinical decision in HNSCC. All the data in this study were obtained with integrated examination, which revealed a more reliable and accurate analysis. The similar studies were rare previously.
This study included two measurements of SUV including SUVmax and SUVmean. It was generally believed that SUVmean could avoid statistical noise and reflect the heterogeneity of tumors, but its stability and reproducibility is poor [6]. This study showed that there was a significant statistical difference in the distribution of SUVmean between different differentiated tumor groups, which was consistent with previous reports [7]. The accuracy of prediction in tumor differentiation of HNSCC was 0.733, which ranked top among all the PET / MR parameters.
Conclusion
The multi parameters of PET / MR can be complementary in diagnosis of tumor differentiation in HNSCC. The combination can further improve the predictive performance.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wang, B., Zhang, S., Yue, K. & Wang, X.-D. The recurrence and survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma: a report of 275 cases. Chin J Cancer 32, 614–618 (2013). 2. Kim, S., Smith, B. D. & Haffty, B. G. Prognostic factors in patients with head and neck cancer. Head and Neck Cancer: A Multidisciplinary Approach. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer 87–111 (2013). 3. Leifels, L. et al. Associations between 18F-FDG-PET, DWI, and DCE Parameters in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Depend on Tumor Grading. Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging 2017, 1–8 (2017). 4. Rasmussen, J. H. et al. Feasibility of Multiparametric Imaging with PET/MR in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. J Nucl Med 58, 69–74 (2017). 5. Varoquaux, A. et al. Diffusion-weighted and PET/MR Imaging after Radiation Therapy for Malignant Head and Neck Tumors. RadioGraphics 35, 1502–1527 (2015). 6. Rankine, L. The Effects of PET Reconstruction Parameters on Radiotherapy Response Assessment and an Investigation of SUV-peak Sampling Parameters. (2013). 7. Brendle, C. et al. Is the standard uptake value (SUV) appropriate for quantification in clinical PET imaging?–Variability induced by different SUV measurements and varying reconstruction methods. European Journal of Radiology 84, 158–162 (2015).Figures