3913
Hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate Imaging Predicts Survival in Rat C6 Glioma Model1Department of Radiology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States, 2Department of Neurology, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
The [1-13C]Lactate/[1-13C]Bicarbonate ratio at 48 hrs post-treatment, as measured in a hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate experiment, was found to accurately predict the survival in rat C6 glioma model treated with a single dose of the anti-VEGF drug Bevacizumab.
Introduction
Two primary metabolic fates of hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyruvate (Pyr) are its reduction to [1-13C]Lactate (Lac) via glycolysis (GLY) or conversion to acetyl coenzyme-A through oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), where it is detected as 13C-Bicarbonate (Bic), and metabolic reprogramming in tumor cells results in preponderance of GLY relative to OXPHOS (Warburg effect)1. A previous cross-sectional hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyr study of C6-glioma-bearing rats treated with the anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) drug Bevacizumab (B-20) demonstrated an acute shift of metabolism from GLY to OXPHOS (as measured by a decrease in the surrogate marker 13C Lac/Bic ratio), an effect that begins to wane for some animals after 48 hrs2. Given that a single dose of B-20 is known to produce a 25% long-term survival in this tumor model, we conducted a longitudinal study to test the hypothesis that the 13C Lac/Bic ratio 48 hrs post B-20 treatment is predictive of survival.Methods
C6 glioma cells (~1x106) were injected into the right striatum of male Wistar rat (N=13, 236-293g) and imaged 10 days post-implantation on clinical 3T (GE PET/MR scanner and SPINlab polarizer, 1H-13C dual-tuned Rf coil, T2-weighted 1H MRI, 125 mM bolus of hyperpolarized [1-13C]Pyr followed by 13C free-induction decay MRSI with 16x16 phase encodes, 5 mm slice, 64 mm FOV, and 5kHz spectral bandwidth, beginning 30s post bolus injection, and post-contrast T1-weighted 1H MRI). Metabolite maps were generated by integrating the corresponding Lac and Bic peaks in absorption mode after applying 15Hz line broadening and interpolating by a factor of 4 in both spectral and spatial dimensions. The rats were then treated with intraperitoneally administered (5mg/kg) anti-VEGF monoclonal antibody B20-4.1.1 (Roche/Genentech, South San Francisco, CA, USA) and again imaged 48 hrs post treatment. All animals were subsequently monitored until they were either euthanized by day 17 due to worsening of symptoms from the tumor (deceased) or lived to 70 days (survivor).
Results & Discussion
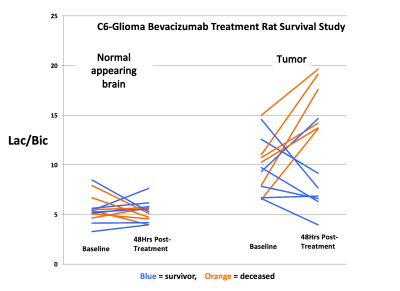
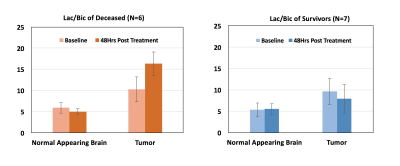
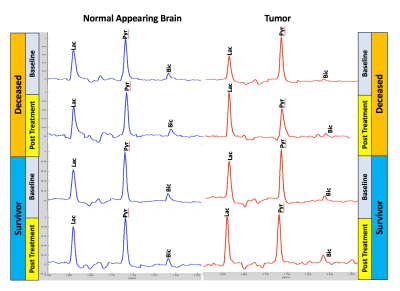
Figure 1 shows summary data for the 13C Lac/Bic ratios measured at baseline and 48-hrs post-treatment from normal appearing brain and tumor regions-of-interest (ROIs). While there were no significant metabolic changes detected in normal appearing brain, all deceased animals (N=6) showed an increase in tumor Lac/Bic at 48 hrs. In contrast, 6 of the 7 rats that survived showed a decrease in tumor Lac/Bic ratio. Mean values of the Lac/Bic ratios for the two cohorts in the healthy and tumor ROIs before and after treatment (Figure 2) clearly depicts the differences between the deceased and the survivor rats (p=0.014, log rank test). Representative normalized spectra comparing the baseline and 48 hrs post treatment metabolic profiles of the deceased and survivor animals (Figure 3) provide insight into the Lac/Bic ratios seen in the tumor ROI: while there is an increased production of lactate via GLY in the non-survivor, the increase of Bic in the survivor suggests a shift of the underlying OXPHOS towards that of healthy tissue in response to the anti-VEGF treatment. The sensitivity and specificity of the 48-hr Lac/Bic ratio for predicting long-term survival were 100% (95% CI: 54.1-100%) and 71.4% (95% CI: 29.0-96.3%) respectively. An increased number of rats would be needed to tighten these confidence intervals. For example, at the observed prevalence for this study of 50%, N=17 would be required to achieve 90% sensitivity and 90% specificity with a 0.2 precision.Conclusion
This study showed that the 48-hrs post-treatment 13C Lac/Bic ratio in a rat C6 glioma model is a potential biomarker for response to anti-VEGF treatment. The decrease of Lac/Bic in the tumor region of the survivors suggest a shift of the underlying GLY/OXPHOS balance towards that of healthy tissue, whereas the deceased animals demonstrated the opposite trend.Acknowledgements
NIH grants R01CA176836, R01EB019018, P41EB01589, S10OD012283, GE Healthcare, and the Lucas Foundation. Thanks to Dr. T. Liang and Dr. J. Rosenberg for help with the statistical analyses.
References
1. Najac C and Ronen SM. MR Molecular Imaging of Brain Cancer Metabolism Using Hyperpolarized 13C Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Oct;25(5):187-196.
2. Park JM, et al. Hyperpolarized (13)C-lactate to (13)C-bicarbonate ratio as a biomarker for monitoring the acute response of anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) treatment. NMR Biomed. 2016 May;29(5):650-9.
Figures