3849
IceVespa: Automated Inline MR Spectral Processing and Fitting on the Clinical Platform1Radiology Center for Advanced MR Development, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC, United States, 2Center for Magnetic Resonance Research, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, United States
Synopsis
The IceVespa module is a flexible add-in functor for the Siemens IceProgramF ICE pipeline for MRS data. Raw MRS data is sent to a Python-based Vespa-Analysis spectral processing node via an XML-RPC client/server. Graphical and tabular spectral analysis fitting results are returned to the ICE pipeline and saved in the standard DICOM workflow. Analysis executes in its own process. XML-RPC was chosen for inter-process communication for its simplicity and flexibility for relocating the processing node using standard HTTP protocols. Combining Python-based IceVespa inline with standard C++ ICE processing increases processing algorithm choice while maintaining clinical access to quantitative MRS measures.
Rationale and Purpose
MRS analysis software provided on clinical scanners can only be utilized for visual inspection of spectra and basic quantification of metabolite ratios. To access advanced post-processing and quantification tools that provide quantitative error estimates, clinical MRS data need to be transferred off the MR scanner to an external workstation. In most cases, this results in the entire processing, analysis and archival workflow taking place outside of the standardized clinical MRI DICOM workflow, which presents an impediment to widespread clinical use1. We describe a flexible add-in module for the Siemens IceProgramF ICE processing pipeline by which raw MRS data is sent to the Python-based Vespa-Analysis spectral processing application and spectral analysis results in the form of graphical and tabular fitting results are returned to the standard DICOM workflow.Architecture and Implementation
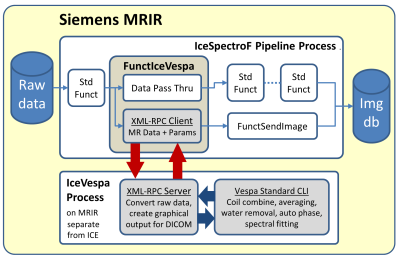
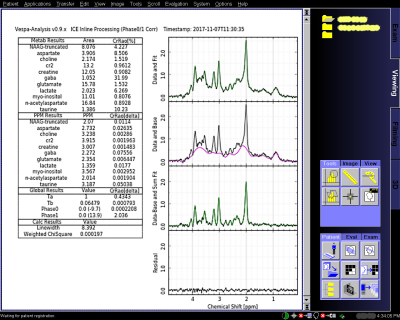
The overarching goal is to create a next generation, turnkey single voxel MRS workflow for clinical research. We chose the Vespa software package for spectral analysis based on its open source software license and comprehensive selection of spectral analysis algorithms. Vespa2 is a cross-platform, Python-based package that provides tools for RF pulse design, spectral simulation, and spectral processing/analysis of MRS data (Vespa-Analysis module). It is OS agnostic and accesses most MR manufacturer data formats. This project modified the Analysis module to work inline with the Siemens IceProgramF ICE processing pipeline, both on the MRIR platform, which removes a significant barrier to clinical usage, namely, the need for offline spectral processing that removes spectral analysis reporting from the clinical workflow. Fig.1 shows project software architecture. Our custom IceVespa functor is inserted into the IceProgramF pipeline after the first (Flags) standard functor. Raw data from coils and averaging is accumulated while also being passed through IceVespa for Siemens processing. Following the last signal average, the IceVespa functor sends the accumulated data to an Analysis processing node on the MRIR, which returns a 512x512 bitmap graphic of the spectral fitting results (Fig.2) and text-based ‘csv’ formatted metabolite fit measures to the IceVespa functor. The graphic is saved to the Siemens image database as a ‘derived image’ in RGB format in a separate series from IceProgramF results. Metabolite fit ‘csv’ measures are stored in a proprietary tag of the derived RGB image and available for export to statistical analysis software. Analysis executes in its own process to avoid incompatible shared library collisions. XML-RPC was chosen for inter-process communication for its low overhead, straightforward interface and availability for both Python and Windows XP Visual Studio 6. XML-RPC also allows the Vespa processing node to be easily relocated to any platform that can be reached using standard Web protocols. The IceVespa functor spawns the remote XML-RPC server process automatically during pipeline initialization and calls an internal quit() method for shutdown during pipeline cleanup. The vespa_process() XML-RPC method is called after all data and acquisition parameters are available, and blocks the IceSpectroF pipeline until completion. All subsequent processing is performed in Python using the standard Vespa-Analysis command line API. IceVespa functionality can be added to any ICE pipeline whose basis is the IceProgramF configurator. Analysis Preset files, that control processing, are in a shared console folder. The sequence name string is passed to the vespa_process() method to inform Preset selection for known sequences, but can also be specified dynamically at run time via a string attribute in the ICE configurator ‘evp’ file.Results and Discussion
An example of an IceVespa derived image result is shown in Fig.2 for a TE=30ms PRESS acquisition on the Siemens 3T platform. Post-processing was completed within ~6 seconds after the last TR. This image remains the same whether viewed on the MR console or exported to an external DICOM viewer. The only difference between a standard Vespa-Analysis installation and the Siemens ICE inline version is that Python (miniconda by Anaconda, Inc.) and the Vespa package is manually installed on the MRIR since it is not attached to the Internet. Standalone Vespa-Analysis saves spectral analysis results into a Vespa Interchange File Format XML schema (VIFF) that preserves a full provenance of all processing and intermediary results. By setting a flag in the ‘evp’ file, Analysis results can also be saved in VIFF format to a shared folder on the MR console for debugging purposes (or if desired for clinical research provenance). This work demonstrates that advanced spectral processing and fitting can be incorporated into the workflow on the scanner without having to take the data offline and is thereby expected to enhance integration of MRS into the clinical workflow.Acknowledgements
Funding from NIH grants 1R01NS080816, 1R01DK093568, P41 EB015894 and P30 NS076408, and excellent technical advice from Philip Semanchuk, PySpoken.comReferences
1. Oz G, Soher BJ, Kaupinnen R, et.al. Clinical proton MR spectroscopy in central nervous system disorders. Radiology 270(3):658-79 (2014)
2. Soher BJ, Young K, Semanchuk P, Todd D. Vespa - Versatile Simulation, Pulses and Analysis, URL https://scion.duhs.duke.edu/vespa/project
Figures