3827
Intravoxel Incoherent Motion MR Imaging in the Differentiation between Benign and Malignant Sinonasal Lesions: Comparison with Conventional Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging1Radiology, Eye & ENT Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 2Jinshan Hospital of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, 3Siemens Healthcare Ltd., Shanghai, China
Synopsis
This study aimed to evaluate the value of intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) in the differentiation between benign and malignant sinonasal lesions and to compare the diagnostic performance of IVIM with conventional diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Our preliminary study shows that ADC, D and f values may be considered as discriminating markers for identifying benign and malignant sinonasal lesions. The combination of D and f values demonstrates significantly higher sensitivity, specificity and accuracy than the ADC value, revealing that IVIM appears to be a more valuable tool than conventional DWI for distinguishing benign from malignant sinonasal lesions.
Introduction
Cross-sectional imaging techniques, such as CT and MRI, play an important role in the differentiation of sinonasal lesions [1-3]. Nevertheless, routine morphological imaging or even quantitative MR features (e.g. ADC map) of benign and malignant sinonasal lesions are often overlap [1-3]. Recently, IVIM MRI has emerged as a promising method for the differentiation of head and neck tumors. The purpose of our study was to investigate IVIM method for distinguishing between benign and malignant sinonasal lesions and to compare the differential diagnostic performance of IVIM with conventional DWI in sinonasal lesions.Materials and methods
Study population
One hundred thirty-one consecutive patients with sinonasal solid masses were recruited in this study (from May 2015 to March 2017). All masses were confirmed by surgery/biopsy and histopathology. Patients who previously had a history of treatment or recurrence were excluded.
MR Techniques
MRI examinations were performed on a 3 T MR scanner (Magnetom Verio, Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) using a 12 channel head coil. Conventional MR sequences including T1WI, T2WI and contrast-enhanced T1WI were performed. Isotropic DWI images were acquired by using a single-shot echo planar imaging sequence with a bi-polar scheme along all three orthogonal axes. Other DWI parameters were as follows: TR/TE = 5200/83 ms, number of averages = 2, acquisition matrix = 320 × 256; field of view = 230 mm2, slices = 5, slice thickness = 5 mm and parallel imaging acceleration factor = 2; eleven different b factors ranging from 0 to 1000 sec/mm2 were used (b = 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 800, and 1000 sec/mm2). The total scan time was 6 minutes 39 seconds.
Image Processing and Analysis
MR signal intensity of b = 0 and 1000 sec/mm2 were employed to calculate ADC on an off-line workstation (Verio; Siemens, Erlangen, Germany). IVIM processing was conducted by using MATLAB (version 7.9, MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA). Statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-tests, receiver operating characteristic curves and logistic regression analyses with 10-fold cross-validation.
Results
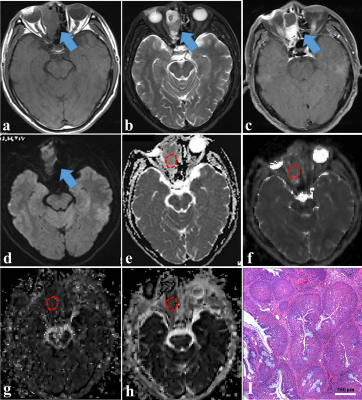
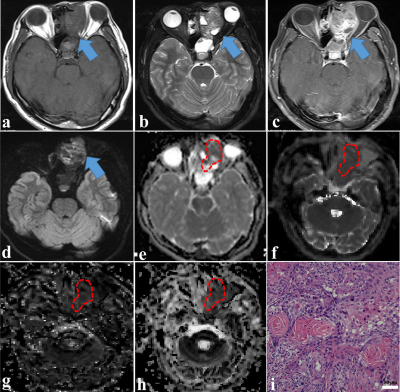
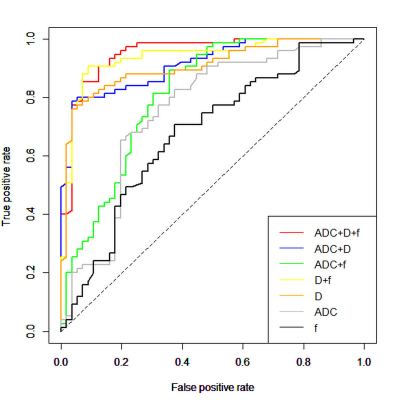
As shown in Figs. 1-2, the mean ADC and D values were significantly lower in the malignant sinonasal lesions than those in the benign sinonasal lesions (both P < .001). The mean f value was higher in the malignant lesions than that in the benign lesions (P = .003). Multi-parametric models can significantly improve the cross-validated AUCs for the differentiation of sinonasal lesions than single parametric models (all corrected P < .05 except D value). The model of D+f provided a better diagnostic performance than ADC value (corrected P < .001).Discussion and Conclusions
IVIM model appears to be a more effective MR technique than the conventional DWI model in the differentiation between benign and malignant sinonasal lesions.Acknowledgements
None.References
1. Eggesbo HB. Imaging of sinonasal tumours. Cancer Imaging 2012;12:136-152
2. Koeller KK. Radiologic Features of Sinonasal Tumors. Head Neck Pathol 2016;10:1-12
3. Wang XY, Yan F, Hao H, et al. Improved performance in differentiating benign from malignant sinonasal tumors using diffusion-weighted combined with dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Chin Med J (Engl) 2015;128:586-592
Figures