3802
Reduction of susceptibility artifacts in MR of permanent prostate gold seed for radiotherapy1Medical Physics & Research Department, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Hong Kong, China, 2Department of Radiotherapy, Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital, Hong Kong, China
Synopsis
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for prostate cancer is a highly precise radiotherapy. Post-implant MR is important for target localization, contouring and treatment planning. A phantom was designed to investigate the susceptibility caused by gold seeds in different orientations relative to B0 field. 2D and 3D acquisition scheme at various resolution, bandwidth and frequency-encoding directions were examined. Our results show that for reduction of susceptibility artifacts and excessive local signal loss, resolution of higher than 0.5mm is recommended, increasing bandwidth with sufficient resolution is more practical than changing frequency-encoding directions. 3D is comparable to 2D sequence in susceptibility artifacts.
Purpose
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) in prostate is a highly precise radiation therapy in which high dose delivery within accuracy of about 1 mm is required [1]. As gold seeds are implanted to serve as markers to improve the accuracy of target localization during SBRT treatment, precise localization of the implanted markers is critical for online image matching and motion management. Accurate anatomical delineation of the prostate gland and surrounding structures are also required for treatment planning [2]. Due to the relative homogeneous soft tissue properties of prostate, post-implant MR image is superb and important while isotropic voxel size is favorable for SBRT planning for better fusion with CT images. As 1x1x1mm3 voxel size is commonly employed for MRI simulation, whether it is sufficient to localize gold seeds accurately is yet to be examined. In order to reduce local susceptibility artifacts from the gold markers, investigation of the influence of gold seed orientations relative to B0 field with various resolution (RESO), bandwidth (BW) and frequency-encoding (FE) directions were performed.Methods
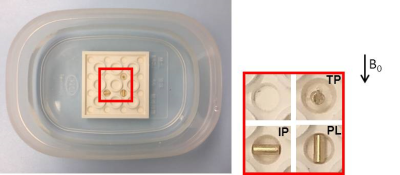
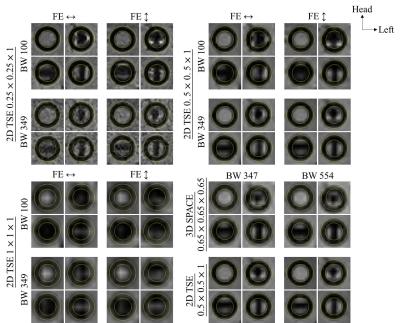
A LEGO® 4x4 plate with holes outer diameter of 4.85 mm was placed in a container filled with water. As shown in Fig. 1, three permanent prostate pure gold markers 1.2 mm in diameter and 3 mm in length (QLRAD, Zwolle, The Netherlands) were placed longitudinally parallel (PL), in-plane perpendicular (IP), and through-plane perpendicular (TP) to B0 field. The LEGO® parts do not give a signal and are therefore not visible on the MR image in contrast to their water-filled holes. The MR images were acquired on a customized MR simulator (Magnetom Aera, SIEMENS Healthineers, Erlangen, Germany) with coronal 2D TSE (TR=5000ms, TE = 18 ms, slice thickness = 1 mm) and 3D SPACE (isotropic voxel size of 0.65 mm, TR = 1600 ms, TE = 19 ms, coronal, FE = head-foot). To examine the effects of in-plane resolution, readout BW and FE direction, 2D TSE was acquired using pixel size of 0.25, 0.5 and 1mm, BW = 100 and 349 Hz/pixel, FE of head-foot and left-right respectively. 3D SPACE was acquired using BW = 347 and 554 Hz/pixel.Results
As shown in Fig. 2, in general, signal void caused by local susceptibility decreased with RESO. In 1mm isotropic RESO, all seeds caused a signal void making the shape of the seeds hardly differentiable. On the other hand, in 0.25 and 0.5mm RESO, the shape of PL seed can be identified in all BW and FE, while the shape of the IP seed can only be preserved in higher BW. For the TP seed, FE dependent susceptibility artifact was prominent in adjacent pixels in lower BW and RESO, while less artifact was found in RESO 0.25 and BW 349 in both FE. Images from 3D and 2D acquisition with comparable BW and RESO exhibited comparable susceptibility effect.Discussion and Conclusions
Current study showed that signal void caused by local susceptibility was more severe in lower RESO and BW. RESO of isotropic 1mm had limited capability to resolve the contours of gold seeds, which may complicate with surrounding tissue signals in prostate. RESO of higher than 0.5mm were found sufficient for reduction of susceptibility artifacts and excessive local signal loss. Although local susceptibility was more prominent along the FE direction, manipulation of the implanted seed orientations is impractical due to implantation techniques and seed migration after implantation. Therefore, altering FE direction to reduce local susceptibility might not be applicable. Instead, increasing BW with sufficient RESO was found to compensate for the FE dependent susceptibility effect efficiently at the cost of reduced signal-to-noise ratio. Since 3D acquisition scheme is useful in isotropic application and offers better fusion with CT images, and local susceptibility was found similar between 3D and 2D acquisition scheme, high resolution 3D SPACE acquisition with wide receiver bandwidth is suggested specifically for gold seed localization and differentiation in prostate SBRT MR-simulation.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Lo SS, et al, Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2010 Jan;7(1):44-54.
[2] Sanfilippo NJ, Cooper BT, Am J Clin Exp Urol. 2014 Dec 25;2(4):286-93.
Figures