3654
Differences in Metabolite Concentration and fMRI Activation in Subjects with Low and High Genetic Risk During Face-Name Paired-Associates Encoding and Retrieval Task in Healthy Adults1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 2State Key Laboratory of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 3Department of Educational Psychology, Chinese University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 4Department of Social Work and Administration, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 5Philips Healthcare, Hong Kong, Hong Kong, 6Alzheimer’s Disease Research Network, The University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, Hong Kong
Synopsis
APOE-ε4 is an important genetic risk factor of early onset of AD. To investigate the possible differences in metabolite concentration and fMRI activation in subjects with high risk of developing AD (APOE-ɛ4 positive) compared to those with low risk, we employed Face-Name Paired-Associates (FN-PA) Encoding and Retrieval Task and evaluated the absolute concentrations of Glx in bilateral hippocampi and whole brain BOLD signal changes. Significant metabolic and activation differences were observed in the left hippocampus of pre-symptomatic subjects with high genetic risk of developing AD compared to subjects with low risk.
Purpose
Aging is the primary risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD)1, the most common form of dementia in elderly populations over 65 years of age, and is of worldwide concern in view of increased global longevity.2 APOE-ε4 is an important genetic risk factor for the etiology of earlier onset of AD.3 To investigate the possible differences in glutamate concentration and fMRI activation in subjects with high risk of developing AD (APOE-ɛ4 positive) compared to those with low risk, we employed Face-Name Paired-Associates (FN-PA) Encoding and Retrieval Task and evaluated the absolute concentrations of glutamate in bilateral hippocampi and whole brain BOLD signal changes.Materials and methods
Subjects and Image acquisition:
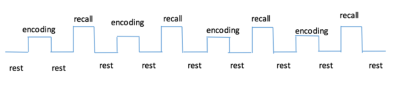
In total 72 subjects were scanned using the same paradigm (FN-PA encoding and retrieval task). Participants serially studied six pairs of names and faces during four blocks, and after memorizing session in each block they were required to recall the name when only presented with the same six faces. Fixation tasks were interleaved between encoding and recalling sessions. (Figure 1) All experiments were performed with a Phlips-3T MR scanner using a standard head coil. Structural images were acquired with 3D fast field echo sequence (3D-T1-FFE sagittal, TR=7ms, TE=3.2ms, Flip angle=8°, voxel size=1×1×1mm3, FOV=256). Functional images were collected by using a gradient-echo echo-planar sequence (parameters: TR=2000ms, TE=30ms, flip angle=90°, voxel size=3×3×4mm3) sensitive to blood-oxygen-level-dependent(BOLD) contrast. After the face-name task, subjects performed the recognition test outside the scanner. Single Voxel Spectroscopy(SVS) was performed on right and left hippocampus with the following parameters(TR/TE=2,000/39 ms, number of signals averaged=128, phase cycles=16, spectral width=2,000 Hz with spectral resolution of 1.95 Hz per point, and free induction decay=1024). Absolute concentration of Glx ([Glx]abs) (summation of glutamate and glutamine), NAA, choline, creatine and mI were measured and quantified using internal water as reference by QUEST in jMRUI (4.0) with cerebrospinal fluid, grey matter and white matter water content corrected.
Data analysis:
The analysis was performed using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM12). APOE-ε4 status was input during second level multiple regression analysis (covariates: ([Glx]abs and APOE-ε4 status, p<0.05, cluster size=810mm3). The mean concentration of MRS([Glx]abs) in bilateral hippocampi was compared. (SPSS v20, two sample t test).
Results
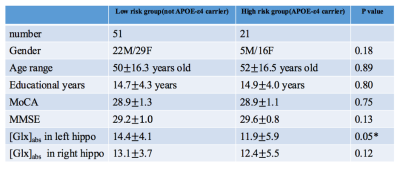
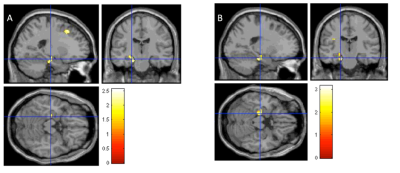
Table 1 presented the statistical results of demographic information, neuropsychological tests and [Glx]abs in low risk and high risk groups. Only [Glx]abs in left hippocampus has significant difference between these two groups. Figure 2 showed that the BOLD signal change in left hippocampus was significantly positive correlated with APOE-ε4 status. (p<0.05, cluster size=810mm3)Discussion and Conclusion:
In this study, metabolic and functional changes were observed in the pre-symptomatic subjects with high genetic risk of developing AD and subjects with low risk. In the left hippocampus, both [Glx]abs and BOLD signal changes had significant differences. During tasks, the left hippocampus of APOE-ε4 carriers had significant higher activations than non carriers. These results potentially offered insights in the pathogenesis of AD-related neurodegenerative. Higher [Glx]abs in APOE-ε4 carriers also reflects the distinct role of left hippocampus.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the funding from State Key Laboratory of Brain and Cognitive Sciences in the University of Hong Kong.References
1. Yankner BA, Lu T, Loerch P. The aging brain. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:41-66
2. Brookmeyer R, Johnson E, Ziegler-Graham K, Arrighi HM. Forecasting the global burden of alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2007;3:186-191
3. Corder E, Saunders A, Strittmatter W, Schmechel D, Gaskell P, Small G, et al. Gene dose of apolipoproteine type 4 allele and the risk of alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921-923
Figures