3607
Investigation of differences in the connectivity between the insular cortex and brain activity and metabolites between male smokers and non-smokers in their 20s1Gimcheon University, Seoul Korea, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
The purpose of the experiment was to investigate differences in the connectivity between the insular cortex out of the brain areas and other brain areas and the concentration of neuro-metabolites between male adult smokers and non-smokers in their 20s so that the results can be utilized as basic data for smoking cessation programs. The Cr concentration in the right insular cortex area of non-smokers is higher than that of smokers. In addition, it could be seen that smokers had stronger connectivity between their right insular cortex area and Gyrus Right, Occipital Fusiform, and Gurus Right areas than non-smokers and that non-smokers had stronger connectivity between their left insular cortex area and the frontal role right than smokers.
Introduction
The purpose of the experiment was to investigate differences in the connectivity between the insular cortex out of the brain areas and other brain areas and the concentration of neuro-metabolites between male adult smokers and non-smokers in their 20s so that the results can be utilized as basic data for smoking cessation programs.Methods
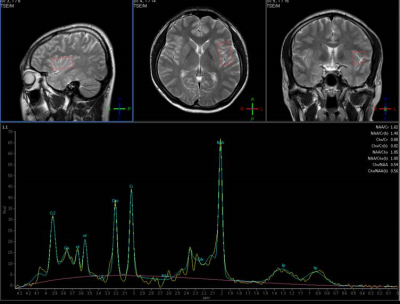
Population of control/experimental study To evaluate differences in activity and metabolites in the brain areas between smokers and non-smokers, a total of 20 experimental subjects consisting of 10 smokers and 10 non-smokers were selected from among males in their 20s. The mean age of the experimental subjects was 23.2±3 years. Smokers were evaluated using the nicotine addiction questionnaire used in a study conducted by karl-Olov [1]. The maximum score of this questionnaire is 11 points and higher scores indicate severer nicotine addiction. The nicotine dependency score of 10 smokers that participated in the present study was 4.1±2. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) and MRS analysis Referring to previous studies that indicated changes in brain metabolites in the insular area out of brain areas of smoker during the processes of smoking cessation and smoking, in the present study, magnetic resonance spectroscopic data were obtained from the same area [2]. All MRS experiments were conducted using a 3.0T 3.0Tesla MRI scanner (Achiva Tx 3.0 T; Philips Medical Systems, Netherlands). Using T2 weighted fast spin echoes, cross section, sagittal plane, and coronal plane images were obtained as shown figure 1. The 1H-MRS images of the insular areas on both sides were separately obtained through point-resolved spectroscopy (PRESS) sequences under the conditions of TR = 1,500 msec, TE = 35 msec, NEX = 32, and 20×20×38 mm3 voxel. Gradient echo planar pulse sequences were used as parameters for acquisition of fMRI images and a total of 3096 functional images were obtained under the conditions of axial, mode = 2D, scan timing: TE = 30 ms, TR = 2200 ms, flip angle = 90, matrix = 64 × 64, slice thickness = 5 mm, 36 slices. Connectivity analysis was and BOLD signals that showed correlations with the insular cortex area selected as a seed were analyzed to statistically investigate differences in the entire brain area between smokers and non-smokers.Results and Discussion
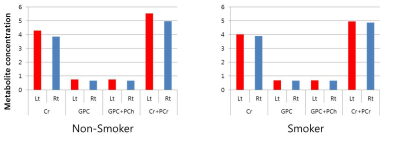
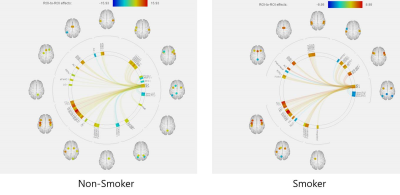
The water scaling concentrations of a the total of eight metabolites produced in the insular cortex area; Aspartate(Asp), Creatine(Cr), Glutamate(Glu), Glutathione(GSH), glucerophosphorylcholine(GPC), N-Acetyl aspartate(NAA), N-Acetyl aspartate Glutamate(NAAG), and phosphorylcholine(PCh) were compared with each other based on statistical averages. The concentrations of the eight metabolites in the right and left insular cortex areas of smokers were analyzed and the results did not show any difference in metabolite concentrations between the left and right insular cortex areas. However, in the case of non-smokers, as shown in Figure 2, the concentrations of Cr, GPC, GPC+Pch, and Cr+PCr were shown to be statistically significantly different between the left and right insular cortex areas. As for differences in metabolite concentrations in the left and right insular cortex areas between smokers and non-smokers, the Cr concentration in the left insular cortex area was identified to be statistically significantly higher among non-smokers because that of smokers was 4.95 while that of non-smokers was 5.49(p=0.01). Although other study groups reported that Glu concentrations of smokers changed in the process of smoking cessation, no statistically significant change was observed in the present study [2]. In particular, compared to non-smokers, smokers had stronger connectivity between the right insular cortex area and Lingual Gyrus Right, Occipital Fusiform Gurus Right, Vermis 4 5, cerebellum 6 right, vermis 6, cerebellum Crus 1 right, Cingulate Gurus posterior division, precuneous cortex, and cerebellum 4 5 right. On the other hand, the left insular cortex area of smokers did not show particularly higher connectivity to any other brain area than that of non-smokers(figure 3). Finally, it was shown that compared to left insular cortex area of smokers, that of non-smokers had stronger connectivity only to the right Frontal Pole area than that of smokers.Conclusion
The Cr concentration in the right insular cortex area of non-smokers is higher than that of smokers. In addition, it could be seen that smokers had stronger connectivity between their right insular cortex area and Gyrus Right, Occipital Fusiform, and Gurus Right areas than non-smokers and that non-smokers had stronger connectivity between their left insular cortex area and the frontal role right than smokers.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Fagerstrom KO. Measuring degree of physical dependence to tobacco smoking with reference to individualization of treatment. Addict Behav. 1978:3(3-4):235-241.
2. Dinur-Klein L, Dannon P, Hadar A, et al. Smoking cessation induced by deep repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the prefrontal and insular cortices: a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Biol Psychiatry . 2014:76(9):742-749.
Figures