3606
High Resolution 3D T1-weighted Black Blood MRI of Human Lenticulostriate Arteries as Biomarker for Small Vessel Diseases1Stevens Neuroimaging and Informatics Institute, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States, 2Neurology, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, CA, United States
Synopsis
The early microvascular changes related to cerebral small vessel disease are still unclear. In this study, we applied a T1-weighted turbo spin echo sequence with variable flip angles for high resolution black-blood MRI to delineate the lenticulostriate arteries (LSA) at 3T. The vessel delineation was rated using a 4-point scale, and then correlated with clinical vascular risk factors as well as measures of executive function, cognitive flexibility and attention. LSA ratings were found to be reliable. Subjects with >4 visible LSA that were minimally tortuous exhibited positive trends with executive function, and male subjects tended to have poorer LSA delineation.
Purpose
The clinical differentiation of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) from vascular cognitive impairment and dementia (VCID) due to cerebral small vessel disease (SVD) is blurred 1,2. The large knowledge gap in SVD is partly because cerebral small vessels, including arterioles, capillaries, and venules, are inaccessible to existing clinical in vivo imaging technologies. Arteriolosclerosis is a common and systemic condition that affects the brain, kidney and retina; and it is strongly associated with aging, diabetes, and hypertension. A new high-resolution black-blood MRI technique has emerged for intracranial vessel wall imaging at 3T with sub-millimeter spatial resolution using 3D turbo spin echo with variable flip angles (T1w-VFA-TSE)3-5. In this study, this 3D TSE sequence was applied for the visualization of perforating lenticulostriate arteries (LSA) to explore early microvascular changes related to SVD.Methods
Fifteen volunteers (9 female, 68±13 years, all Latinos) over the age of 60 from the Los Angeles Latino Eye Study (LALES) cohort were scanned on a Siemens 3T Prisma scanner using a 20-channel head coil. Each subject underwent two repeated MRIs ~2 weeks apart to evaluate the test-retest repeatability. A 3D T1w TSE sequence with VFA, typically used for vessel wall imaging3-5, was chosen for small vessel imaging with its inherent excellent contrast between vessels and tissue due to good blood suppression properties. The imaging parameters were optimized for small vessel imaging to be the following: voxel size=0.52x0.52x0.5 mm3 interpolated to 0.26x0.26x0.5 mm3, 166 sagittal slices (with two saturation bands to avoid signal wrapping), TE/TR=12/1000ms, ETL=41, scan time=9:05 min. Two of the scans utilized ECG triggering with an acquisition window of 1000 ms to reduce pulsatile motion artifacts.
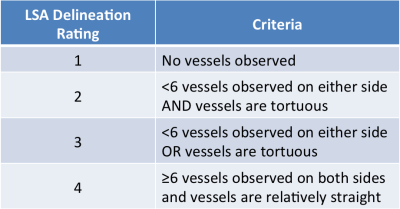
The following patient information was collected: gender, age, hemoglobin A1C to determine diabetes risk, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, cholesterol and LDL to determine hyperlipidemia risk. The NIH Toolbox Flanker Inhibitory Control and Attention Test (Flanker) was used to measure executive control and attention, and the Dimensional Change Card Sort Test (DCCS) was used to measure cognitive flexibility and attention. The Global Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) was evaluated for 9 subjects. To evaluate the LSA quality in the T1w-TSE-VFA images, a 4-point rating scale was developed as described in Table 1 and evaluated by two independent raters. Cohen’s kappa coefficient was used to determine inter-rater agreement between two unique raters. The average LSA delineation (LSAD) rating was correlated pairwise with the patient information, the NIH Toolbox scores, and Global CDR. Test-retest repeatability was assessed by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC).
Results and Discussion
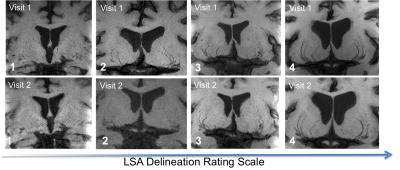
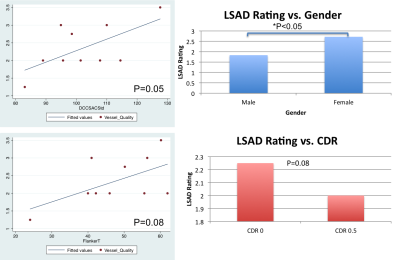
The Cohen’s kappa was found to be 0.7565, indicating decent agreement between the raters for the LSA delineation rating. The ICC was 0.93 for LSA ratings between repeated scans, indicating a high level of test-retest repeatability. As shown in Figure 1, the LSA delineation can be seen for various subjects across the rating scale, and are reliable between two visits. With the pairwise correlations (Figure 2), we found a significant reduction of LSAD ratings in males compared to females (p<0.05), as can be observed by the subject with a LSAD rating of 1 in Figure 1. The age corrected standard score for DCCS was positively correlated with LSAD rating (p=0.05), indicating stronger cognitive flexibility and executive function in subjects with less tortuous small vasculature. The Flanker fully corrected T-score also showed a positive trend with higher LSAD rating (p=0.08). CDR was not collected for all 15 subjects, but amongst the 9 subjects who had CDR scores, there is a trend for reduced LSAD in subjects with CDR of 0.5 vs. those with CDR of 0 (p=0.08), suggesting LSA count and tortuosity may serve as a potential imaging marker for very mild dementia (CDR=0.5). Despite the small sample size in this preliminary study, trends are already being observed between LSA features and measures of executive function and attention, as well as very mild clinical dementia.Conclusion
High resolution black-blood T1w-VFA-TSE is a newly developed technique that could aid in the delineation of lenticulostriate and other perforating arteries 6. With improved visualization and segmentation of the LSAs, morphological features of LSAs may serve as a potential imaging marker of cerebral small vessel diseases such as vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. As this work continues, more data samples will be collected to confirm these preliminary findings.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Institute of Health (NIH) grant UH2-NS100614.References
1. Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2011; 42(9): 2672-713.
2. Schneider JA, Arvanitakis Z, Bang W, Bennett DA. Mixed brain pathologies account for most dementia cases in community-dwelling older persons. Neurology 2007; 69(24): 2197-204.
3. Qiao Y, Steinman DA, Qin Q, et al. Intracranial arterial wall imaging using three-dimensional high isotropic resolution black blood MRI at 3.0 Tesla. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 34(1): 22-30.
4. Qiao Y, Zeiler SR, Mirbagheri S, et al. Intracranial plaque enhancement in patients with cerebrovascular events on high-spatial-resolution MR images. Radiology 2014; 271(2): 534-42.
5. Fan Z, Yang Q, Deng Z, et al. Whole-brain intracranial vessel wall imaging at 3 Tesla using cerebrospinal fluid-attenuated T1-weighted 3D turbo spin echo. Magn Reson Med 2016.
6. Ma SJ, et al. Evaluation of Whole Brain and ZOOMit T1-weighted Turbo-Spin Echo (TSE) for Visualization of Human Lenticulostriate Arteries at 3.0 T: A Preliminary Study. ISMRM 2017, Honolulu, HI.
Figures