3455
4D Flow MRI assessment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy –the comparison with pressure gradient measured by Doppler ultrasound-1Radiolody, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan, 2Cardiology, Nippon Medical School, Tokyo, Japan, 3Radiology, Nihon University, Tokyo, Japan, 4Philips Electronics Japan Ltd., Tokyo, Japan
Synopsis
The purpose of this study was to compare the flow abnormality based on 4D Flow MRI data with the PG measured by Doppler ultrasound. we enrolled 9 patients who underwent echocardiography followed by 4D Flow MRI. Helical grade of HOCM group was higher than that of HNCM group (2.33±0.47 vs. 1.33±0.47, p=0.032). There was no significant difference between HG and each characteristic of HCM (PG, septal thickness, septum/free wall ratio and the presence of SAM). 4D Flow MRI can visualize abnormal helical flow of ascending aorta in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.
Introduction
The obstruction of LV outflow tract (LVOT) is independently associated with the adverse outcome in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). It is assumed that the obstruction links to the increase of cardiac loading due to impairing the efficiency of cardiac output. To evaluate this impairment, the pressure gradient (PG) of LVOT is measured by Doppler ultrasound in clinical setting. However, this method doesn’t take post stenotic recovery into account, which results in overestimation of disease severity. As an alternative, time-resolved 3D phase-contrast (4D Flow) MRI have been tried for the assessment of comprehensive flow information. Previous studies from one group suggest that the obstruction of LVOT leads to abnormal flow in ascending aorta (AAo) which may relate to disease severity (1,2). However, there is no study comparing the abnormal blood flow visualized by 4D Flow MRI data with the conventional method, PG measured by Doppler ultrasound. The purpose of this study was to compare the flow abnormality based on 4D Flow MRI data with the PG measured by Doppler ultrasound.Materials and Methods
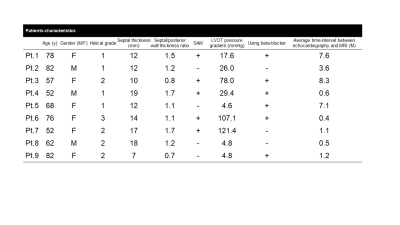
Patients; We prospectively recruited 11 patients who were clinically suspected HCM and referred to cardiac MRI during July and October 2017. For further analysis, we enrolled 9 out of 11 patients (67.7 ± 11.7, male 3) who underwent echocardiography followed by 4D Flow MRI. The average time interval between echocardiography and MRI examinations was median 1.1 months (range: 0.4-8.3). Four patients were already treated with a beta-blocker at the time of echocardiography.
MR acquisition; We performed cardiac MRI including 4D Flow MRI using a 3.0-T MRI unit (Achieva; Philips Healthcare, Best, The Netherlands). The parameters of 4D Flow MRI and are as follows (TE/TR/FA=4.4ms/2.5ms/11degrees; resolution=1.7*1.7*2.0mm; VENC=200cm/s (VENC range 400cm/sec); SENSE factor 2; elliptical partial k-space coverage in phase-and slice-encoding direction (3); free breath acquisition with abdominal belt for restricting respiratory motion; and acquisition time 8-15 min.). The main difference of parameters in the current study from the previous one is using 3T MRI and non-respiratory gating acquisition which impairs 4D Flow MRI data with only small extent compared to the acquisition with respiratory gating (1,2,4).
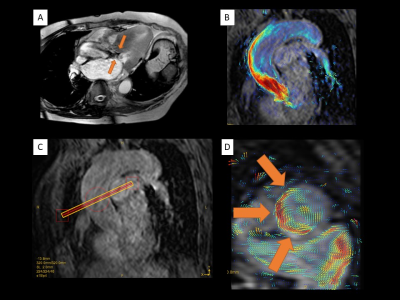
MR analysis; We analyzed all data using pathline statistics on GTFlow software (version 3.1.0, GyroTools, Zurich, Switzerland). Based on the previous study, we classified the flow patterns of AAo into 3 categories (no helical flow in the AAo=1, mild/moderate helical flow (<360 degrees of rotation) in the AAo =2, and severe helical folw (>360 degrees of rotation) in the AAo=3) (2).
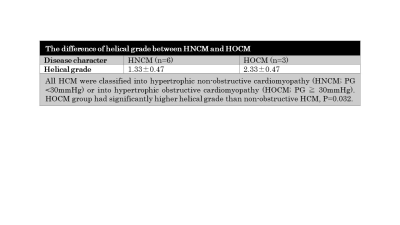
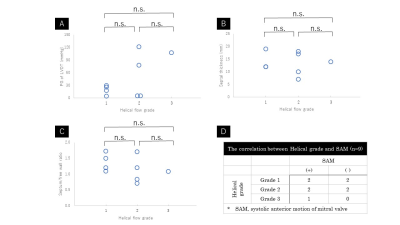
Statistics; To verify the difference of flow characteristics between hypertrophic non-obstructive cardiomyopathy (HNCM, PG < 30mmHg) and hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM, PG ≧ 30mmHg), the helical grade was compared between these two groups. To clarify the key anatomical factors related to the abnormal blood flow of AAo, each characteristic (PG, septal thickness, septum/free wall ratio and the presence of systolic anterior motion of mitral valve (SAM)) was compared between each helicity group. All comparisons were performed using ANOVA or Mann–Whitney U-test.
Results
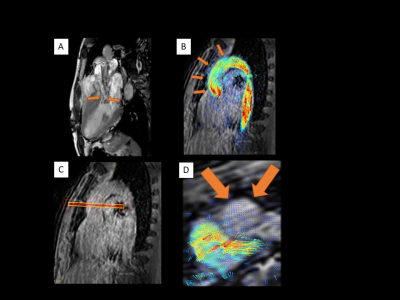
Out of 9 patients, 4 patients were rated into HG=1, 4 patients into HG=2, 1 patient into HG=3 (Fig. 1). Helical grade of HOCM group was higher than that of HNCM group (2.33±0.47 vs. 1.33±0.47, p=0.032) (Fig. 2). There was no significant difference between HG and each characteristic of HCM (PG, septal thickness, septum/free wall ratio and the presence of SAM) (Fig. 3). Representative cases are shown in Fig. 4 and 5.Discussion
The current study revealed that HOCM diagnosed by PG has abnormal helical flow of ascending aorta more frequently than HNCM. However, there is no clear relationship of increasing helicity with PG or other anatomical characteristics. The disturbance of cardiac output may be caused by the combination of several anatomical characteristics. This result is in consistent with the previous study (1,2). Further evaluation of the clinical relevance such as the response after medication or percutaneous transluminal septal myocardial ablation is needed.Conclusion
4D Flow MRI can visualize abnormal helical flow of ascending aorta in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Number 17K18160), Kurata Grants from the Hitachi Global Foundation (Grant Number 1309) and research grants from Fukuda Foundation for Medical Technology.References
1. van Ooij P, Allen BD, Contaldi C, et al. 4D flow MRI and T1 -Mapping: Assessment of altered cardiac hemodynamics and extracellular volume fraction in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;43:107-114.
2. Allen BD, Choudhury L, Barker AJ, et al. Three-dimensional haemodynamics in patients with obstructive and non-obstructive hypertrophic cardiomyopathy assessed by cardiac magnetic resonance. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;16:29-36.
3. Sekine T, Amano Y, Takagi R, Matsumura Y, Murai Y, Kumita S. Feasibility of 4D flow MR imaging of the brain with either Cartesian y-z radial sampling or k-t SENSE: comparison with 4D Flow MR imaging using SENSE. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2014;13:15-24.
4. Nordmeyer S, Riesenkampff E, Crelier G, et al. Flow-sensitive four-dimensional cine magnetic resonance imaging for offline blood flow quantification in multiple vessels: a validation study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;32:677-683.
Figures