3425
mridata.org: An Open Archive for Sharing MRI Raw Data1University of California, Berkeley, Berkeley, CA, United States, 2Radiology Department, Stanford University, Stanford, CA, United States
Synopsis
Current machine learning techniques for image reconstruction require large number of datasets for training, yet the number of public MRI raw datasets is limited. We present mridata.org as an open archive for researchers to share their MRI raw data. The website is designed to facilitate sharing MRI datasets, with features including automatic ISMRMRD conversion from uploaded vendor specific files. We hope that with contributions from many researchers, this website can provide more datasets to train and validate machine learning models for MRI reconstruction.
Introduction
Machine learning has the potential to leverage existing database of MRI data to provide more accurate reconstruction with less computation. However, current machine learning techniques require large number of datasets for training, and the number of public MRI raw datasets is limited. An alternative is to use preprocessed MR magnitude images for training, but this can result in degradation in quality as it inherently throws away information about k-space sampling and image phase.
We present mridata.org as an open archive for researchers to share their MRI raw data. Our previous iteration of the website has featured fully-sampled knee datasets1 for downloading. We have redesigned the website to enable uploading MRI datasets from any registered user, and added features to facilitate easy uploading and downloading. We hope that with contributions from many researchers, this website can provide more datasets to train and validate machine learning models for MRI reconstruction.
Features
To facilitate the sharing of MRI raw datasets from different researchers, mridata.org supports the following features:
Automatic ISMRMRD conversion
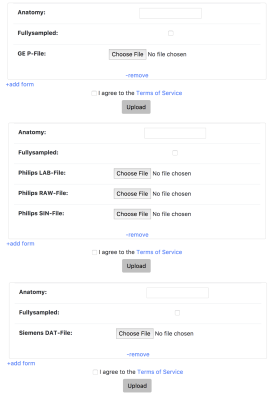
mridata.org leverages existing effort from Inati et al.2 to standardize MRI raw datasets from different vendors with the ISMRMRD format. All datasets on the website are provided in the ISMRMRD format, and ISMRMRD files can be uploaded directly to the website. Using and extending scripts to convert vendor specific data files to ISMRMRD, the website supports uploading files from GE, Siemens, and Philips scanners. Once uploaded these vendor specific data files are automatically converted to ISMRMRD in the background. An screenshot of the uploading portals is shown in Figure 2.
Automatic parameter extraction and thumbnail generation
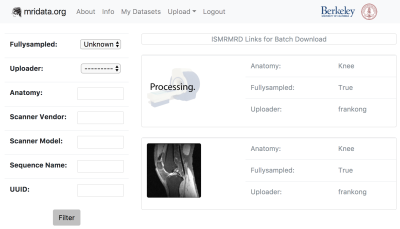
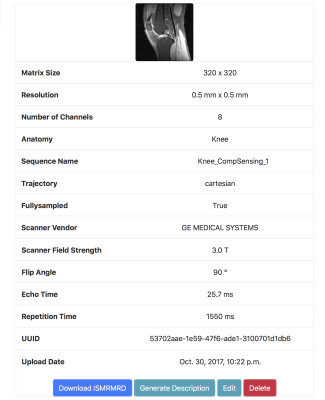
Useful scan parameters, such as matrix size, spatial resolution, and TE/TR, are extracted from ISMRMRD files, and displayed online to facilitate searching the appropriate datasets. Figure 2 shows the main page of the website, which enables the user to filter desired datasets with specified parameters. Thumbnails are also automatically generated by performing a zero-filled reconstruction of a slice of the received data, which provides previews of the datasets. An example of the data card containing the parameters, and a thumbnail is shown in Figure 3.
Unique permanent link and description generation
Each dataset has their own unique ID, and an associated permanent link, which can be included in papers or scripts. In addition, a readable description is automatically generated for each dataset. For example:
The data was acquired on a GE Discovery 750 3T scanner, with an 8-channel coil array. Scan parameters include matrix size of 320 x 320, spatial resolution of 0.5 x 0.5 mm2, flip angle of 90.0 degree, and TE/TR of 25.661ms/1550.0ms.
Web Architecture
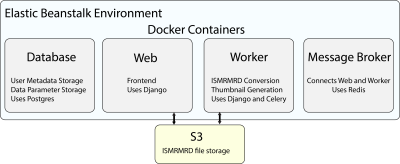
mridata.org is built using Django, a Python web framework. The website is hosted on the AWS Elastic Beanstalk environment, and packaged using Docker containers. Tasks, such as converting file formats to ISMRMRD, are distributed using Celery. PostgresSQL is used for database, and Redis is used for message broker between web frontend and tasks. Uploaded ISMRMRD datasets are stored in AWS S3. Figure 4 shows a graphical overview of the web architecture.
Conclusion
We have presented mridata.org, a open archive for sharing MRI raw datasets. With features such as automatic ISMRMRD conversion, and thumbnail generation, mridata.org facilitates the process of sharing MRI raw datasets from different MRI vendors.Acknowledgements
We thank Michelle Tamir for the design of the mridata.org logo.References
[1] Epperson K, Sawyer AM, Lustig M, Alley M, Uecker M. Creation Of Fully Sampled MR Data Repository For Compressed Sensing Of The Knee. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Meeting for Section for Magnetic Resonance Technologists, Salt Lake City, Utah, USA, 2013.
[2] Inati, S. J., Naegele, J. D., Zwart, N. R., Roopchansingh, V., Lizak, M. J., Hansen, D. C., Liu, C.-Y., Atkinson, D., Kellman, P., Kozerke, S., Xue, H., Campbell-Washburn, A. E., Sørensen, T. S. and Hansen, M. S. (2017), ISMRM Raw data format: A proposed standard for MRI raw datasets. Magn. Reson. Med., 77: 411–421. doi:10.1002/mrm.26089
Figures