3392
Near real-time parallel-transmit pulse design1School of Psychology / CUBRIC, Cardiff University, Cardiff, United Kingdom
Synopsis
With many MRI scans lasting several minutes, patient motion is a common problem, especially with uncooperative subjects such as paediatric patients or patients with dementia or Parkinson’s. Realizing the finer-resolution that higher field strengths offer through the availability of increased SNR necessitates even longer scans, exacerbating this problem. While prospective motion correction techniques can compensate for motion at lower field strengths, such techniques are not directly applicable at higher field strengths, when more complicated parallel-transmit pulses are used. This study proposes a pulse design technique that can design multi-spoke and simultaneous multi-slice parallel-transmit pulses in less than one second, while adhering to peak-voltage limits, local and global SAR.
Introduction
This study proposes a parallel-transmit pulse-design method that can design pulses in near real-time, with the long term goal of prospective motion correction at UHF. Initial results show three-spoke three-slice SMS pulses can be designed in 0.7 seconds.
Many imaging protocols, specifically at ultra-high-field (UHF) suffer from long acquisition times with individual protocols exceeding 20min1. Patient motion might become unavoidable especially with longer scans or less cooperative patients, which makes sedation common practice in paediatric imaging2-5, or for patients with Parkinson’s6 or dementia7. However, sedation is invasive and can cause adverse effects2-4. While prospective motion correction techniques8,9 can be used to compensate for motion at lower fields, such calculations may not be directly applied at UHF with parallel-transmit pulses. To compensate for the inhomogeneity artifacts caused by the shorter wavelength at higher fields, parallel-transmit (pTx) pulses have been used for single-10-15 and simultaneous-multi-slice excitation16-22, with local SAR16 and temperature constraints18,21. However, the complexity of parallel-transmit pulse-design increases computation times to beyond feasible for prospective motion correction. This study aims to reduce pulse-design computation times to near real-time to allow prospective motion correction.
Methods
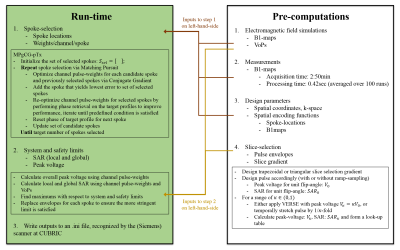
With slice-/slab-selection being the most common type of excitation, and fast pulse-design being the main goal, small-tip-angle spoke-trajectories were prescribed as they allow separation of spoke-selection and slice-selection. This reduces the size of the computation domain for the former, and the latter can be precomputed.
- Slice-selection: A library of unit flip-angle slice-selection pulse envelopes and gradients were precomputed23. By i) temporally stretching pulses, or ii) using variable-rate-selective-excitation (VERSE24), the library was populated for a range of peak-voltage and energy values.
- Spoke-selection: Spokes were selected and pulse-weights were designed by adapting the Matching-Pursuit-guided-Conjugate-Gradient25 (MPgCG) algorithm to pTx. While selecting the nth-spoke, pulse-weights were optimized via CG for the previously selected spokes and the candidate spoke. After selecting a new spoke, pulse-weights were re-optimized for all spokes with CG, where the phase of the target profile was relaxed to improve results. Figure 1 and Ref25 outline the algorithm.
- System and safety limits: To reduce computational cost, Virtual Observation Points were used26. When the same envelopes are used for each channel on any spoke, SAR calculation reduces to i) finding the self- and cross-terms of pulse-weights across channels at each VoP for that spoke, ii) multiplying with spoke envelope energy, iii) repeating (and summing SAR) over spokes. After local and global SAR and peak-voltages were calculated for each spoke, the envelopes and gradients were replaced (as necessary) using the library to satisfy limits i) simultaneously, or ii) sequentially (first: system limits, second: safety limits; may yield different envelopes for each spoke).
Simulations were made in Matlab (Mathworks Inc. Natick, MA, USA) on a quad-core PC with Intel i7-6700 CPU and 32GB RAM, using 8-channel B1-maps for the abdomen (resolution:83x58), SAR VoPs (local and global) and system characteristics published by the ISMRM for the RF pulse-design challenge22,27. Pulses were designed for different number of i) spokes, ii) slices (single-, 3-, 5-, 7-slices), iii) transmit-coils, iv) candidate spokes (default: 11x11) and v) VoPs. Also, computation times for different SAR-management approaches summarized above were compared.
Results and Discussion
All pulse-design times reported in this section include selecting spokes, optimizing channel pulse-weights, replacing envelopes to satisfy local and global SAR and peak-voltage limits, and writing the outputs to a scanner-recognized file; and were averaged over 100 pulses designed with the same parameters.
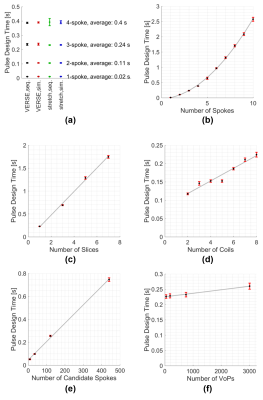
With the proposed method, pulse-design times are 0.02 seconds for a single-spoke, 0.24 seconds for three-spokes (Figure 2a) and slightly below a second for a 6-spoke pulse (Figure 2b). Pulse-design times vary quadratically with the number of spokes and linearly with the number of simultaneously excited slices, coils, candidate spokes, and (weakly with) VoPs (Figure 2b-f). As a lookup table is used, computations times are not affected significantly by which approach the system and safety limits are satisfied (Figure 2a).
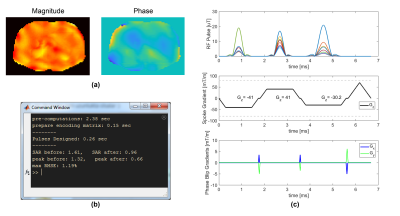
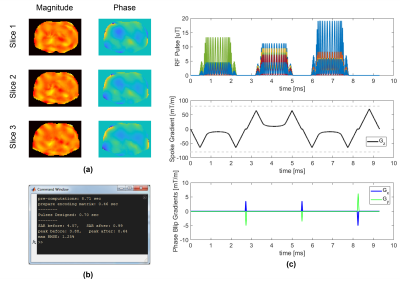
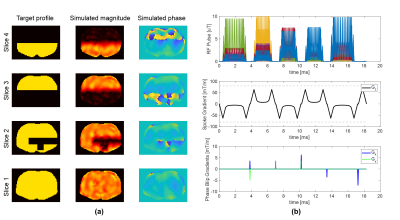
Figure 3 shows a single-slice 3-spoke pulse, which was designed in 0.26 seconds, and its simulated excitation profile. Figure 4 shows a 3-slice 3-spoke SMS-pulse, which was designed in 0.7 seconds. Figure 5 shows the method can efficiently design pulses for arbitrarily defined target profiles as well. No difference in root-mean-squared-error was observed for Figures 3-5 when more candidate spokes were used.
In practice, the time that passes after acquiring B1maps and before applying the next sequence would also include a one-off B1-map processing and computing the candidate spokes, which took 0.41 and 0.17 seconds, respectively (100runs).
Conclusion
A method was proposed that can design SMS pTx pulses in less than a second. Future work includes incorporating B0 off-resonance, real-time field measurements from a field-camera and motion-tracking information for prospective motion correction with real-time pulse redesign.Acknowledgements
The author would like to thank Arcan Erturk and the ISMRM for making the simulation data available online.References
1. Van Essen DC, Smith SM, Barch DM, Behrens TEJ, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K. The WU-Minn Human Connectome Project: An overview. NeuroImage 2013;80:62-79.
2. Malviya S, Voepel-Lewis T, Eldevik OP, Rockwell DT, Wong JH, Tait AR. Sedation and general anaesthesia in children undergoing MRI and CT: adverse events and outcomes. Br J Anaesth 2000;84(6):743-748.
3. Havidich JE, Beach M, Dierdorf SF, Onega T, Suresh G, Cravero JP. Preterm Versus Term Children: Analysis of Sedation/Anesthesia Adverse Events and Longitudinal Risk. Pediatrics 2016;137(3).
4. Mallory MD, Travers C, McCracken CE, Hertzog J, Cravero JP. Upper Respiratory Infections and Airway Adverse Events in Pediatric Procedural Sedation. Pediatrics 2017.
5. Boriosi JP, Eickhoff JC, Klein KB, Hollman GA. A retrospective comparison of propofol alone to propofol in combination with dexmedetomidine for pediatric 3T MRI sedation. Pediatric Anesthesia 2017;27(1):52-59.
6. Schwarz ST, Afzal M, Morgan PS, Bajaj N, Gowland PA, Auer DP. The ‘Swallow Tail’ Appearance of the Healthy Nigrosome – A New Accurate Test of Parkinson's Disease: A Case-Control and Retrospective Cross-Sectional MRI Study at 3T. PLOS ONE 2014;9(4):e93814.
7. Prasher V, Cumella S, Natarajan K, Rolfe E, Shah S, Haque MS. Magnetic resonance imaging, Down's syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: research and clinical implications. J Intellect Disabil Res 2003;47(2):90-100.
8. Ward HA, Riederer SJ, Grimm RC, Ehman RL, Felmlee JP, Jack CR. Prospective multiaxial motion correction for fMRI. Magn Reson Med 2000;43(3):459-469.
9. Maclaren J, Herbst M, Speck O, Zaitsev M. Prospective motion correction in brain imaging: A review. Magn Reson Med 2013;69(3):621-636.
10. Katscher U, Börnert P. Parallel RF transmission in MRI. NMR in Biomedicine 2006;19(3):393-400.
11. Setsompop K, Wald LL, Alagappan V, Gagoski B, Hebrank F, Fontius U, Schmitt F, Adalsteinsson E. Parallel RF transmission with eight channels at 3 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 2006;56(5):1163-1171.
12. Zelinski AC, Wald LL, Setsompop K, Alagappan V, Gagoski BA, Goyal VK, Adalsteinsson E. Fast slice-selective radio-frequency excitation pulses for mitigating B+1 inhomogeneity in the human brain at 7 Tesla. Magn Reson Med 2008;59(6):1355-1364.
13. Grissom W, Yip C-y, Zhang Z, Stenger VA, Fessler JA, Noll DC. Spatial domain method for the design of RF pulses in multicoil parallel excitation. Magn Reson Med 2006;56(3):620-629.
14. Gras V, Vignaud A, Amadon A, Le Bihan D, Boulant N. Universal pulses: A new concept for calibration-free parallel transmission. Magn Reson Med 2017;77(2):635-643.
15. Pendse M, Rutt B. IMPULSE: A Generalized and Scalable Algorithm for Joint Design of Minimum SAR Parallel Transmit RF Pulses. 2015.
16. Guérin B, Gebhardt M, Cauley S, Adalsteinsson E, Wald LL. Local Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), Global SAR, Transmitter Power, and Excitation Accuracy Trade-Offs in Low Flip-Angle Parallel Transmit Pulse-design. Magn Reson Med 2014;71(4):1446-1457.
17. Guérin B, Setsompop K, Ye H, Poser BA, Stenger AV, Wald LL. Design of parallel transmission pulses for simultaneous multislice with explicit control for peak power and local specific absorption rate. Magn Reson Med 2015;73(5):1946-1953.
18. Deniz CM, Carluccio G, Collins C. Parallel transmission RF pulse-design with strict temperature constraints. NMR in Biomedicine 2017;30(5):e3694-n/a.
19. Wu X, Schmitter S, Auerbach EJ, Moeller S, Uğurbil K, Van de Moortele P-F. Simultaneous multislice multiband parallel radiofrequency excitation with independent slice-specific transmit B1 homogenization. Magn Reson Med 2013;70(3):630-638.
20. Wu X, Schmitter S, Auerbach EJ, Uğurbil K, Van de Moortele P-F. Mitigating transmit B(1) inhomogeneity in the liver at 7T using multi-spoke parallel transmit RF pulse-design. Quantitative Imaging in Medicine and Surgery 2014;4(1):4-10.
21. Boulant N, Wu X, Adriany G, Schmitter S, Uğurbil K, Van de Moortele P-F. Direct control of the temperature rise in parallel transmission by means of temperature virtual observation points: Simulations at 10.5 tesla. Magn Reson Med 2016;75(1):249-256.
22. Grissom WA, Setsompop K, Hurley SA, Tsao J, Velikina JV, Samsonov AA. Advancing RF pulse-design using an open-competition format: Report from the 2015 ISMRM challenge. Magn Reson Med:n/a-n/a.
23. Pauly J, Le Roux P, Nishimura D, Macovski A. Parameter relations for the Shinnar-Le Roux selective excitation pulse-design algorithm [NMR imaging]. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1991;10(1):53-65.
24. Conolly S, Nishimura D, Macovski A, Glover G. Variable-Rate Selective Excitation. J Magn Reson 1988;78(3):440-458.
25. Kopanoglu E, Constable RT. Radiofrequency pulse-design using nonlinear gradient magnetic fields. Magn Reson Med 2015;74(3):826-839.
26. Eichfelder G, Gebhardt M. Local specific absorption rate control for parallel transmission by virtual observation points. Magn Reson Med 2011;66(5):1468-1476.
27. ISMRM RF Pulse-design Challenge. http://challenge.ismrm.org/. 2016.
Figures