3355
Comparison of SPGR Phase-Sensitive Inversion-Recovery and FIESTA Phase-Sensitive Inversion-Recovery MRI at 3.0T for the assessment of Late Gadolinium Enhancement in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy1Radiology Department, Peking University Third Hospital, Beijing, China, 2GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance(CMR) imaging is now accepted as a valuable tool for the evaluation of many cardiac disease. It is particularly useful for the assessment of cardiomyopathies because it can depict different myocardial enhancement patterns on inversion-recovery(IR) late gadolinium-enhanced(LGE) images. This study would like to compare breath-holding SPGR PSIR with free-breathing FIESTA PSIR sequences and evaluate the feasibility of FIESTA for the assessment of LGE in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Purpose
When we applied phase-sensitive inversion-recovery for the assessment of late gadolinium enhancement(LGE), it can enhance the contrast between the LGE areas and the myocardium. However, the SPGR PSIR sequences are acquired under breath-holding (14s per slice) and an optimal inversion recovery time, the success rate mostly based on the patient compliance. The FIESTA PSIR sequence allows patients breath free. In this study, we would like to compare breath-holding SPGR PSIR with free-breathing FIESTA PSIR sequences and evaluate the feasibility of FIESTA for the assessment of late gadolinium-enhanced in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.Materials and Method
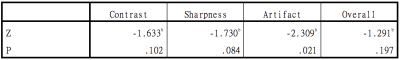
We reviewed 21 HCM patients(9 women,12 men; mean age 58.38 + 12.75 years; range 31-78 years )who underwent contrast-enhanced CMR imaging including breath-holding SPGR PSIR and free-breathing FIESTA PSIR imaging studies. All studies were performed on a 3.0T MR (GE Discovery 750). The patients were scanned in the supine position using a dedicated 32-channel cardiac coil. In all patients, images were acquired using electrocardiogram-gated cine imaging by a steady-state free-precession sequence in the three long cardiac axes, short axes and LGE imaging. About 9 minutes after injection of 4 mmol/kg of a gadolinium-based contrast agent, the SPGR PSIR sequence that covered the left ventricle from the base to the apex was operated. The parameters were as follow, SPGR PSIR, FOV: 350mm, thickness: 8mm, spacing: 2mm, TE: Min full, Flip Angle: 25, TI: 280ms----350ms, Matrix: 224x192, BW: 41.67KHZ, and 14 seconds per slice; FIESTA PSIR, FOV: 350mm, thickness: 8mm, spacing: 2mm, TE: Min full, Flip Angle: 45, TI: 260---350ms, Matrix: 152x152, Reconstruction: 512x512, BW: 31.25KHZ, within the acceptable time window of 30-40 seconds. The images were blindly reviewed and analyzed by two independent observers who have 4 and 8 years’ experience of MR diagnosis, respectively. The LGE location was recorded based on the 17-segment model of the American heart association. The image quality, including the contrast between LGE areas and the myocardium, the sharpness of the LGE margin, image artifact and overall image quality, was independently by the two observers on a 4-point scale. Image sharpness and contrast were scored as 1=poor, 2=fair, 3=acceptable, 4=good. Image artifact was scored as 1=severe, interfering with the evaluation; 2=moderate, partially interfering;3=mild, not interfering; 4=minimum to no artifact. Overall image quality was scored as 1=poor,2=fair, 3=acceptable, 4=good. When the rating of the two observers disagreed, the worse score was used for final determinations. Nonparametric rank sum test is used for data that do not conform to the normal distribution. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistically significant differences. We used software SPSS 22.0 for the data analyses.Results
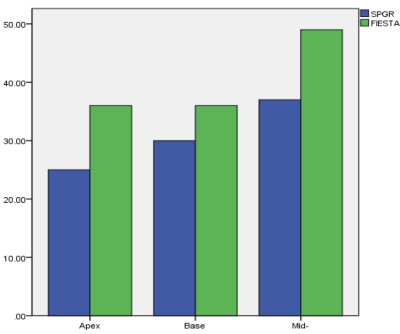
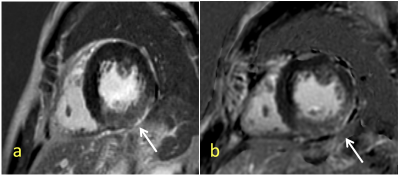
The numbers and distributions of LGE lesions are shown in Figure 1. More LGE lesions were detected on FIESTA PSIR images. The scores for the visual evaluation of LGE Lesions on SPGR and FIESTA images have shown as the Table1. There was no significantly difference on contrast and sharpness between SPGR and FIESTA which p value were 0.102 (>0.05) and 0.084 (>0.05) respectively. A representative case is shown in Figure 2.Discussion and conclusion
The images have no significantly difference between SPGR PSIR and FIESTA PSIR on the contrast, sharpness. Some images on FIESTA have more artifact. More LGE lesions were detected on FIESTA PSIR images, so we think the FIESTA sequence is more sensitive to LGE than the SPGR. However, we need more samples to verify the results. So it is feasible to apply the FIESTA PSIR sequence to detect the LGE lesions. Meanwhile FIESTA PSIR can increase the success rate because that it allows patients breath free and needs less time to acquire images (30s---40s, in all).Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Mahrhold HWagnerA , Judd RM, et al. Delayed enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance assessment of non-ischaemic cadiomyopathies . Eur Heart J 2005;26:1461-1474
2.Kosuke Morita RT, Daisuke Utsunomiya, MD, Seitaro Oda, MD, Masanori Komi, RT, Tomohiro Namimoto, MD, Toshinori Hirai, MD, Masahiro Hashida, RT, Seiji Takashio, MD, Megumi Yamamuro, MD, yasuyuki Yamashita, MD. Comparison of 3D Phase-Sensitive Inversion-Recovery and 2D Inversion-Recovery MRI at 3.0T for the assessment of late Gadolinium Enhancement in Patients with Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Acad Radiol 2013;20:752-757
3.Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, et al. Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart:a statement for heathcare professionals from the Cardiac imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association.Circulation 2002;105:539-542
Figures