3280
Temporal evolution of functional connectivity of the intrinsic networks in mild traumatic brain injury1Department of Medical Imaging, First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University, XI AN, China, 2The Key Laboratory of Biomedical Information Engineering, Ministry of Education, Department of Biomedical Engineering, School of Life Science and Technology, Xi’ an Jiaotong University, XIAN, China, 3Department of Radiology, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China, 4Neurosurgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital and Yuying Children's Hospital of Wenzhou Medical University, Wenzhou, China
Synopsis
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) often leads to disconnection of the brain intrinsic networks. Our study was to investigate how SN interacts with CEN/DMN can be viewed from the observation of how network connectivity damage affects other networks as a function of time, as well as its impact on cognition and emotion. The results suggests that intrinsic brain networks in mTBI patients showed continued damage from acute to sub-acute phase after injury. Function connectivity of SN interacts with CEN/DMN are especially susceptible in mTBI patients and the damage for inter-network functional disconnection will lead to high level cognitive dysfunction.
Purpose:
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) often leads to the nerve damage through the disconnection of the brain network, and its functional effects can be carried out on a large scale connectivity network. Central executive network (CEN) and default mode network (DMN) are important intrinsic networks and reported impair in mTBI patients. During the task with high cognitive requirements, salience network (SN) plays a key and causal role in the conversion between CEN and DMN, and the dynamic switching between these two networks. In this case, the abnormal of connectivity of the SN with CEN and DMN should disrupt the regulation of associated networks in mTBI patients [1, 2]. So the purpose of our study was to investigate how SN interacts with CEN and DMN can be viewed from the observation of how network connectivity damage affects other networks as a function of time in mTBI patients, as well as its impact on cognition and emotion.Method:
Fifty-five acute mTBI patients (32 men), twenty-five one month after mTBI patients (15 men) and 40 age matched healthy controls (13 men) were included in this study. GE Discovery MR 750 was used to acquired BOLD EPI data (TR/TE = 2500/30 ms, flip angle = 90°, field of view (FOV) = 216mm×216mm, matrix = 72×72, slice thickness = 3 mm and slice gap = 0). Functional MRI data were analyzed using the Data Processing Assistant for Resting-State fMRI (DPARSFA) [3]. Independent component analysis (ICA) was using the group ICA (GICA) of the fMRI toolbox (http://www.nitrc.org/projects/cogicat/). In this study, we use subject-order independent group ICA and perform GICA 100 times to obtain 40 independent components (ICs). The SN was identified by visual inspection, as previously described [4]. For each SN component, each voxel's z-score was defined as the resting state network internal network functional connectivity (FC). Meanwhile, we adopt the ROI based method to extract CEN and DMN and a family-wise error (FWE) method with threshold of P <0.05 is used to correct multiple comparisons. Next, we analyze the group differences in internetwork FC between SN and CEN/DMN. Basing on these results, we further performed correlation analyses between the neuropsychological scale and networks FC differences.Results:
Internetwork FC between SN and CEN
By comparing the difference between patients with acute mTBI and health controls, increased FC was found in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (dlPFC) and decreased in the posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) in mTBI patients. In one month, FC values in the PPC and dlPFC regions were higher than those in health controls.
Internetwork FC between SN and DMN
The FC values of PCC and ventromedial prefrontal cortex (vmPFC) in mTBI patients were higher than those in health controls at acute phase. In one month, the FC values in the PCC were increased in the mTBI patients compared with the controls.
Correlation analyses between the neuropsychological scale and networks FC differences
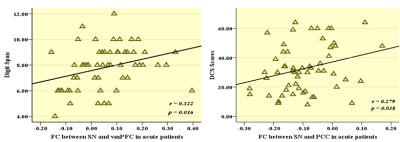
The FC value of SN and vmPFC showed significant positive correlation with Digit Span (r=0.322, P= 0.016), the FC value of SN and PCC showed significant positively correlated with the DCS scores (r=0.279, P=0.038).
Discussion:
Compared with healthy controls, acute mTBI patients showed increase FC in the dlPFC and the trend continued until one month. Decreased in the PCC were only showed in acute phase and more pattern of increased FC values in the PPC and dlPFC regions were found in one month. These findings suggested that the internetwork FC disconnection between SN and CEN partly due to local and diffuse damage effect on the network activity, but also because the brain is a dynamic system, the interaction of whole brain activity over time and rapidly changing complex. The increased FC of PCC and vmPFC in mTBI patients in acute phase showed significant positive correlation with digit span and DCS scores, respectively. These results may further reflect damage in special areas may be associated with specific cognitive function, the internetwork functional connectivity with SN and DMN may be an important predictor on memory and emotion. Continued increase FC in DMN was also found in one month. These results suggests the similarity feature co-variation between these two networks change over timeConclusion:
The impact of large-scale brain networks abnormal in mTBI patients showed continued damage from acute to sub-acute phase after injury. Function connectivity of SN interacts with CEN and DMN are especially susceptible in mTBI patients and the damage for internetwork functional disconnection will lead to high level cognitive dysfunction.Acknowledgements
All authors acknowledge the support of the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants No. 81371630, 81571752, 81571640, 81371530, the National key research and development plan of China, 2016YFC0100300, the Shaanxi Nova program(2014KJXX-34), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the National Key Research and Development Plan of China under Grant No. 2016YFC0103001.References
[1] Sharp DJ et al., Nat Rev Neurol. 2014.10(3):156-166.
[2] Bonnelle V et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012.109(12):4690-4695.
[3] Seeley WW et al.,J Neurosci. 2007. 27(9):2349-2356.
[4] He X et al.,Hum Brain Mapp. 2014. 35(7):3446-3464.
Figures