3266
Volume and surface-based structural analyses in active Crohn’s Disease Patients1National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre in Gastrointestinal and Liver disease at Nottingham University Hospitals NHS Trust, Queens Medical Centre Campus, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom, 2Sir Peter Mansfield Imaging Centre, University of Nottingham, Nottingham, United Kingdom
Synopsis
Structural brain changes in Crohn’s Disease (CD) have been studied in remission, however the data is inconsistent and not assessed in the active disease state. Grey matter volume (GMV) and cortical thickness (CT) were measured using VBM and CAT12/FreeSurfer in 25 active CD patients and age-matched healthy controls (HC). CD patients showed reduced CT and GMV in frontal and motor areas. Both CT and GMV were negatively correlated with proinflammatory markers, indicating these changes could be due to chronic inflammatory response. CAT and Freesurfer measures were highly comparable.
Introduction
Crohn’s Disease (CD) is a chronic, relapsing systemic inflammatory bowel disease. Reflecting the systemic nature of the inflammatory response, CD has been associated with several extra-intestinal manifestations. Structural and functional changes in the Central Nervous System have been described in CD1. Alterations in GMV2,3,4 and CT3,5,6 have been previously documented in adult CD patients in remission, however data is inconsistent and not explored in patients with active CD. Here, we investigate alterations in GMV and CT in patients with active CD, and their correlation with inflammatory markers (Interleukin-6 (IL-6), and faecal calprotectin (FCP)). We compare volume-based (computational anatomy toolbox, CAT) with surface-based (FreeSurfer) analysis to calculate cortical thickness.Methods
Subjects and MR Acquisition: 25 active ileal/colonic CD patients and 25 healthy controls (HC) age-, BMI- and gender-matched were scanned. Active CD was defined as Harvey Bradshaw index >5 and CRP > 5mg/dl, or FCP >250µg/g or assessed through ileocolonoscopy or magnetic resonance enterography. Serum measures of IL-6 and FCP were acquired at inclusion. Anatomical T1-weighted brain images were acquired on a 3T Philips Achieva scanner with a 32-channel receive coil (1 mm isotropic resolution; TE/TR = 8.3/3.8 ms, FA = 8°, SENSE factor = 2, 160 slices, 256 x 256 matrix).
Data Analysis: The
average cortical thickness - using
both CAT12 and FreeSurfer (v5.3), and GMV - using voxel
based morphometry in SPM 12, were first computed for each group. Whole cortex average thickness was compared between CAT and
FreeSurfer methods using a paired t-test. A two sample t-test general linear
model (GLM) analysis was performed to assess group
differences between CD and HC. The correlation of IL-6 and FCP in CD with cortical
thickness and GMV was performed. Age and total
intracranial volume (TIV) were included as covariates
of no interest. For both CAT and FreeSurfer smoothing kernels of 15 mm
were used, and 12mm for GMV. ROI
analysis was performed for cortical thickness (Desikan-Killiany 40 atlas) and
GMV (Neuromorphometric
atlas) using CAT.
Results
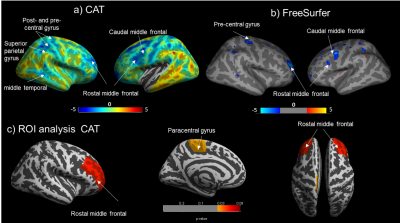
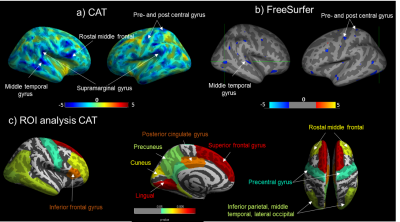
Cortical thickness (CT): No significant difference in average GMV or cortical thickness were found between CD and HC groups for both CAT and FreeSurfer. For both groups, average CT values were significantly higher when using CAT compared to FreeSurfer, (p<0.001). When assessing CT between groups, significant cortical thinning in the right rostral middle-frontal area was found in CD compared with HCs using both CAT and FreeSurfer, with additional areas of cortical thinning identified using CAT, Fig1. Correlating IL-6 with CT in CD showed cortical thinning in the right superior-frontal and right lingual regions with increasing IL-6 levels for both CAT and FreeSurfer, with CAT showing additional cortical thinning as shown in Fig2. No significant positive correlations were found between IL-6 or FCP with CT.
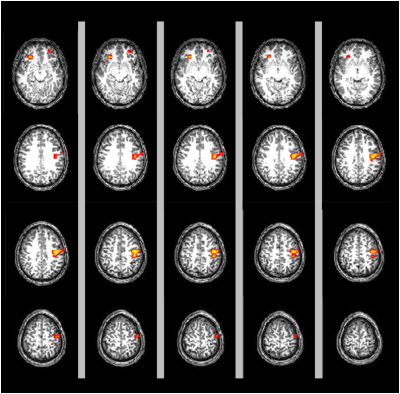
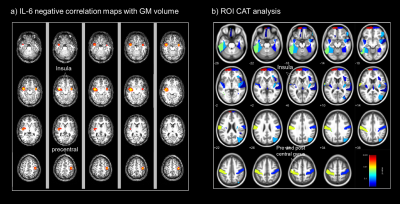
GMV: A significant decrease in GMV was found in CD compared with HC in pre- and post-central gyrus, Fig3. IL-6 was negatively correlated with the GMV in bilateral insula and pre- and post-central gyrus Fig4. FCP was negatively correlated with the right insula (P=0.02, uncorrected). No positive correlations were found between IL6 and FCP with GM volume.
Discussion
This is the first study to assess alterations in brain’s structure in active CD patients. We found a significant reduction in CT in the rostral middle-frontal cortex in CD. This region is functionally important for executive function, including attention and working memory and was found to be negatively correlated with IL-6 in CAT. The reduction in cortical thickness could be due to high levels of neurotoxic proinflammatory cytokines1 . In addition, the negative correlation of IL-6 and FCP with GMV in CD patients in the insula region could be indicative of impaired pain processing in these patients, the insula being an integral part of the pain matrix. Cortical thinning in the right superior frontal region3 and loss of GMV in the pre- and post-central gyrus3 have been previously reported in CD patients in remission.Conclusion
A significant reduction in CT and GMV in cortical areas has been shown in patients with active CD compared with HCs. This observation may be associated with a chronic inflammatory response. In future work, we aim to validate these findings in a cohort of 40 CD patients. Investigating structural brain changes in active CD will aid our understanding of the cross-linking between chronic inflammation, brain structural changes and behaviour in CD, with the aim of informing new medical and psychological therapies. CAT and FreeSurfer measures were highly comparable, with a few exceptions.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Dolapcioglu, C. & Dolapcioglu, H. Structural brain lesions in inflammatory bowel disease. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol.2015; 6(4), 124–130.
2. Agostini, A. et al. New insights into the brain involvement in patients with Crohn’s disease: A voxel-based morphometry study. Neurogastroenterology & Motility.2013; 25(2), 147–154 .
3. Bao, C. H. et al. Alterations in brain grey matter structures in patients with Crohn’s disease and their correlation with psychological distress. J. Crohn’s Colitis. 2015; 9(7), 532–540.
4. Erp, S. van et al. Cerebral magnetic resonance imaging in quiescent Crohn’s disease patients with fatigue. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017; 23(6), 1018 –1029.
5. Nair, V. A. et al. Structural imaging changes and behavioral correlates in patients with Crohn’s disease in remission. Front. Hum. Neurosci.2016;10, 1–11.
6. Thomann, A. K. et al. Altered markers of brain development in Crohn’s disease with extraintestinal manifestations - A pilot study. PLoS One. 2016;11(9), 1–14.
Figures