3215
The value of DWI with Readout Segmentation of Long Variable Echo-trains in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Lesions of the Tongue1the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this study was to assess the role of readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains(RESOLVE) DWI in differentiating benign and malignant lesions of the tongue. 120 patients with lingual lesions underwent preoperative RESOLVE DWI. The results demonstrated that the mean ADC values of benign lesions of the tongue were significantly higher than malignant lesions. Using an ADC value of 1.25×10-3 mm2/s as the threshold value, the sensitivity and specificity were 94.64%, 93.75% respectively. RESOLVE can offer high quality DWI of tongue. The ADC value can be applied in differential diagnosis between benign and malignant lesions of the tongue
Purpose
Pre-operative imaging plays an important role in treatment selection and surgical planning. conventional MRI are used to localize lingual masses and delineate their extent. But, accurate diagnosis and differentiating malignant from benign pathologies are likely to be difficult because of unspecific and overlapping imaging findings[1].In this work, we investigate the diagnostic value of readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains(RESOLVE) DWI in the evaluation of benign and malignant lesions of the tongue. 120 patients with lingual lesions confirmed by pathology were retrospectively analyzed, all patients underwent preoperative routine MRI and RESOLVE DWI. This study demonstrated that the mean ADC values of benign lesions of the tongue were significantly higher than malignant lesions.Material and Methods
120 patients with lingual lesions confirmed by pathology were retrospectively analyzed, all patients underwent preoperative routine MRI and RESOLVE DWI (b-values of 0 and 1000 s/ mm2), the ADC average values were calculated, t’ test were used to compare the ADC values of benign and malignant lesions of the tongue. Diagnostic performance of ADC was compared using receiver operating characteristic curves (ROC). Using an ADC value of 1.25×10-3 mm2/s as the threshold value for diagnosing benign and malignant lesions of the tongue and comparing with pathological results, the result obtained had a sensitivity of 94.64%, specificity of 93.75%.Results
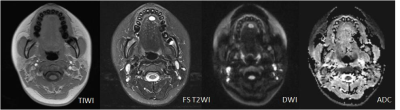
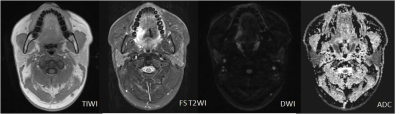
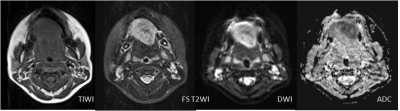
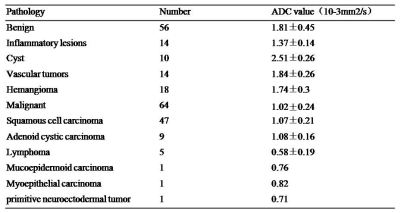
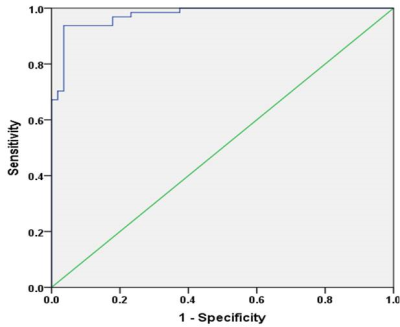
All lesions were solitary, including 56 benign lesions and 64 malignant tumors. The mean ADC values of benign lesions(Figure 1) and malignant tumors(Figure 2 and 3) were (1.81 ± 0.45)×10-3 mm2/s and (1.02 ± 0.24)×10-3 mm2/s (Table 1), there was statistically significant differences between them (t’= 12.21, P <0.001). The areas under the ROC of ADC differentiating benign and malignant lesions of the tongue was 0.976±0.011(Figure 4). Using an ADC value of 1.25×10-3 mm2/s as the threshold value for diagnosing benign and malignant lesions of the tongue and comparing with pathological results, the result obtained had a sensitivity of 94.64%, specificity of 93.75%. ADC value had high correlations compared with pathological results, Kappa value was 0.883.Discussion
We report the preliminary use of the readout segmentation of long variable echo trains(RESOLVE) sequence, a novel magnetic resonance(MR)scanning technique based on a readout segmented echo planar imaging(EPI)strategy. RESOLVE enables high-resolution diffusion-weighted imaging(DWI)by minimizing susceptibility distortions and T2* blurring[2]. We applied the sequence to investigate the diagnostic value in the evaluation of benign and malignant lesions of the tongue. In this article, RESOLVE-DWI clearly exposed structures that were obscured or severely distorted by artifacts on usual single-shot EPI-DWI[3-4]. Abdel Razek[5] et al used the ADC threshold value was 1.22×10-3 mm2/s. The results of this study demonstrated that the mean ADC values of benign lesions of the tongue were significantly higher than malignant lesions. Using an ADC value of 1.25×10-3 mm2/s as the threshold value for diagnosing benign and malignant lesions of the tongue and comparing with pathological results, the result obtained had a high sensitivity and specificity.Conclusion
RESOLVE can offer high quality of tongue diffusion-weighted images. The ADC value can be applied in differential diagnosis between benign and malignant lesions of the tongue.Acknowledgements
This study was supported in part by grants in from Key Scientific Research Project of Henan University (17A320041) and Medical Science Research Project of Henan Province(201602085)References
[1] Alberico RA, Husain SH, Sirotkin I. Imaging in head and neck oncology[J]. Surg Oncol Clin N Am, 2004, 13(1): 13-35.
[2] Ishida G, Oishi M, Morii K, Hasegawa K, et al. Application of brain diffusion-weighted imaging performed sing readout segmentation of long variable echo trains[J]. No Shinkei Geka, 2015, 43(1): 31-40.
[3] Zhao M, Liu Z, Sha Y, et a1. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the evaluation of sinonasal lesions:A comprehensive comparison of image quality in single-shot echo-planar imaging[J]. Magn Reson lmaging, 2016, 34(2): 166-172.
[4] Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weightedimaging using readout segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition[J]. Magn Reson Med, 2009, 62(2): 468-475.
[5] Abdel Razek AA, Gaballa G, Elhawarey G, et al. Characterization of pediatric head and neck masses with diffusion-weighted MR imaging[J]. Eur Radiol, 2009, 19(1):201-208.
Figures