3195
Atypical Imaging Features of Renal Pelvic Urothelial Carcinoma That Mimics Central Renal Cell Carcinoma:Utility of monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched exponential Diffusion-weighted imaging models1Department of Radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wu Han, China
Synopsis
Multi-b values DWI are feasible and useful in the noninvasive tissue characterization of renal tumors. DDC and f may provide additional information and could lead to improved differentiation with better sensitivity and specificity between central renal cell carcinoma (RCC) from renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma compared with conventional diffusion parameters.
Purpose
To quantitatively compare and evaluate the potential of various diffusion parameters obtained from monoexponential, biexponential, and stretched exponential Diffusion-weighted imaging models in differentiating between central renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma, with pathologic examination as the reference standardIntroduction
As the renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma grows, centripetal infiltration into the renal parenchyma is common1. Differentiating renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma from central RCC is important because of the differences in surgical management and prognosis. Prior studies suggested that biexponential and stretched exponential DWI models might provide more accurate information about water diffusion2.The purpose of this study was to quantitatively evaluate the potential clinical value of various diffusion parameters obtained frommonoexponential, biexponential, and stretched exponential DWI models in differentiating those two tumors.
Materials and Methods
The institutional review board approved this retrospective study and waived the informed consent requirement. 47 patients with either pathologic analysis-confirmed central renal cell carcinoma (n=29) or renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma (n=18) were assessed by using multi-b values DWI(0~1700 sec/mm2)on 3-T MRI. An isotropic apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) was calculated from diffusion weighted images by using a monoexponential model. A pseudo-ADC (ADCfast), true ADC (ADCslow), and perfusion fraction (f) were calculated from diffusion weighted images by using a biexponential model. A water molecular diffusion heterogeneity index (α) and distributed diffusion coefficient (DDC) were calculated from diffusion-weighted images by using a stretched exponential model. All parameters were compared between central RCC and renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma by using the Student’s t test or Mann–Whitney U test depending on homogeneity of variance. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were performed to determine the optimal thresholds, the sensitivities, and specificities for differentiation.Results
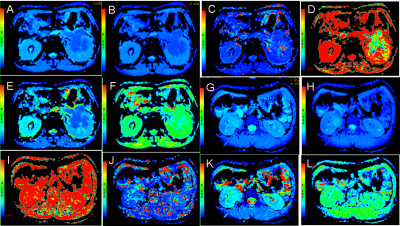
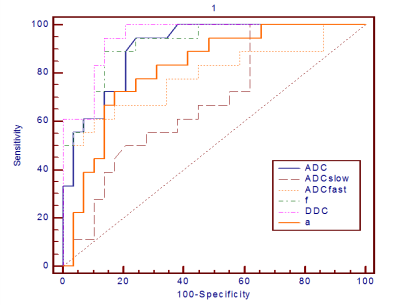
ADC, ADCslow, ADCfast, f and DCC values were significantly lower in the renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma group than in the central RCC group (All P <0.05). α value were slightly higher in the renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma group than in the central RCC group(P <0.05) (Fig.1). The AUC values for DDC (0.950), f (0.921) and ADC (0.906) were significantly greater than those for ADCslow (0.679), ADCfast (0.789) and α (0.818) in this differentiation (Fig.2). The AUC, sensitivity, specificity and the cutoff value, respectively, for differentiating RCC from renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma for DDC, f were as follows: DDC, 0.950, 86.2%, 94.4%, and 1.425×10-3 mm2/s; f, 0.921, 86.2%, 88.9%, and 0.273.Discussion and conclusion
In this study, the preliminary data from our study demonstrate that multi-b values DWI are feasible and useful in the noninvasive tissue characterization of renal tumors. DDC and f may provide additional information and could lead to improved differentiation with better sensitivity and specificity between central renal cell carcinoma (RCC) from renal pelvic urothelial carcinoma compared with conventional diffusion parameters.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Wong-You-Cheong JJ, Wagner BJ, Davis CJ Jr.Transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary tract:radiologic-pathologic correlation. RadioGraphics1998; 18:123–142; quiz, 148
2. Bai Y, Lin Y, Tian J, et al. Grading of Gliomas by Using Monoexponential, Biexponential, and Stretched Exponential Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging and Diffusion Kurtosis MR Imaging. RADIOLOGY. 2016;278: 496-504.