3113
Diffusional changes of perivascular space in focused ultrasound induced Blood-Brain Barrier disruption in rat brainHeajung Choi1, Huijin Song2, Kyung Eun Jang1, Hyunsil Cha1, Eunji Kim1, Mujin Yang1, Jiung Yang1, Hoesu Jung3, Mun Han4, Taekwan Lee3, Juyoung Park4, and Yongmin Chang1,5
1Department of Medical & Biological Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 2Institute of Biomedical Engineering Research, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 3Laboratory Animal Center, Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 4Medical Device Development Center, Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation, Daegu, Republic of Korea, 5Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea
Synopsis
Focused ultrasound (FUS) induces microbubble oscillation, which loosens the tight junction of the endothelial cells in the brain and opens Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB). In this study, we opened the BBB of rat brain using the MRI guided FUS to investigate the changes of diffusivity in perivascular space using diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Our results showed that ADC of the perivascular space increased after sonication suggesting the increased water diffusion in perivascular space after BBB opening. Therefore, our study suggests that ADC change can be a possible imaging marker for opening of BBB.
Introduction
There were several methods to disrupt the BBB, including injection of drugs or chemical agents [1]. However, these strategies have not been shown the effective delivery of drugs and still remains safety issues due to invasiveness and non-targeted method. FUS combined with microbubbles disrupts the BBB noninvasively and reversibly at targeted regions. The aim of this study was to investigate the change of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) in perivascular space after BBB opening by MRI guided FUS intervention.Materials and Methods
All of the procedures in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) and Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation (DGMIF). A total of 4 male Sprague-Dawley rats (250 – 350 g weight) were used for this study. They were anesthetized during all procedures of the experiment and the catheter for injection was placed in the vein. A single targeted region was sonicated (0.5 – 0.7 MPa) transracially in the left hemisphere in 4 rats using a 1 MHz FUS transducer with 10 ms bursts of ultrasound wave at 1 Hz pulse repetition frequency for 120 s, combined with intravenous injection of a microbubble ultrasound contrast agent (Definity, 80 μl/kg). The MRI scanner was 9.4 T Bruker System (BioSpec 94/20 USR, Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA) and T1 and T2 weighted MR images were used to guide FUS sonication on the targeted region and confirmed the BBB disruption using T1 contrast agent (Magnevist®, Bayer). DWI images were obtained with b-value of 1000. The ADC map was processed using Diffusion Toolkit, TrackVis (Wang, Athinoula A. Martinos center for Biomedical imaging). The difference of signal intensity on ADC map was compared by nonparametric tests using IBM SPSS 19 software.Result and Discussion
Figure 1 showed the contrast enhanced T1 weighted images indicating opening of the localized BBB and ADC maps after MRI guided FUS in 4 rats. ADC value of the ultrasound sonicated region (6.63 x 10-4 5.83 x 10-5) was significantly higher than the control area (9.23 x 10-5 6.41 x 10-5) (Figure 2). In case of hemorrhagic disruption instead of BBB opening, the ADC value was decreased (Figure 3). The increased ADC in perivascular space after sonification demonstrated the increased water diffusion in perivascular space after BBB opening. One possible explanation for the increase of ADC is that due to the loosed tight junction of BBB, water moves from intravascular space to perivascular space and thus water mobility increased in perivascular space. Another possibility is that the expression level of aquaporin-4, which is known as water channel at the BBB, was modulated by sonification to cause water diffusion changes.Conclusion
Our results showed that the increase of ADC in perivascular space after sonication is associated with successful BBB opening with MRI guided FUS intervention suggesting that ADC change can be a possible imaging marker for opening of BBB.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] De Boer, A. G. & Gaillard, P. J., Strategies to improve drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier, Clinical Pharmacokinetics 46, 553-576, doi: 10.2165/00003088-200746070-00002, 2007Figures
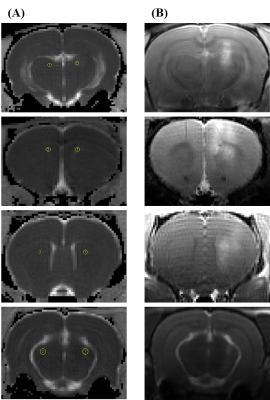
Figure
1. ADC maps from DWI 1 hour after sonication (A) and contrast enhanced T1 weighted
images (B) in 4 rats. Contrast enhanced T1 images showed that contrast agent was
delivered into the perivascular space with BBB opening and the signal intensity
is higher than control area on T1 weighted image.
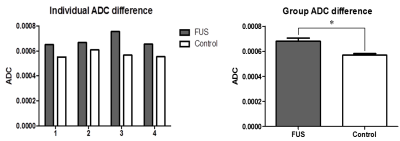
Figure
2. Graph of individual ADC difference and group ADC difference. ADC value of
focused ultrasound (FUS) sonicated region is higher than control are in all 4
rats. Group analysis was processed using non-parametric test and there was a
significant difference between FUS and control group. (p < 0.05)
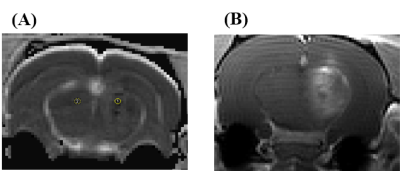
Figure 3. ADC map (A) and contrast enhanced T1 weighted
image (B) in case of hemorrhagic disruption after MRI guided FUS
intervention. The hemorrhagic region showed significantly decreased ADC value.