3088
Brain White Matter Microstructure Changes in Alzheimer disease with Type 2 diabetes:a DKI study1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Synopsis
In this study, the groups were respectively used as the people with Alzheimer disease with type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer disease without type 2 diabetes and healthy person, the effect of high blood glucose on the microstructure in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and the changes on microstructure in patients with AD patients were studied used DKI study, and it was concluded that the high blood glucose level may have certain damage to the microstructure of the white matter. In conclusion, DKI study can evaluate secondary brain microstructure changes from hyperglycemia in T2DM patients.
Target audience
Researchers interested in brain changes in patients with Diabetes Mellitus Type 2.Purpose
To initially detect the changes of diffusion on brain white matter (WM) damage in Alzheimer disease with Type 2 diabetes(AD+T2DM), without Type 2 diabetes(AD-T2DM) and healthy person(HC) by measuring the diffusion kurtosis data.Methods
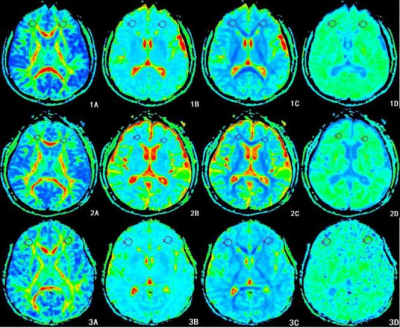
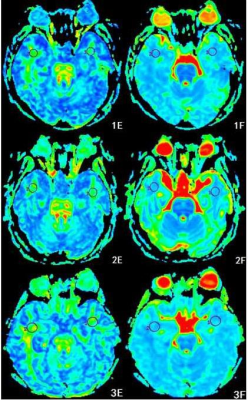
This prospective study was approved by the hospital ethics committee. The study was divided into AD+T2DM group(13 cases, 6 males, age 74.46±8.26 yrs), AD-T2DM group(22 cases, 9 males, age 70.82±8.72 yrs) and HC group(20 cases, 8 males, age 66.00±5.15 yrs). The mental status was evaluated for everyone through MMSE and MoCA scores by two neurologists.All performed MR protocols included conventional MRI, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI). DKI was done with the dual spin echo(SE-EPI) sequence(b=0s/mm2, 1000s/mm2, 2000s/mm2, and diffusion sensitive gradient field is 15 directions). Bilateral MK, Ka, Kr, MD, Da, Dr and FA values of the superior frontal gyrus(SFG) and middle temporal gyrus(MTG) were manually measured twice by two radiologists.One-Way ANOVA was used to compare the diffusion parameters in all regions between groups. The diffusion parameters in all regions compared AD+T2DM versus AD-T2DM, AD+T2DM versus HC and AD-T2DM versus HC used two independent samples t-test. In AD+T2DM and AD-T2DM groups, Spearman's correlations between DKI parameters and MMSE, MoCA scores were also calculated to investigate the relationship between the diffusion changes of white matter and the cognitive ability.Result
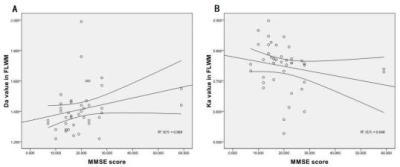
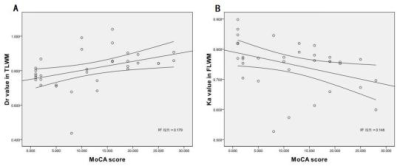
FA, MD, Dr, Ka value in SFG and FA, Dr value in MTG had significant differences among the three groups(all P< 0.05).Compared with those in AD-T2DM group, FA value generally increased, but only in MTG was significant(P< 0.05), and then Dr value generally decreased, but only in MTG was significant(P< 0.05) in AD+T2DM group.In comparison with HC group, FA, Ka value decreased in SFG and FA value decreased in MTG, and then MD, Dr value increased in SFG and Dr value increased in MTG both in AD+T2DM and AD-T2DM(all P< 0.05).In AD+T2DM and AD-T2DM groups, Da value in SFG showed the positive correlation with MMSE score(r=0.383, P=0.012). Simultaneously, the Ka value has the best negative correlation with MMSE score(r=-0.374, P=0.015). The Dr value in MTG has the best positive correlation with MoCA score(r=0.532, P=0.001, and then the Ka value in SFG has the best negative correlation with MoCA score(r=-0.498, P=0.003).Discussion and Conclusion
T2DM is a common chronic metabolic disorder, characterized by chronic hyperglycemia. In addition to (cardio) vascular disease, T2DM is associated with various pathophysiological cerebral abnormalities, accelerated cognitive decline, and dementia in older subjects[1]. In this studies, compared with the HC group, significant abnormal diffusion in the SFG and MTG illustrate the significant abnormal diffusion due to brain neurons are swollen and denatured, the brain structure becomes loose and less complicated when T2DM or AD occurs. Whereas, obvious anomalous diffusion in the MTG illustrate the microstructure complexity changes may related to the formation of Louis corpuscles, microglia aggregation in AD+T2DM than AD-T2DM group[2, 3].There is a clear relationship between DKI parameters and MMSE and MoCA score in AD+T2DM and AD-T2DM group which is indicated that the brain microstructure changes reflected in DKI parameters are consistent with the mental state of the brain. Furthermore, DKI can be used to detect the microstructure changes in white matter.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Yang S Q, Xu Z P, Ying X, et al. Altered Intranetwork and Internetwork Functional Connectivity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With and Without Cognitive Impairment[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6:32980.
[2] Biessels G J. Brain MRI correlates of cognitive dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: the needle recovered from the haystack?[J]. Diabetes Care, 2013, 36(12):3855.
[3] Biessels G J, Reijmer Y D. Brain changes underlying cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: what can we learn from MRI?[J]. Diabetes, 2014, 63(7):2244.
Figures