3036
Dysprosium based liver-specific ultra-high field MRI T2 contrast agent1Department of Medical &Biological Engineering, Kyungpook National Univesity, Daegu, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of, 2Department of Molecular Medicine & BK21 Plus KNU Biomedical Convergence Program, Kyungpook National Univesity, Daegu, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of, 3Institute of Biomedical Engineering Research, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of, 4Laboratory Animal Center, Daegu-Gyeongbuk Medical Innovation Foundation, Daegu, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of, 5Department of Radiology, Kyungpook National Univesity, Daegu, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
Synopsis
[Dy(EOB-DO3A)] is prepared according to the general
synthetic methods, and characterized by spectroscopic analysis.Therelaxivities
that measured at 9.4 T animal MRI are r1
= 1.01, r2 = 2.80 mM-1s-1.We
observe acceptablenegative-enhancement with liver T2-weighted image,
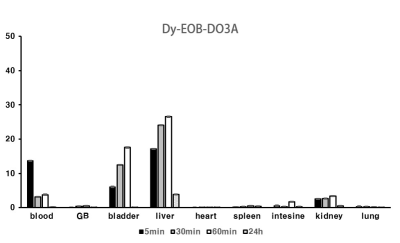
alsoconfirm about 30% liver accumulation within 1 h post-injection at
inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectrometer data.
Introduction
To date, the majority of commercially available T1 liver low-molecular MR contrast agents (CAs) are gadolinium chelates. However, other lanthanide ions such as dysprosium (Dy) relax water protons via a Curie relaxation mechanism that increases with the magnetic field strength. Therefore, Dy-based chelate can be very efficient T2 CA at the ultra-high field MRI. Here, for the first time, we try to synthesize low-molecular dysprosium complex that has liver-specific function as a high field T2 MR CA and examine its physical, biological properties with various methods.Materials and Methods
All reagents were purchased from commercial sources and used as received. Characterization of the synthesized compounds have been determined by analytical spectroscopic methods.(1) T1 measurements were carried out using an RARE-inversion recovery method with variable inversion times (TI) at1.5 T (64 MHz, GE healthcare, USA), 9.4T (400 MHz, bruker, Germany) both. For T2, the multi-slice multi-echo (MSME) sequence was adaptedwith 70 echoes at 1.5 T, 9.4 T. R1, R2 relaxation times were obtained from the nonlinear least-squares fit of the mean pixel values at variable TI and TE, respectively. The relaxivities (r1 and r2) were then calculated as a slope of linear fit of relaxation rate along with concentrations. The in vivo T2 weighted MR image was obtained at 9.4 T animal MRI equipment (bruker, BioSpec 94/20, Germany). In these studies, the mice (20 ~ 23 g) were anesthetized by 1.5% isoflurane in oxygen. MR images were acquired before and after intravascular injection of [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] (dose: 0.2mmolDy/kg). Also image parameters of axial images for fast spin-echo, RARE are as follows: Repetition time (TR) = 2500 msec; echo time (TE) = 18.33msec; 35 X 35 X 30 mm field of view (FOV); 128 X 128 X 30 matrix size; 1.0 mm slice thickness; RARE factor = 8; scan time of each image = 40 sec. Biodistribution of [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] was assessed with ICP-MS, ICR mice (6 weeks, 21~24 g) were used in this study.(2)Result and Discussion
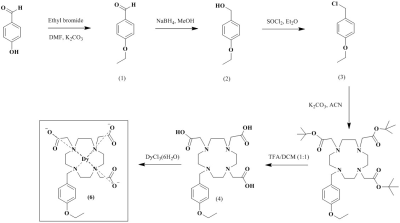
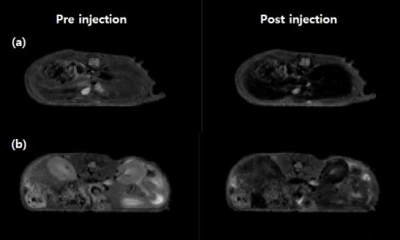
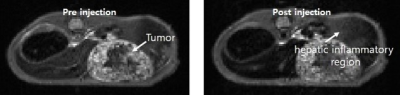
Scheme 1 shows the synthesis of [Dy(EOB-DO3A)], and the high-resolution FAB mass was obtained with this complex. Relaxivities of this dysprosium complex are r1 = 0.16, r2 = 0.16 mM-1s-1at low field MRI. But at high filed (9.4 T) are r1 = 1.01, r2 = 2.80 mM-1s-1. This field-dependence relaxivity is due to increasing of curie relaxation portion that increases over external magnetic field especially in T2 relaxation.(3) Unfortunately, r2value is lower than iron based nano-agent in high field. That results from the ligand (EOB-DO3A) structure that has carboxyclic acid arm as a strong electron withdrawing group. We are ongoing structure-activity studies with several ligands to overcome the low T2 relaxation. To assess the liver targeting property, ICP-MS of this complex was obtained according to post-injection time courses. Like in Figure 1, liver accumulation of the complex are about 30% within 1 h post-injection time. After 24 h, the complex is almost excreted from mice body. In vivo MRI experiment, [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] shows acceptable liver enhancement immediately after tail vein injection. As shown in Figure 2, it is excreted via urinal and hepatointestinal courses both. Figure 3 shows the axial T2-weighted MR images of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) model nude mice which were obtained by tail vein injection with [Dy(EOB-DO3A)]. The signal differencesbetween normal hepatocytes and tumor cells are obvious in post-injection image. Therefore, [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] demonstrated the probability to detect liver tumor and differentiate the margin between normal and abnormal liver cells.
Conclusion
We have successfully synthesized [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] as a high field liver targeting MRI CA.The results show that it might be useful as T2 agent in ultra-high field MRI. In addition, it is also demonstrated that [Dy(EOB-DO3A)] is valuable to diagnose liver cancer with hepatobiliary property.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
(1) Ah Rum Baek, J. Med. Chem.2017, 60, 4861-4868
(2) Hee-Kyung Kim, J. Med. Chem.2013, 56, 8104-8111
(3) Todd C. Soesbe, Magn. Reson. Med.2011, 66, 1697-1703