3015
Cardiac MRI assessment of the effects of dietary Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) on the adverse cardiac consequences of sepsis in ratAmidou Sissou Traore1, Thibault Leger2, Guilhem Pagès1, Lucie Cassagnes3,4, Azarnoush Kasra5, Jean-Marie Bonny1, and Luc Demaison2,6
1UR270 QuaPA, INRA, Saint-Genès Champanelle, France, 2UNH, INRA, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 3Department of diagnostic and interventional radiology, Clermont Ferrand University Hospital, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 4IGT, Institut Pascal, UMR 6602, CNRS, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 5Heart Surgery Department, Clermont Ferrand University Hospital, Clermont-Ferrand, France, 6CRNH, Clermont Auvergne University, Clermont-Ferrand, France
Synopsis
Severe sepsis is one of the leading cause of death in the intensive care units (ICU) or in short time after discharge from ICU. Developing a rat model of early sepsis involving caecal ligation and puncture, we undertaken this cardiac MRI study to quantitatively assess myocardial function and the protective effect of dietary EPA. Our results showed that, in the exception of the rate of contraction, cardiac functions are less impacted in the early hyperdynamic phase of sepsis with no/or milder modulation of dietary EPA.
Introduction
Severe sepsis is a serious syndrome requiring adequate medical care. It results in multi-organ damage with a significant toxicity: during the early phase of sepsis, cardiac mechanical activity is increased, but it progressively declines until cardiac failure. In the Western societies, the consumption of omega6 (w6) polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) is too high whereas that of omega3 (w3) PUFA is too low. Yet the consequences of sepsis could be altered by dietary PUFA which modulate the inflammatory process. The aim of this study was to determine the effects of dietary eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA or C20:5 w3) on the adverse cardiac consequences of sepsis.Materials
Female Wistar rats (n = 32) were fed with a diet deficient in w3 PUFA (n=16) or with a regime enriched with EPA (n=16) (187 mg/day) for 14 days. Each group was then submitted (n=8) or not to sepsis by caecal ligation and puncture (n=8). 48h after the surgical intervention, the animals were anaesthetized with isofurane for cardiac MR imaging.Methods
High resolution cine MR imaging was carried out at 11.7T (500MHz) with a 72-mm inner diameter volume coil. Ten to 12 contiguous 1-mm slices were acquired to cover the heart from the base to the apex using short-axis left ventricular (LV) bright blood cine imaging protocol based on the navigator self-gated FLASH sequence (repetition time (TR) / echo time (TE) 6/2.5 ms, flip angle (FA) 8 degrees, field of view (FOV) 5x5 cm, matrix 256x256, slice thickness 1 mm, oversampling 400). 16 movie frames were reconstructed per slice. After imaging session, rats were euthanized and the heart removed for analysis of mitochondrial function. Image analysis was performed using software Segment [1]. Semi-automatic segmentation of the LV was performed as described in [2] to obtain morphological and functional parameters, e.g., end diastolic volume (EDV), end systolic volume (ESV), ejection fraction (EF), heart rate (HR) and cardiac output (CO), along with the contraction and relaxation rates, which were derived from the time evolution of EDV.Results
Figure 1 show an example of segmentation results allowing the determination of the rates of contraction and relaxation. Sepsis did not alter significantly the EDV, ESV, EF, HR and CO. The rate of relaxation was not modified by the pathologic event either (Figure 2). However, the speed of contraction tended to be increased (p = 0.085) with the sample size used in the present study. Dietary EPA had no noticeable influence on the parameters of cardiac morphology and function. In omega-3 deficient animals, early sepsis induced an alteration of mitochondrial function in sepsis compared with control rats: i) drop in mitochondrial respiration (p <0.001); ii) decline in ATP production (p <0.05); iii) increased release of ROS (p <0.05). This difference according to the operation undergone is not found in EPA animals.Discussion and conclusion
That sepsis tended to increase the rate of contraction indicates that the pathology was in its early hyperdynamic phase with an activation of cardiac function. Since in omega-3 deficient animals, early sepsis induced drop in mitochondrial respiration (p <0.001) in sepsis compared to control rats, with no difference observed in EPA animals, the absence of difference in MRI global cardiac functions may attributed either the anesthesia or to the early state of sepsis not perceptible in MRI.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] http://segment.heiberg.se
[2] Riegler, J., Cheung, K. K., Man, Y. F., Cleary, J. O., Price, A. N. and Lythgoe, M. F. (2010), J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, 32: 869–877
Figures
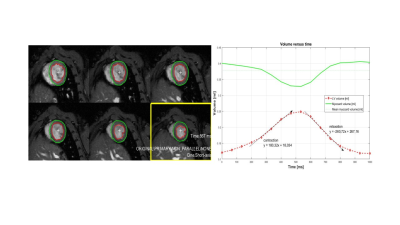
Figure
1: Representative illustration showing the results
of semi-automated segmentation of the left ventricular volume (left) and the
extracted evolution in time of the endocardium and epicardium curve (right).
The rates of contraction and relaxation were derived from the slop of systolic
and diastolic phases respectively.
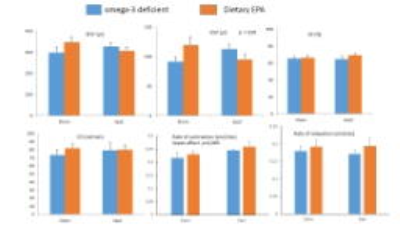
Left
ventricular functional parameters for control (sham operated) (n=16) and sepsis
(n=16) rats. In each group, rats were fed without (n=8) and with dietary EPA (n=8).
Data are mean and the bars are standard deviation of the mean. EF = (EDV-ESV)/EDV,
CO = (EDV-ESV)/HR