Changwu Zhou1, Chun Yuan2,3, Wei Wang1, Cheng Li4, and Xihai Zhao3
1Radiology, The affiliated hospital of YangZhou University, YangZhou, China, 2Department of Radiology, University of Washington, Washington, American Samoa, 3Center for Biomedical Imaging Research, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tsinghua University School of Medicine, Beijing, China, 4Radiology, Department of Radiology, Zhongda Hospital, Medical School of Southeast University, Nanjing, China
Synopsis
The circle of Willis
(COW) is an important intracranocervical collateral circulation system. We
hypothesized that the integrity of COW may affect the characteristics of
carotid plaques by influencing carotid hemodynamics. This study investigated the relationship between incompleteness of COW and the
compositional features of atherosclerotic plaques in carotid arteries. We found
that the incompleteness of circle of Willis is associated with vulnerability of
carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques.
Our findings suggest that integrity of circle of Willis may play a role in
occurence of high risk plaque features, particularly intraplaque hemorrhage and
fibrous cap rupture.
Introduction
The circle of Willis
(COW) is an important intracranocervical collateral circulation system [1].
COW can maintain adequate blood flow through its potential redistribution
function according to the anatomical morphology of COW, especially in patients
with cerebrovascular diseases [2-5]. We hypothesized that the
integrity of COW may affect the characteristics of carotid plaques by influencing
carotid hemodynamics. This study sought to investigate the relationship between
incompleteness of COW and the compositional features of atherosclerotic plaques
in carotid arteries.Methods
Study sample: Four
hundred and eighty-two symptomatic patients (mean age 61.2±10.4 years, 315
males) enrolled in a multicentre study of A Chinese Atherosclerosis Risk Evaluation
II (CARE-II, NCT02017756) were recruited in this study. All patients underwent
a routine 3D TOF MR angiography (MRA) for intracranial arteries and 2D
multicontrast MR vessel wall imaging for carotid arteries on a 3.0T MR scanner
(Philips Achieva TX) with a 8-channel dedicated carotid coil. The imaging
parameters for TOF MRA are as follows: 3D TOF: fast field echo, repeat
time/echo time 25/3.5 ms, flip
angle 20°, field of view 4.5×20×20 cm3, and spatial resolution
0.7×0.7×1.4 mm3. Carotid multicontrast MR vessel wall imaging was
performed using a standard protocol including TOF, T1W-QIR, T2-MDIR, and
MP-RAGE with published parameters [6]. The study protocol was
approved by institutional review board and written consent form was obtained
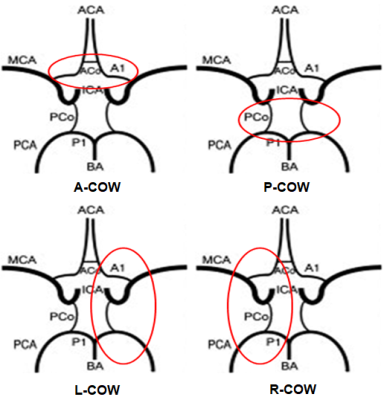
from each subject. Image review: The circle of Willis (COW) was divided
into four parts anatomically (Fig. 1):
anterior COW (A-COW), posterior COW (P-COW), left COW (L-COW) and right COW (R-COW).
The integrity of COW was evaluated. The absence of any structure on MRA images
in each of the four parts was considered as incompleteness of COW. For example,
the absence of anterior communicating artery (or left anterior cerebral artery:
ACA-A1 or right ACA-A1) was considered as incompleteness of A-COW. Carotid MR
images were reviewed by two radiologists with >5 years’ experience in
cardiovascular MR imaging using “CASCADE” (UW, Seattle, USA). Presence/absence
of plaque components, such as calcification, lipid-rich necrotic core,
intraplaque haemorrhage (IPH), and fibrous cap rupture was determined. Statistical
analysis: The prevalence of incompleteness of COW according to different plaque compositions in carotid arteries
was calculated and compared using Chi-square analysis.Results
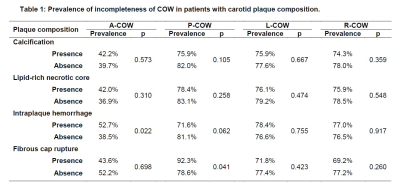
Of 482 patients, 421 (87.3%) had the incompleteness in COW. The prevalence
of incompleteness was significantly higher in P-COW than A-COW (79.7% vs.
40.7%, p<0.001). There was no significant difference between L-COW and R-COW
(77.0% vs. 76.6%, p=0.939). For carotid plaque characteristics, 48.1%, 73.0%, 15.4%
and 8.1% patients were found to have calcification, LRNC, IPH, and fibrous cap
rupture, respectively. The
prevalence of incompleteness in A-COW was significantly higher in patients with
IPH than those without IPH (52.7% vs. 38.5%, p=0.022) (Table 1, Fig. 2), especially the absence of anterior communicating
artery (69.2%, p=0.001). The prevalence of incompleteness in P-COW was
significantly higher in patients with FCR than those without FCR (92.3% vs.
78.6%, p=0.041, Table 1). No
significant differences were found in prevalence of incompleteness in COW
between patients with and without calcification and LRNC (all p>0.05, Table
1).Discusion and Conclusion
The incompleteness of circle of Willis is associated with vulnerability
of carotid artery atherosclerotic plaques.
Our findings suggest that integrity of circle of Willis may play a role in
occurence of high risk plaque features, particularly intraplaque hemorrhage and
fibrous cap rupture.Acknowledgements
We present this study on behalf of CARE-II study collaborators.References
[1] Sallustio F, et al. Stroke.
2008;39:1894-7.
[2] Tanaka H, et al. AJNR.
2006;27:1770-5.
[3] Liebeskind D. Stroke. 2003;34:2279-84.
[4] Rutgers DR, et al.
Stroke. 2004;35:1345-9.
[5] Hendeikse J, et al. Radiology.
2005;235:184-9.
[6] Xihai Zhao, et al. SVN.
2017.