2953
Cardiac Balanced SSFP 2D Cine DENSE for Myocardial Strain with comparison to Spiral 2D Cine DENSE1MRI Research Center, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States, 2Siemens Healthineers, Malvern, PA, United States
Synopsis
Quantification of myocardial strain has been previously demonstrated with echo-planar and spiral sequence versions of Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echoes (DENSE). However, the non-conventional k-space acquisition of these previous efforts has hindered their integration into mainstream cardiac MRI application. Here we present a more conventional balanced SSFP (bSSFP) version of 2D Cardiac Cine DENSE and compare its performance to 2D Spiral Cine DENSE in normal human subjects. In vivo human scans at 3T demonstrated good agreement of myocardial radial (Err) and circumferential (Ecc) strain values between bSSFP Cine DENSE and Spiral Cine DENSE that also agree with previous literature.
Purpose
Quantification of human myocardial strain has been previously well demonstrated with echo-planar and spiral sequence versions of Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echoes (DENSE)1-3. However, the non-conventional k-space acquisition of these previous efforts has hindered their integration into mainstream cardiac MRI (CMR) application. A common imaging method favored in CMR is balanced Steady-State Free Precession (bSSFP) that’s known for high SNR and versatility. Past efforts to integrate displacement encoding methods into bSSFP has had limited success4, 5. Here we present a bSSFP version of 2D Cardiac Cine DENSE that incorporates complementary in-plane and through-plane encoding for effective artifact suppression and GRAPPA acceleration. The bSSFP Cine DENSE is demonstrated in human subjects at 3T and its performance is compared to Spiral 2D Cardiac Cine DENSE.Methods
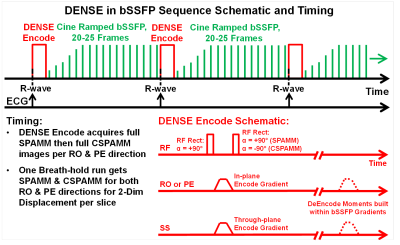
Fig 1 illustrates the bSSFP Cardiac Cine DENSE sequence that runs continuously as steady-state with ECG-trigger to acquire data on every heartbeat. The DENSE encode uses a standard 1-1 SPAMM/CSPAMM module selectable for in-plane, or through-plane, or both simultaneously. The cine bSSFP readout is customized with ramped start-up flip angle for fast approach to steady-state and modified gradients to incorporate the DENSE de-encode moments while maintaining gradient moment nulling. The end of cardiac R-R cycle can incorporate either α/2 magnetization restore method, or just run spoil gradients before the next triggered DENSE encode. Within one 25-second breath-hold, four DENSE acquisitions are performed that include cine SPAMM and CSPAMM in both readout (RO) and phase encode (PE) axes directions with simultaneous through-plane encoding. A second 12-second breath-hold is required to acquire a through-plane only encoded phase reference image necessary for bSSFP DENSE reconstruction. For performance comparison, a Spiral 2D Cine DENSE sequence was used with as similar imaging parameters as possible on the same 2D image slices. Imaging parameters included for both bSSFP and Spiral DENSE: Slice thickness = 8 mm, pixel size = 2x2 mm, cine frames = 20, Averages = 1, in-plane encode = 0.1 cyc/mm, through-plane encode = 0.08 cyc/mm; bSSFP DENSE only: FOV = 256x224 mm, matrix = 128x112, Bandwidth = 977 Hz/Pixel, GRAPPA acceleration = x2, flip angle = 30°; Spiral DENSE only: FOV = 320 mm, matrix = 160x160, Interleaves = 10, flip angle = 12°, Simple 3-point XY encoding. DENSE image and strain analysis were performed offline using customized Matlab programs (Mathworks, Natick, MA). Five healthy human subjects, 21-27yo, 2 female, with informed consent, were scanned in a 3T Verio scanner (Siemens, Erlangen, Germany) with a 32-chan anterior/posterior RF coil array (Invivo, Gainesville, Florida). DENSE slice locations included 1-3 mid-left ventricular (LV) short-axis (SA) views. Myocardial LV SA, six sector and global average strain values for radial (Err) and circumferential (Ecc) directions were calculated and compared between bSSFP and Spiral DENSE methods.Results
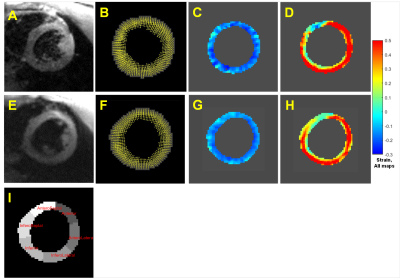
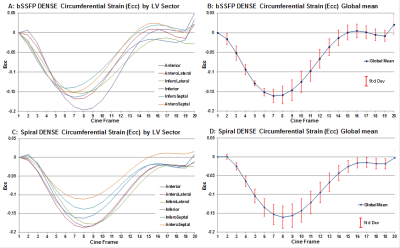
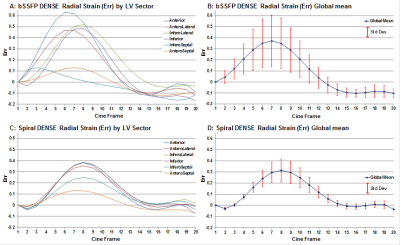
From all subjects, bSSFP and Spiral DENSE scans provided displacement encoded and reference image sets suitable for strain analysis. Fig 2-4 presents representative DENSE image and analysis product results comparing bSSFP to Spiral DENSE and they show good agreement. Fig 2 shows good agreement between bSSFP and Spiral DENSE displacement field, and strain maps. Fig 3 & 4 show good agreement of circumferential (Ecc) and radial (Err) strain values. Note that bSSFP DENSE, by design, tracks over 90% of the cardiac R-R cycle while Spiral DENSE typically tracked approximately 70-80% of the R-R cycle. However, bSSFP DENSE showed more T1 fading and noise-induced variation in the late-diastole frames. This is evident in the Fig 3 & 4 strain graphs showing bSSFP DENSE tracking more of the R-R cycle but with noisy final frames. Spiral DENSE had 3-times better SNR than bSSFP DENSE, but spiral had blurring that may effect its accuracy. While bSSFP and Spiral DENSE showed agreement per subject, variation was high across subjects with global mean Ecc = 0.15±0.25 (Mean±StdDev) and Err = 0.38±0.33.Discussion
This first practical CMR application of bSSFP DENSE in human cardic strain quantification is a promising start. The bSSFP and Spiral DENSE strain results agree through the first two-thirds of the R-R cycle. The Spiral DENSE presently has higher SNR and scan efficiency. More bSSFP DENSE optimization and acceleration is required to acquire all data per slice within one breath-hold, and/or expand to 3D capability, with/without respiratory gating methods. Sequence design and parameter trade-offs for minimizing DENSE encode interuptions to the bSSFP steady-state signal are still in work.Conclusions
We developed and demonstrated a practical bSSFP 2D Cine DENSE sequence for human CMR application. Future work will improve its speed, flexibility and overall performance.Acknowledgements
Special thanks for assistance by Dr. Martha Forloines, Mr. Julio Yanes, and Ms. Lily Strassberg.References
1. Aletras AH, Ding S, Balaban RS, Wen H. “DENSE: Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echoes in Cardiac Functional MRI”, J Magn Reson. 1999; 137(1): 247–252.
2. Kim D, Gilson WD, Kramer CM, Epstein FH, “Myocardial Tissue Tracking with Two-dimensional Cine Displacement-encoded MR Imaging: Development and Initial Evaluation”, Radiology 2004; 230:862-871.
3. Zhong X, Spottiswoode BS, Cowart EA, Gilson WD, Epstein FH, “Selective Suppression of Artifact-Generating Echoes in Cine DENSE Using Through-Plane Dephasing”, MRM 2006; 56:1126-1131.
4. Cowart EA, Gilson WD, Kramer CM, Epstein FH, “Imaging 3D Myocardial Motion with SSFP Cine DENSE”, Proc. Intl. Soc. Mag. Reson. Med. 11, 2004.
5. Kim D, Kellman P, “Improved cine displacement-encoded MRI using balanced steady-state free precession and time-adaptive sensitivity encoding parallel imaging at 3T”, NMR Biomed 2007; 20(6):591-601.
Figures