2909
Assessing myocardial infarct in lymphatic insufficient mice by rotating frame relaxation times1A. I. Virtanen Institute, University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland, 2Diagnostic Imaging Center, Kuopio University Hospital, Kuopio, Finland
Synopsis
Relaxation times T2, T1ρ and RAFFn were applied to study alterations in myocardial infarct (MI) in control and in mice with insufficient lymphatic system (VEGFR3). The findings are supported by cardiac functional parameters and histology. We found significant difference between VEGFR3 and control in TRAFF4 (p<0.05) 8 days after MI and between pre-MI and post-MI time points in T2 (p<0.01). Relaxation times increased significantly (p<0.05) after MI in all measurements. We conclude that TRAFF4 gain information of alterations of fibrosis in lymphatic insufficiency after MI.
Introduction
Lymphatic system regulates many processes involved in cardiac physiology and pathology, such as inflammatory reactions1, tissue fluid balance2 and atherosclerosis3,4 which can change the function of myocardium. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR3) is one of the key molecules in the development and maintenance of lymphatic system. T2 relaxation time increase has related to edema5 and increased water content which is associated with necrosis in the acutely ischemic myocardium. Increased longitudinal rotating frame relaxation time (T1ρ) has been related with later tissue remodeling i.e. granulation tissue formation and fibrosis6,7. Novel rotating frame relaxation time method to decrease specific absorption rate is relaxation along a fictitious field in nth rotating frame (RAFFn) which has shown to increase at myocardial infarct (MI) area compared to remote myocardium8. Here we applied T2, T1ρ and RAFFn relaxation time measurements TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 to study alterations of cardiac lymphatic system, its effects on MI and the role of VEGFR3 in cardiac lymphatics. We measured left ventricular (LV) functional parameters and support our findings with histology.Methods
Approximately 13-17 week old female and male VEGFR3 mice (n=8) expressing lymphatic insufficiency were used with 12 normal mice serving as a control group. MI was induced to all mice (n=20) by ligating the left anterior descending (LAD) artery. All experiments were done using 9.4 T magnet interfaced with Bruker BioSpec console. Gradient echo cine (TR=8.0ms, TE=1.9ms, thickness=1.0mm, matrix=192x192, number of cine frames=10-11) were acquired and double adiabatic Hahn echo (TE=0.05-14ms) was applied to measure T2 relaxation at 0, 8 and 42 days after MI. Adiabatic continuous wave T1ρ (pulse power 1250Hz, durations 0-57ms), TRAFF2 and TRAFF4 (RF powers: 1250Hz and 648Hz, respectively duration 2.26ms, pulse train lengths=0-36.2ms) relaxation times were measured 8 days after MI (n=5). Fast imaging with steady state precession readout (TR=5ms, TE=2ms) after weighting pulse was used.Results
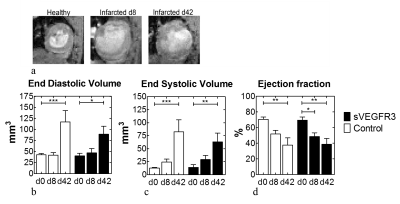
A significant difference in TRAFF4 between VEGFR3 and control mice were found at day 8 (Figure 1a). T1ρ, TRAFF2 and T2 relaxation times increased significantly after infarct in both VEGFR3 and control mice groups but no difference was found between the groups at day 8 (Figure 1b-d). Dilation of the LV was detected in both groups (Figure 2a). Also, increased end systolic volume and end diastolic volume caused decreased stroke volume and ejection fraction at 8 days after infarct (Figure 2b-d).Discussion
Elevated T2 at days 8 and 42 are most likely due to long-lasting edema in myocardium. Presence of edema has been shown to increase T2 and modify the development of fibrosis. Based on similar T2 at day 8, decreased lymph flow in VEGFR3 has not have an impact on long-lasting edema in infarct area. Furthermore, significant increase of TRAFF4 in VEGFR3 group compared to control group cannot be due to difference in edema, but more likely due to increased fibrosis. Histology showed that VEGFR3 mice had different composition of fibrotic scar compared to control group since VEGFR3 had less histological staining of collagen I and III compared to control group. Additionally, extracellular volumes (ECV) were higher at VEGFR3 group (16%) compared to control group (12%). These results together with increased levels of extracellular matrix proteins (e.g. α-SMA) in VEGFR3 group, supports the increased fibrosis in VEGFR3 mice compared to control mice. Increased levels of extracellular matrix proteins lead to stiffness of myocardium after MI which is reflected as a decreased ejection fraction. All of these findings supports elevated fibrosis in VEGFR3 group and may explain why rotating frame relaxation times were elevated in VEGFR3 mice at 8 days after MI.Conclusion
RAFF4 relaxation time TRAFF4 can be
used to determine and to gain information of altered fibrosis in lymphatic
insufficient myocardial infarction mouse model. Furthermore, alterations in
lymphatic morphology after myocardial infarct are reflected in cardiac function
parameters.Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Finnish Academy Center of Excellence, Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research, ERC Advanced Grant, Finnish Cultural Foundation (Kymenlaakso Regional Fund), The Paolo Foundation and Urho Känkänen Foundation.References
1. Kim K. W. et al. Immune Netw. 2017;17:68-76. 2. Breslin, J. W. Microvasc. Res. 2014;96:46-54. 3. Milasan, A. et al. Future Sci. OA 1, FSO61; 2015. 4. Vuorio, T. et al. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014;34:1162-1170. 5. Abdel-Aty H et al. J Magn Reson Imaging 2017;26:452–459. 6. Mustafa HSN et al. Magn Reson Med 2013;69:1389-1395. 7. Witschey WR et al. J Cardivasc Magn Reson 2012;15:14-37. 8. Yla-Herttuala E et al. Quantification of myocardial infarct area based on TRAFFn relaxation time maps- comparison with Late Gadolinium Enhancement, T1ρ and T2 in vivo. Submitted (2017)
Figures