2696
Real-time cardiac MR imaging based on a radial bSSFP sequence with trajectory auto-correction1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Guangzhou Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shenzhen, China, 3MR Collaborations NE Asia, Siemens Healthcare, Shenzhen, China, 4Centers for Biomedical Engineering, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
Synopsis
Conventional cardiac cine imaging is based on ECG-triggering, which is difficult to be used in arrhythmic patients. Real-time cardiac cine technique based on radial sampling scheme is an alternative approach for imaging the arrhythmic patients. However, the technique is often hampered in trajectory error due to system gradient delay. To address this issue, a novel real-time cardiac cine technique was developed based on a radial bSSFP sequence with trajectory error auto-correction. Preliminary results demonstrated that the proposed technique can improve the image quality and has potential to be clinically useful for the arrhythmic patients.
Introduction
Conventional cardiac cine MR imaging is based on ECG-triggering, which is difficult to be used in arrhythmic patients due to the patients’ irregular heartbeats and thus complicated cardiac phase synchronization. Real-time cardiac cine imaging technique based on radial sampling scheme is an alternative approach for imaging the arrhythmic patients. However, the technique is hampered in trajectory error due to system gradient delay. To address this issue, a novel real-time dynamic cardiac MR technique was developed based on a radial bSSFP sequence with trajectory error auto-correction and evaluated in patients with and without arrhythmia.Methods
Sequence and Reconstruction: All acquisitions were based on a radial bSSFP sequence which employs radial trajectory and sliding window sampling scheme [1]. Inspired by Ianni et al [2], a reconstruction method was developed for jointly estimating the radial trajectory errors, coil sensitivities, and dynamic images. The reconstruction can be described as Eq. (1).
$$argmin \frac{1}{2}\parallel d-PF(\triangle k)S\rho\parallel_2^2 + \lambda\parallel\rho\parallel_1^1$$ (1)
where P is sampling matrix, F is NUFFT operator with trajectory correction Δk, ρ denotes image, d is acquired data, S is coil sensitivity , λ is the regularization parameter, and G is the sparsify transform operator. An alternative iterative algorithm was used for solving Eq. (1).
Experiment: IRB-approved cardiac cine imaging was performed in 14 patients (8 with arrhythmia) on 3T (Siemens Verio, Germany) with a 32-element cardiac coil. Multi-slice 2D short-axis cine images were obtained in a stack of 7-12 contiguous slices spanning the entire left ventricle from the base to the apex. Imaging parameters included: TR/TE=3.0/1.52ms, FOV=220mm, bandwidth =1359Hz/pixel, spatial resolution=1.4×1.4×8.0mm3, temporal resolution=36ms. Conventional cine cardiac MR imaging with ECG-triggering was also conducted for comparison.
Image Analysis: Left ventricular (LV) function parameters, including LV end-diastolic volume (LV-EDV), LV end-systolic volume (LV-ESV), and LV ejection fraction (LV-EF), were calculated and compared with those obtained by the conventional approach in patients without arrhythmia. To investigate if the proposed method can improve the cardiac imaging in the presence of arrhythmia, contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) between blood and myocardium were calculated for the arrhythmic patients. The agreement on the measurements of LV-EDV, LV-ESV and LV-EF between the proposed and conventional methods was statistically analyzed using linear regression. And the CNR difference between the proposed and conventional methods was also analyzed by Wilcoxon sign-rank test. Statistical significance was defined as p < 0.05.
Results & Discussion
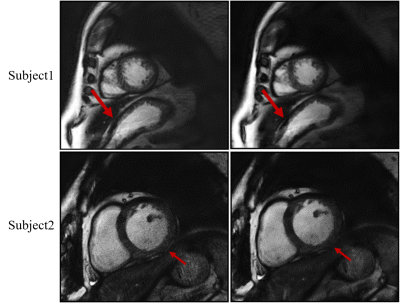
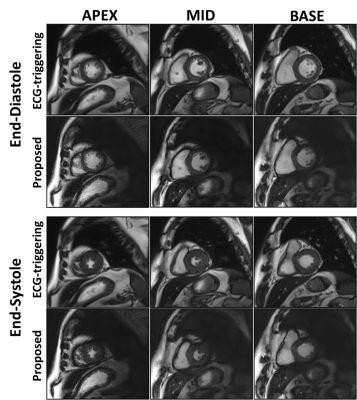
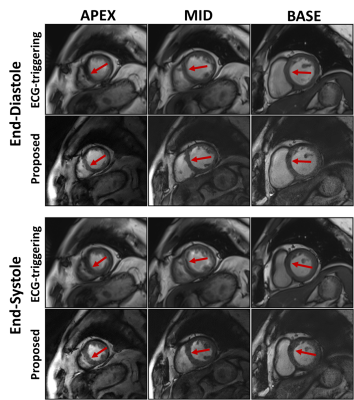
Using the proposed method to correct the radial sampling trajectories, reconstructed image quality was improved in terms of less signal intensity modulation and less image blurry (Figure 1). Cardiac cine images obtained by the proposed method were comparable with those by conventional approach (Figure 2). In addition, LV-EDV (75.5±25.3 ml vs. 75.6±24.7 ml, R2=0.995), LV-ESV (39.0±24.7 ml vs. 38.6±25.4 ml, R2=0.994) and LV-EF (50.9% vs. 51.8%, R2=0.966) between the proposed and conventional methods were well in agreement. This demonstrated that the proposed method was feasibility for accurately evaluating patient’s LV function. For the study of the patients with arrhythmia, the proposed method provided significant improvement of image quality with much less motion artifacts and better CNR (12.3±3.4 vs. 9.1±3.9, p = 0.004) between blood and myocardium (Figure 3).Conclusion
A real-time cardiac cine technique with auto trajectory correction was developed and evaluated on patients. Preliminary results demonstrated that the proposed technique has potential to be clinically useful for the patients with arrhythmia.Acknowledgements
National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFC0100302), Natural Science Foundation of China(81571669, 61201442) and the Natural Science Foundation of Shenzhen (JCYJ20160331185933583, GJHZ20150316143320494, KQCX2015033117354154), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong (2014B030301013).References
[1] Zhang S, Block K T, Frahm J. Magnetic resonance imaging in real time: advances using radial FLASH [J]. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2010, 31(1): 101-109.
[2] Ianni J D, Grissom W A. Trajectory Auto-Corrected image reconstruction [J]. Magnetic resonance in medicine, 2016, 76(3): 757-768.
Figures