2370
BOLD activation pattern of dominant versus non-dominant hand wrist extension task in stroke patients and healthy subjects1Centre for Biomedical Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, New Delhi, India, 2Department of Biomedical Engineering, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, NEw Delhi, India, 3Department of Psychiatry, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, NEw Delhi, India, 4Department of Neurology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, NEw Delhi, India, 5Department of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, All India Institute of Medical Sciences, NEw Delhi, India
Synopsis
Flexor-hypertonia being the most common symptom of stroke, overcoming it by attaining wrist-extension can be judged as key function of recovery of stroke. We compared activation pattern of dominant versus non-dominant hand movements of wrist-extension of 6 healthy-subjects with 6 dominant and 6 non-dominant stroke using fMRI. Results in healthy-subjects show differences in activation-pattern of dominant and non-dominant hand. Stroke patient’s results shows ipsilesional activation-pattern with dominant-hemisphere stroke with activation in motor, sensory area and cerebellum as compared to no ipsilesional activation-pattern in non-dominant hemisphere stroke. These results might have further implication in structuring rehabilitation-protocol for different hemisphere stroke differently.
Purpose:
In chronic stroke, physiotherapy plays an important role in rehabilitation and recovery. Coarse and fine motor movements may be verified by wrist-extension and finger-movement tasks, which are used in various fMRI studies1. Also, wrist extension exercise is important in stroke recovery, as it involves complex movement of various muscles. The BOLD activation for tasks by affected and unaffected hand may have a bias because of the hand dominance. The effect of hand-dominance in stroke, less impairment and better training response being an important factor in dominant-hand paresis has been demonstrated by2. Also, effect of dominant and non-dominant hand during this complex-movement has not been documented in healthy-subjects as well as patients with stroke, as has been for other simple motor-movements e.g. finger-tapping, finger-extension3.Methods:
After the ethics approval, patients with stroke (n=12), with Left Middle Cerebral Artery (LMCA) (n=6; M) and Right Middle Cerebral Artery (RMCA) (n=6; M) stroke with less than 2 years of chronicity and healthy-subjects right-handed (n=6, M:F=4:2,Age=21-30Yrs) were enrolled. Participants were asked to perform self-paced sequential full range of motion of wrist-extension tasks of 6 minutes each using block-design paradigm of 40-seconds active and rest state each by(a) left-hand only (Non-Dominant Hand, NDH), (b) right-hand only (Dominant Hand, DH) and (c) both hand simultaneously (BL), in supine position with palms facing downwards. To assess the robustness the data was acquired twice on same 6 healthy-subjects with a gap of 8-14 weeks.
Data was acquired using 3T MR scanner (Achieva, Philips Healthcare) with 31 transverse slices, TR=2000ms, TE=30ms, voxel-size:3.6x3.6x5mm. Slice time correction, realignment, normalization using mean-image and smoothing with 8x8x8mm FWHM filter was performed. General Linear Model (GLM) was employed on preprocessed and smoothed images. Constructed contrast maps were used for group-analysis. One sample t-test was performed for each task with voxel-level threshold p-value<0.01 (FDR-corrected) for healthy and p <0.001 (uncorrected) for patients. We have specifically focused on cerebellum and motor-regions.
Human Motor Area Template (HMAT) was used for Region of Interest (ROI) analysis. For each region in ROI analysis, mean of BOLD-signal was calculated for each participant and one sample t-test was performed (p<0.01, uncorrected). To evaluate lateralization and voxel-wise activation in each ROI, second level analysis was performed using masked regions (small-volume analysis) with p<0.01 (FWE-corrected) and cluster-threshold of 10 voxels. Lateralization-index (LI) was calculated using: LI=(Left ROI – Right ROI)/(Left ROI + Right ROI).
Results:
Healthy-subjects: Repeat scan of healthy subjects was used for BOLD and ROI analysis as it was less noisy as compared to scans acquired earlier.
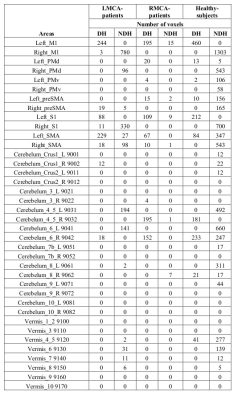
ROI analysis: NDH evoked larger clusters in motor-areas as compared to DH (tables 1,2 and figure1)
Lateralization: Laterality index using number of activated-voxels (LIN) for NDH revealed activation in contralateral M1, S1, PMd and ipsi- and contra-lateral SMA, preSMA, but no activation in PMv. DH task revealed activation in contralateral M1, S1, preSMA and ipsi and contralateral in SMA but no activation in PMd, PMv. BL motor task revealed activation in bilateral M1, S1, SMA, preSMA and right hemispheric PMd, but no activation in PMv (table 1).
Laterality Index using peak t-value (LIt) for DH shows high contralateral t-value in all ROIs (i.e. positive values for LIt) whereas NDH showed variable findings. NDH shows high contralateral t-value (i.e. negative values for LIt) in M1, S1, preSMA, PMd, but shows high ipsilateral t-value (i.e. positive values) in SMA and PMv. BL shows high t-values in right M1, S1, preSMA, PMv and in left SMA, PMv (table 1).
Patients: When compared to healthy-subjects, in both groups of patients irrespective of side of stroke, contralateral SMA was observed to be more activated for dominant-hand movement and less activated for non-dominant hand movement. The LMCA-patient showed larger activation in ipsilesion-hemisphere (M1=244,S1=88) as compared to RMCA-patient (M1=0,S1=0) when unaffected-hand does the movement (table-2).
Discussion:
In healthy-subjects, SMA activation showed hemispheric-asymmetry as left-SMA is consistently more active during DH, NDH and BL tasks (table 1). Consistent left preSMA activation was observed in NDH. BL showed high activation in right preSMA (table 1). In both group of patients, activation pattern in SMA was different for dominant and non-dominant side stroke. Activation was also observed in contralateral-hemisphere for both group of patients (LMCA-M1=3,S1=11,RMCA-M1=15,S1=9). This activation might be because of the reorganization within contralateral hemisphere, compensating for the functional loss of motor region. As compared to non-dominant hemisphere stroke, dominant-hemisphere stroke observes ipsilesional motor activation and ipsi-cerebellum activation. Recruitment of ipsilesional neurons (table 2) might indicate greater functional recovery reorganizational pattern as compared to recruitment of contralateral neurons as also observed by Richards et al.4.Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank SERB, Department of Science and Technology, Govt. of India for proving financial support for this project, project number YSS/2015/000697.References
[1] J. Newton, A. Sunderland, S. E. Butterworth, A. M. Peters, K. K. Peck, and P. A. Gowland, “A Pilot Study of Event-Related Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Monitored Wrist Movements in Patients With Partial Recovery,” Stroke, vol. 33, no. 12, 2002. [2] S. McCombe Waller and J. Whitall, “Hand dominance and side of stroke affect rehabilitation in chronic stroke.,” Clin. Rehabil., vol. 19, no. 5, pp. 544–51, Aug. 2005. [3] T. Hanakawa, S. Parikh, M. K. Bruno, and M. Hallett, “Finger and face representations in the ipsilateral precentral motor areas in humans.,” J. Neurophysiol., vol. 93, no. 5, pp. 2950–8, May 2005. [4] L. G. Richards, K. C. Stewart, M. L. Woodbury, C. Senesac, and J. H. Cauraugh, “Movement-dependent stroke recovery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of TMS and fMRI evidence.,” Neuropsychologia, vol. 46, no. 1, pp. 3–11, Jan. 2008.Figures