2121
Diffusion tensor imaging reveals altered brain development of MECP2 overexpressing rat in cerebellar and limbic structures1Institute of Neuroscience, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
In this study, we used diffusion tensor imaging to investigate the effect of MECP2 overexpressing (MECP2-OE) on the rat brain development. Our results showed the MECP2-OE mainly affected the cerebellar fiber tracts and limbic structures. Behavior tests showed the MECP2-OE rats presented significant defects of social interaction than the wild type (WT) rats.
Objective
Methyl-CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2) has a crucial role in neural development. The duplication of MECP2 can cause severe autism-like symptoms. However, the effect of MECP2 overexpressing (MECP2-OE) on the brain development remains unknown. In this study, diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) was carried out to investigate the brain development in MECP2-OE rats.Methods
DTI acquisition and processing Ninety-six SD rats were selected from three time points, P14 (WT=11, OE=16), P21 (WT=15, OE=21) and P28 (WT=15, OE=18), for in vivo DTI acquisition. Imaging was performed on a 9.4T MRI scanner with EPI sequence. Five non-diffusion-weighted images and 30 diffusion weighted images (b = 1000 s/mm2) were acquired for each animal. The acquisition parameters were TR 2000ms, TE 19ms, FOV 29 mm × 23 mm, matrix size 145 × 115, 50 contiguous coronal slices with a slice thickness of 0.4 mm, Δ 8.5 mm, δ 2.5 mm and 6 averages. DTI image volumes of each animal were corrected for eddy current distortion, and were then used to generate FA maps using the FSL. All the other FA maps were nonlinearly registered to a presentative one with the FNIRT of FSL. Two-way ANOVA in SPM was applied to analyze the effects of the age and MECP2-OE.
Social behavior test WT (n=14) and MECP2-OE (n=14) male rats, aged 8-9 weeks, were tested in a three chamber apparatus. On the test day, animals were allowed for 30 min habituation to its environment. A three-step procedure was performed. First, the tested animal was placed in the center chamber, and allowed to freely move over all three chambers for 10 min. Second, sociability was tested, in which a male intruder (Animal 1) in one mesh bucket was introduced to one of the side chambers, while the other bucket was kept empty. The test animal was allowed to explore both the chambers for 10 min. Lastly, the social novelty was tested by switching the familiar intruder into the other chamber and introducing a novel male intruder (Animal 2) to the chamber. The tested animal was monitored for 10 min as well.
Reseults
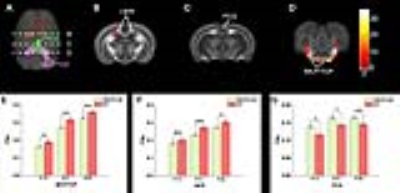
Altered brain development of MECP2-OE rat in cerebellar and limbic structures The results showed the effect of MECP2-OE was mainly located in cerebellar and limbic structures (Fig. 1 A-D, P<0.005, minimal cluster size 5 voxels). MECP2-OE rats presented significantly decreased fractional anisotropic (FA) value in the cerebellar fiber tracts, including the transverse fibers of the pons (TFP) and the bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles (MCP) connected with it, than that of the WT rats at all the time points we studied (Fig. 1 A, D and E). The decrease of FA value was also observed in the limbic structure, the hippocampus (Hipp), at P21 and P28 (Fig. 1 A, B and F). Interestingly, the MECP2-OE rats showed increased FA value in another limbic structure, the posterior part of cingulate cortex (PCG, Fig.1 A, B and G).
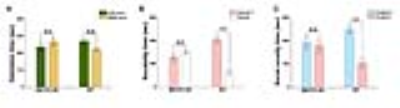
Social behavior defects of MECP2-OE rats During the first 10-min habituation period, no preference was observed to either side chamber (Fig. 2 A). When the first intruder animal was placed, WT rats spent significant (P<0.001) more time with their kinds than the empty chamber (Fig. 2 B). Such a preference was not seen in MECP2-OE rats (Fig. 2 B). During the last 10-min social novelty time, the WT rats showed a clear tendency of social novelty by spending a longer time with the stranger animal than with the familiar one (Fig. 2 C; P<0.001). Such social novelty was disappeared in MECP2-OE rats (Fig. 2 C).
Discussions
In this study, DTI was used to study to effect of MECP2-OE on the rat brain development. Compared with WT, the MECP2-OE rats displayed decreased FA value in cerebellar fibers, including TFP and the MCP connected with it. Similar FA observation had been reported in adolescent autism patients 1. Postmortem study of autism has revealed reduced number of relatively aligned apical dendrites in the HIPP 2. This may be potential interpretation of decreased HIPP FA value observed in this study. Oblak et al., have shown that the PCG in autism showed increased presence of white matter neurons 3. If the same case was presented in MECP2-OE rats, this may accounted for the increased FA in MECP2-OE rats. The results of behavior test showed the MECP2-OE rats presented significant defects of social interaction, a typical autism behavior, than WT rats. Thus, our results suggest that MECP2-OE rats may be provided as potential animal model to study the pathology of cerebellar and limbic structures in autism.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Shukla DK, Keehn B, Lincoln AJ, Muller RA. White matter compromise of callosal and subcortical fiber tracts in children with autism spectrum disorder: a diffusion tensor imaging study. J Am Acad Child Psy. 2010; 49 (12):1269-1278.
2.Raymond GV, Bauman ML, Kemper TL. Hippocampus in autism: a Golgi analysis. Acta Neuropathological. 1996; 91 (1):117-119.
3.Oblak AL, Rosene DL, Kemper TL, Bauman ML, Blatt GJ. Altered posterior cingulate cortical cyctoarchitecture, but normal density of neurons and interneurons in the posterior cingulate cortex and fusiform gyrus in autism. Autism Res. 2011; 4 (3):200-211.
Figures