1945
Microstructural Changes in Brain Gray Matter Nuclei of Patients with Parkinson's Disease:A Study Based on MR Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging1Affiliated Hospital Of BeiHua University, Jilin, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Parkinson's disease is the most common extrapyramidal disease in the elderly people, and the overall prevalence rate is increasing year by year. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) which was an based on the extension of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to reflect the diffusion motion of water molecules in the non-Gaussian distribution between tissues have been proved reliable for the brain microstructural changes. Previous studies have shown that DKI could facilitate the detection of subtle structural changes in the gray matter nuclei of patients with PD, which may be related to the reduction of dopaminergic neurons, iron deposition and gliosis.
Introduction
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the most common extrapyramidal disease in the elderly people, and the overall prevalence rate is increasing year by year. Diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) is a MRI technique to reflect the non-Gaussian diffusion motion of water molecules among tissues, which can more sensitively describe the complexity of microstructure[1-3]. Based on DKI, we aimed to evaluate the microstructural changes of brain gray nuclei in Parkinson's disease.Methods
Totally 9 PD patients (6 females and 3 males; aged 65.00±11.49 years old) and 12 healthy controls (HC) (9 females and 3 males; aged 67.58±10.28 years old) were included in this study. All the subjects were informed of the purpose of this study. And the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Beihua University Hospital, Jinlin, China. The DKI images were acquired based on a 3T MR scanner (Ingenia; Philips, Best, the Netherlands) with the following parameters: TR=3332ms, TE=101ms, matrix=112×110, FOV=220×220mm2, 18 slices, slice thickness=4 mm with no gap. Three b values from 0 to 2000 sec/mm2(0,1000,and 2000 sec/mm2).In Figure 1, DKI- and DTI- derived parameters including mean kurtosis (MK), axial kurtosis (AK), radial kurtosis (RK),mean diffusivity (MD), axial diffusivity (AD), radial diffusivity (RD), fractional anisotropy (FA) were calculated by using diffusion kurtosis estimator (DKE) software. Then region of interests (ROI) were placed on the bilateral predetermined structures including bilateral substantia nigra, red nucleus, head of caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus and thalamus by using ImageJ software. Nonparametric Rank-Sum test was applied between PD and HC groups.Results
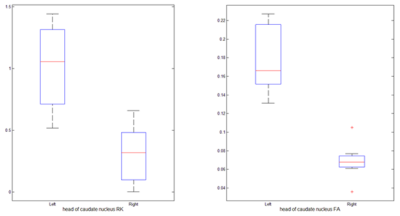
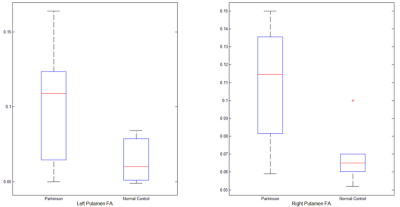
A comparison within the HC group showed that MK, RK and FA values of the left and right heads of caudate nucleus were significantly different (P<0.05) and details were shown in Figure 2. Furthermore, obvious differences of RK and FA values were also found between the left and right heads of caudate nucleus within the PD group (P<0.05) and the details were shown in Figure 3. As shown in Figure 4, compared with the HC group, FA was increased in bilateral putamen in the PD group (P<0.05).Discussion
In the present study, the results showed that there were differences in the parameters of the caudate nucleus heads between the left and right, which might be due to the difference in the dominant hemisphere between the left and right hemispheres and the involvement of iron deposition. The FA value of putamen in PD patients was increased compared to HC, which was different from the conclusions in other literatures[4]. Possible reason might lie in the relatively small sample size selected in the study, and the presence of subclinical patients or gliosis in the control group. There were some extreme values in the processing of statistical analysis, which might be caused by the artifact and distortion of anatomical structure. Further study will include more subjects and investigate the effect of iron deposition on the microstructural changes of the gray matter nuclei in PD patients with different stages.Conclusion
Parkinson's disease is associated with abnormal deposition of iron, which could account for microstructural changes in brain gray matter nuclei of patients with PD by DKI.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Hui ES,Cheung MM,Chan KC,et al.B-value dependence of DTI quantitation and sensitivity in detecting neural tissue changes. Neuroimage.2010,49(3):2366-2374.
[2]Yoshida M,Hori M,Yokoyama K ,et al.Diffusional kurtosis imaging of normal-appearing white matter in multiple sclerosis:Preliminary clinical experience.Japanese Journal of Radiology.2013,31
[3]Y Sun,J Sun,Y Zhou,et al. Assessment of in vivo microstructure alterations in grey using DKI in internet gaming addiction.Behavioal and Brain Functions.2014,10(1):37.
[4]Wang JJ,Lin WY,Lu CS,et al.Parkinson disease:diagnostic utility of diffusion kurtosis imaging.Radiology. 201 1,261(1):210-217.
Figures
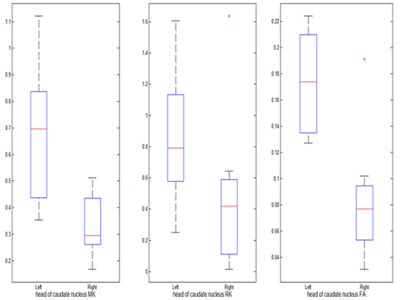
Figure 2. The MK RK and FA values showed significant difference (P<0.05) between the left and right heads of caudate nuclei of HC group. The central red mark is the median; the edges of the box are the 25th and 75th percentiles; the whiskers are the most extreme data points; red cross are outliers.