1912
Ferumoxytol vascular imaging of the central nervous system in pediatric patients compared to noncontrast MRA: a single center’s initial experience1Vanderbilt Children's Hospital, Nashville, TN, United States
Synopsis
Ferumoxytol-enhanced MRA allows for improved visualization and characterization of vascular pathologies in the brain compared to noncontrast MRA.
Purpose
Ferumoxytol, an iron oxide nanoparticle coated by a carbohydrate shell, is increasingly reported as an off-label blood pool contrast agent for MR angiography (MRA). We explore its use in the central nervous system (CNS) and in pediatric patients and compare the quality to noncontrast MRA. Noncontrast MRA is known to cause flow related artifacts, especially in cases of significant vessel tortuosity, vessel narrowing, wall thickening, or slow vascular flow.Materials and methods
Use of ferumoxytol for MRA was approved by the pharmacy and therapeutics committee. We retrospectively included patients from our initial three cases undergoing brain MRI for vascular abnormalities such as Takayasu’s arteritis and Loeys-Dietz Syndrome in 2017.
Three children underwent MRA examinations at 3.0 T MRI with precontrast MRA of the brain and vascular imaging after administration of diluted ferumoxytol at a dose of 3 mg/kg over 15 minutes.
The scoring of the following arteries including internal carotid artery (distal cervical segment, petrous segment, cavernous segment, supraclinoid segment), middle cerebral artery, anterior cerebral artery, anterior communicating artery, vertebral artery, basilar artery, posterior inferior cerebellar artery, anterior inferior cerebellar artery, superior cerebellar artery, posterior cerebral artery, and posterior communicating artery were reviewed on a standard PACS station. This was scored on noncontrast MRA and with ferumoxytol-enhanced MRA according to a three-point subjective score, where a score > 2 was considered diagnostic. The three-point scale was as follows: 1=Poor, precluding confident assessment; 2=Adequate for confident assessment of stenosis or occlusion, and 3=Excellent vascular definition sufficient for evaluation of fine detail. These arteries were also assessed for vessel caliber, tortuosity, stenosis and wall thickening.
Results
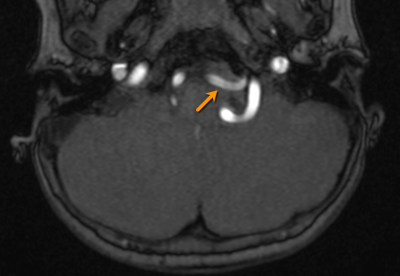
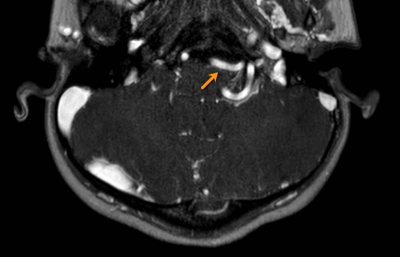
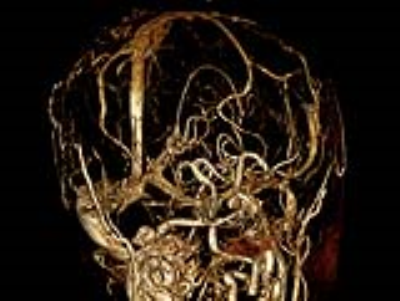
The noncontrast MRA resulted in flow related artifacts with loss of signal in smaller vessels as well as significant tortuous vessels (Figures 1, 2). The average image quality scores for selected arteries was between 1.8 – 2.4 for noncontrast MRA and 2.8 – 2.9 for post Ferumoxytol cases (Figure 3). Ferumoxytol allowed to confidently detect and characterize vascular abnormalities including tortuosity, stenosis, and wall thickening. None of the patients had an adverse reaction to the ferumoxytol.Conclusion
Ferumoxytol-enhanced MRA is a promising agent for the detection of vascular abnormalities in the brain. Additionally, can interrogate multiple territories in one study, due to ferumoxytol’s highly stable intravascular time. Therefore, from our early experience, ferumoxytol is a potential alternative to gadolinium-based contrast agents for high resolution neuro MR angiography.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures