1860
Decreased myelin water fraction in the corpus callosum at 6 months post mild traumatic brain injury1Radiology, UBC MRI Research Centre, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2Psychiatry, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 3Radiology, Diagnostic & Therapeutic Neuroradiology, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4Physics and Astronomy, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 5Psychiatry, British Columbia Provincial Neuropsychiatry Program, Vancouver, BC, Canada
Synopsis
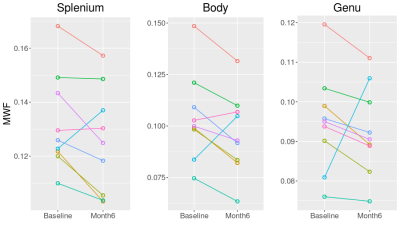
Monitoring mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) presents challenges for conventional MRI and underlying myelin changes are not well understood. Myelin water fraction (MWF) presents an opportunity to examine myelin changes post injury. At 6 months post injury, corpus callosum genu and body MWF decreased from baseline (acute) in 8 out of 9 subjects. Splenium MWF decreased in 7 out of 9 subjects. When averaged across subjects, the average decrease in MWF was 2% for the genu and 5% for the splenium, not significantly different from baseline; the lack of significance was due to large MWF increases in one of the participants.
Introduction
Mild traumatic brain injury (TBI) is difficult to characterize on conventional imaging and underlying pathology can persist after initial symptoms subside. Myelin plays an important role in TBI but the underlying effects of injury to myelin are not well understood, nor is the time course of myelin damage or dysfunction. DTI has been used extensively to examine mTBI white matter changes however, it is not specific to myelin changes and basic imaging outcomes such as FA have yielded conflicting results [1], [2]. Myelin water fraction (MWF) has been used to study myelin in both healthy brain tissue but also in neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases as well [3]–[7]. Recently it has also been used to examine acute concussion recovery in athletes [8], severe TBI at 3 months post-injury [9] and a chronic mixed severity TBI group [10]. Here we use MWF to examine changes between baseline (within two weeks of injury) and 6 months after mild traumatic brain injury.Method
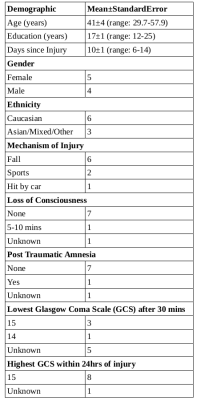
All subjects were recruited from the Vancouver General Hospital emergency room and were diagnosed with a mild TBI, based on physician concussion diagnosis with standard World Health Organization criteria for Loss of Consciousness, (<30 minutes) Post Traumatic Amnesia (<24 hours) and Glasgow coma scale (15-13). MRI scans were collected as soon as possible post injury (6-14 days) and then again at approximately 6 months post injury. Subject demographics are given in Table 1. MRI scans were completed on a 3T Philips Achieva scanner. Sequences included a 3DT1 structural scan (MPRAGE TR=3000 ms, TI = 821 ms, 1x1x1mm voxel with 155 slices) for registration and segmentation of corpus callosum regions (splenium, genu, body) and a 3D 48-echo Gradient and Spin Echo (GRASE) T2 relaxation sequence with an EPI factor of 3 (TR=1073, echo spacing = 8ms, 20 slices acquired at 1 x 2 x 5 mm and 40 slices reconstructed at 1 x 1 x 2.5 mm, FOV 230 × 190 × 100 mm, acquisition time 7.5 min) for MWF determination [11], [12]. FSL [13] was used to register GRASE/MWF to a halfway space between Baseline and Month6 space. 3DT1 was registered with MNI space and JHU-ICBM [14] ROIs of different CC regions were then registered onto the MWF halfway space. Average MWF were determined within each ROI and were compared between baseline and month 6 using a paired t-test.Results
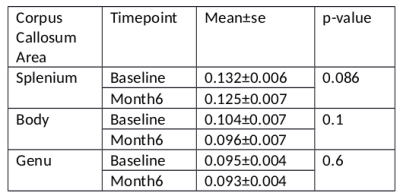
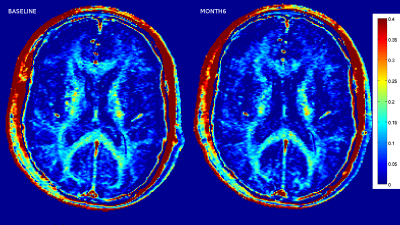
Sample MWF maps from a mTBI subject are given in Figure 1. The average MWF is given in Table 2 and MWF for each subject between baseline and month 6 are given in Figure 2. Over the 6 months post injury, the MWF in the genu and body of the corpus callosum decreased in 8 of the 9 subjects. In the splenium of the corpus callosum, MWF decreased in 7 of the 9 subjects. Across all subjects, paired T-test statistics showed that neither decrease was significant (p>.1) although there was a trend for decline in the splenium (p=0.086).Discussion
The two subjects with
increased MWF in the SCC were the youngest subjects we examined; we hypothesize
that recovery of myelination may be more rapid in younger individuals, however
this would need to be examined further. One of these subjects also demonstrated
an increase in MWF in the GCC and BCC, this subject was the second youngest
with no obvious indicators in demographics for being different than the other
subjects. A previous study of MWF in mTBI found a return to pre-injury MWF
after 2 months [8], here we find a
decrease in MWF most subjects between two weeks and six months. The T2
component that arises from myelin has been found not to be able to distinguish
between myelin debris and intact myelin [15], increase in myelin
debris and subsequent myelin debris clearance, may be able to explain these
differences. Our previous study [10], in a mixed TBI severity cohort
found significantly lower MWF in chronic TBI compared to matched controls,
however this was mostly driven by severe TBI. In the near future, this study
will be accumulating more mild TBI subjects as well as controls to be
measured at baseline and compared at month 6 to determine if change in MWF
differs between controls and mTBI.Acknowledgements
Thanks to :
- UBC MRI Research Centre Technologists
- Philips HealthCare
- Patients
- Irene Vavasour
- Angela Aquino
References
[1] M. B. Hulkower, D. B. Poliak, S. B. Rosenbaum, M. E. Zimmerman, and M. L. Lipton, “A Decade of DTI in Traumatic Brain Injury : 10 Years and 100 Articles Later,” Am. J. Neuroradiol., vol. 34, pp. 2064–2074, 2013.
[2] P. A. Narayana, “White matter changes in patients with mild traumatic brain injury: MRI perspective,” Concussion, vol. 2, no. 2, p. CNC35, 2017.
[3] C. Laule, I. M. Vavasour, S. H. Kolind, D. K. B. Li, T. L. Traboulsee, G. R. W. Moore, and A. L. MacKay, “Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Myelin,” Neurotherapeutics, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 460–484, 2007. [4] D. J. M. Lang, E. Yip, A. L. Mackay, A. E. Thornton, F. Vila-Rodriguez, G. W. Macewan, L. C. Kopala, G. N. Smith, C. Laule, C. B. Macrae, and W. G. Honer, “48 echo T2 myelin imaging of white matter in first-episode schizophrenia: Evidence for aberrant myelination,” NeuroImage Clin., vol. 6, pp. 408–414, 2014.
[5] C. Laule, I. M. Vavasour, G. R. W. Moore, J. Oger, D. K. B. Li, D. W. Paty, and A. L. MacKay, “Water content and myelin water fraction in multiple sclerosis: A T 2 relaxation study,” J. Neurol., vol. 251, no. 3, pp. 284–293, 2004.
[6] S. W. Flynn, D. J. Lang, A. L. MacKay, V. Goghari, I. M. Vavasour, K. P. Whittall, G. N. Smith, V. Arango, J. J. Mann, A. J. Dwork, P. Falkai, and W. G. Honer, “Abnormalities of myelination in schizophrenia detected in vivo with MRI, and post-mortem with analysis of oligodendrocyte proteins.,” Mol. Psychiatry, vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 811–820, 2003.
[7] C. Laule, E. Leung, D. K. B. Li, A. L. Traboulsee, D. W. Paty, A. L. Mackay, and G. R. W. Moore, “Myelin water imaging in multiple sclerosis : quantitative correlations with histopathology,” no. February, 2006.
[8] A. D. Wright, M. Jarrett, I. Vavasour, E. Shahinfard, S. Kolind, P. Van Donkelaar, J. Taunton, D. Li, and A. Rauscher, “Myelin water fraction is transiently reduced after a single mild traumatic brain injury - A prospective cohort study in collegiate hockey players,” PLoS One, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 1–16, 2016.
[9] J. Y. Choi, J.-W. Baek, J. Lee, and J. Kim, “Evaluation of Myelin Damage in Diffuse Traumatic Brain Injury using ViSTa-MWI,” in ISMRM 25th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, 22-27 April, 2017.
[10] B. Russell-Schulz, I. Vavasour, J. Zhang, A. L. Mackay, S. Porter, D. Fawcett, I. J. Torres, W. Panenka, L. A. Boyd, and N. Virji-Babul, “Decrease in myelin water fraction of global white matter and white matter tracts in traumatic brain injury (TBI),” in ISMRM 24th Annual Meeting & Exhibition, 07-13 May, 2016.
[11] J. Zhang, I. Vavasour, S. Kolind, R. Baumeister, A. Rauscher, and A. L. Mackay, “Advanced Myelin Water Imaging Techniques for Rapid Data Acquisition and Long T2 Component Measurements,” in ISMRM 23rd Annual Meeting & Exhibition,30 May-05 June, 2015.
[12] T. Prasloski, A. Rauscher, A. L. MacKay, M. Hodgson, I. M. Vavasour, C. Laule, and B. Madler, “Rapid whole cerebrum myelin water imaging using a 3D GRASE sequence,” Neuroimage, vol. 63, no. 1, pp. 533–539, 2012.
[13] M. Jenkinson, C. F. Beckmann, T. E. J. Behrens, M. W. Woolrich, and S. M. Smith, “FSL,” Neuroimage, vol. 62, no. 2, pp. 782–790, Aug. 2012.
[14] S. Mori, S. Wakana, PCM van Zijl, and L.M. Nagae-Poetscher. MRI Atlas of Human White Matter. Elsevier, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2005).
[15] S. Webb, C. A. Munro, R. Midha, and G. J. Stanisz, “Is Multicomponent T 2 a Good Measure of Myelin Content in Peripheral Nerve ?,” vol. 645, no. February 2002, pp. 638–645, 2003.
Figures