1839
Voxel-based morphometry using silent T1-weighted sequence elucidates the brain volume difference between autism spectrum disorder and children with typical development1Radiology, Osaka University, Suita, Japan, 2United Graduate School of Child Development, Osaka University, Suita, Japan
Synopsis
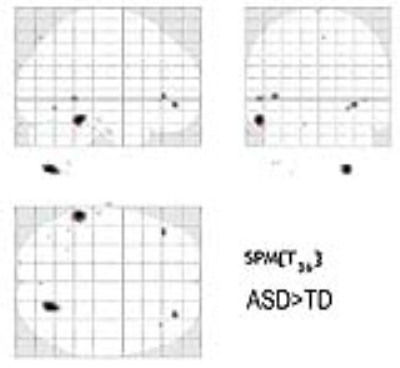
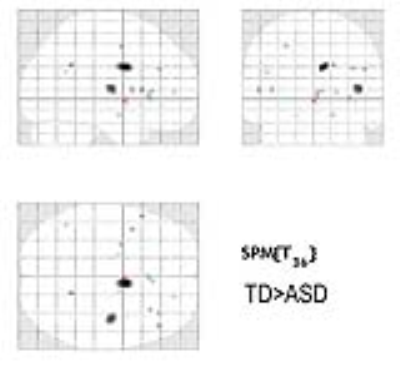
Silent MR sequences are expected to be useful and promising in the evaluation of hyperacusia patients, especially autism spectrum disorder (ASD). The aim of this research was to apply silent T1W to evaluate the brain volume changes between ASD and children with typical development (TD). Results showed that the brain volume of ASD was significantly increased at the left inferior temporal lobe and the right cerebellar tonsils and decreased at the right insular cortex and the right medial frontal lobe compared to that of TD. Silent T1W sequence can detect brain volume difference between ASD and TD.
Background and Purpose: Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by impaired social interactions, repetitive behavior, and communication. Auditory hypersensitivity is one of the clinical features in patients with ASD1. The acoustic noise of MRI is a major hurdle to perform MR exam in ASD. Favorably, recent developments in the silent MRI technique have dramatically reduced acoustic noise by employing fewer changes in gradient excitation levels2 T1-weighted (T1W) images are based on a three-dimensional (3D) gradient-echo imaging technique with a very short TE and an inversion preparation and reported very similar contrast of brain myelination3. The purpose of this study was to apply silent T1W to evaluate the brain volume changes between ASD and children with typical development (TD).
Methods: 20 patients with ASD (All male, Mean age 11.6y: 9-14y) and age-matched TD children (All male, Mean age 11.6y: 6-14y) were included in this study. 3T-MRI(Discovery MR750W)using a 24-channel-head coil was performed by silent T1W, TR/TE=880/0.016msec, FOV=240mm, Matrix=240X240, slice thickness 1.0mm and 0.5mm gap, 480 slices, acquisition time 5m10s. All images were preprocessed and analyzed using Statistical Parametric Mapping 12 (SPM12) running on Matlab(R2013b). Silent T1W image was segmented into gray matter (GM), white matter (WM), and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Subsequently, the segmented GM images were spatially normalized using the diffeomorphic anatomical registration through exponentiated lie algebra (DARTEL) algorithm and smoothed with an 8-mm full width at half maximum (FWHM) Gaussian kernel. After preprocessing, two sample t-tests were performed between the ASD and the TD groups to detect regional differences in GM and WM images (p<0.001 uncorrected).
Results: The brain volume of ASD was significantly increased at the left inferior temporal lobe and the right cerebellar tonsils compared to that of TD (fig1). The brain volume of ASD was significantly decreased at the right insular cortex and the right medial frontal lobes (fig2).
Discussion The review of structural MRI research of ASD reveals that there are many conflicting results regarding MR volume evaluation4. Patient’s age, processing methods, and software are key factors in these discrepancies. The brain volume (both GM and WM) dramatically changes from childhood to adulthood and there are great differences among individuals. In this study, we showed the brain volume difference using silent MRI, which is a useful sequence for hyperacusia ASD patients.
Conclusions: Silent T1W sequence can detect brain volume difference between ASD and TD.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgment.References
1. Hitoglou M, Ververi A et al. Childhood autism and auditory system abnormalities. Pediatr Neurol. 2010 May;42(5):309-14.
2. Alibek S, Vogel M, Acoustic noise reduction in MRI using Silent Scan: an initial experience. Diagn Interv Radiol 2014; 20:360–363.
3. Matsuo-Hagiyama C, Watanabe Y et al. Comparison of Silent and Conventional MR Imaging for the Evaluation of Myelination in Children Magn Reson Med Sci. 2017 Jul 10;16(3):209-216.
4. Chen R, Jiao-y et al. Structural MRI in Autism Spectrum Disorder Pediatr Res 69: 63-68. 2011