1824
A voxel-based diffusion kurtosis imaging study of whole-brain in chronic alcohol dependent patients1Department of Radiology, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, 2GE Healthcare China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
In the present study, diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI), which is based on the method of voxel-based analysis(VBA), was used to investigate the alterations of microstructure of white matter and gray matter in chronic alcohol dependent patients. Thirty patients with chronic alcohol dependence and twenty healthy volunteers were scanned with DKI. Compared with the healthy control group, the brain regions associated with visual information processing, memory, movement coordination and emotional control capacity have been found to be abnormal in different degrees.
Introduction
Chronic alcohol dependence is an addictive disorder, which is characterized by the excessive craving and uncontrollable drinking and seriously endanger the patients' psychological and physical health[1]. DKI, independent of gaussian distribution model, can more accurately reflect the water diffusion movement of non-gaussian distribution of living tissues[2]. The microstructure changes of the gray matter can be evaluated due to it does not depend on the spatial orientation of microstructure. Different from the traditional hand drawn ROI, different subjects can be matched to the standard space and have the whole brain analysis by VBA, the result is relatively stable[3]. This study was performed to make some progress on the early diagnosis and prognosis of this disease.Methods
Thirty patients with chronic alcohol dependence and twenty healthy volunteers were examined by DKI. Three b values (0, 1000, 2000 s/mm2) and 25 directions were collected. The raw data were pretreated and the relevant parameters were obtained by DKE software. VBA processing and statistical analysis were performed between chronic alcohol dependence group and healthy control group.Results
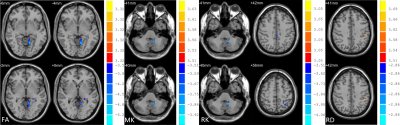
There was no significant difference between the two groups in age and education (P>0.05)(Table 1). Compared with the healthy control group, the FA value, MK value and RK value were decreased while the RD value was increased in chronic alcohol dependence group, and there was significant difference between the two groups respectively(P<0.001, Ke>30). There was no significant difference between the two groups in the other parameters (AD, MD, AK, FAk). Compared with the healthy control group, the FA values of left lingual gyrus and left hippocampus increased; the MK value of left cerebellum posterior lobe reduced; the RK value of left cerebellum posterior lobe, left middle cingulum, left superior parietal gyrus reduced; and the RD value of the left inferior parietal gyrus increased in chronic alcohol dependence group (Table 2, Figure 1).Discussion
Alcohol is a dependent psychoactive substance, and a large number of long-term drinking will lead to alcohol dependence. Alcohol dependence comprises a cluster of physiological, behavioral and cognitive phenomena, that is the strong desire of drinking and unable to control drinking behavior although know the harmful consequences of drinking. Short-term withdrawal can also produce a series of withdrawal symptoms[4]. This study found that DKI parameter values of chronic alcohol dependence were different in brain areas, mainly in the left lingual gyrus, left hippocampus, left cerebellum posterior lobe, left middle cingulum, left superior parietal gyrus, left inferior parietal gyrus, presenting an obvious left hemispheric dominance. These brain regions are mainly related to visual[5], learning and memory[6], voluntary movement[7-8], cognitive and emotional control[9]. We also found pathological changes and injury are more likely to occur in left hemisphere by chronic alcohol consumption. In addition, it should be noted that all subjects in this study were right-handed man. Further investigations are needed to study about whether the women or left-handed person have the same abnormal brain regions.Conclusion
There are dominant areas of brain injury in patients with chronic alcohol dependence, which mainly manifested in the decrease of visual information processing, memory, movement coordination and emotional control capacity. The DKI parameters can reflect the changes of the whole brain microstructure of chronic alcohol dependent patients and provide imaging basis in the diagnosis of chronic alcohol dependence.Acknowledgements
We are gratefully thankful for the support and assistance from Yang Fan of the Advanced Application Team of GE Healthcare China.
References
[1] Schuckit, MA. Alcohol-use disorders[J]. Lancet, 2009,373(9662):492-501.
[2] Hui ES, Cheung MM, Qi L, et al. Towards better MR characterization of neural tissues using directional diffusion kurtosis analysis[J]. Neuroimage, 2008,42(1):122-134.
[3] Van Hecke W, Leemans A, Sage CA, et al. The effect of template selection on diffusion tensor voxel-based analysis results[J]. Neuroimage, 2011,55(2):566-573.
[4] American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed)[M]. VA: American Psychiatric publishing, 2013,490-503.
[5] Schankin CJ, Maniyar FH, Sprenger T, et al. The relation between migraine, typical migraine aura and "visual snow"[J]. Headache. 2014, 54(6):957-966.
[6] Knierim JJ. The hippocampus[J].Curr Biol, 2015,25(23):R1116-1121.
[7] Dai XJ, Nie X, Liu X, et al. Gender differences in regional brain activity in patients with chronic primary insomnia: evidence from a resting-state fMRI study[J]. J Clin Sleep Med, 2016,12(3):363-374.
[8] Luo X, Guo L, Dai XJ, et al. Abnormal intrinsic functional hubs in alcohol dependence: evidence from a voxelwise degree centrality analysis[J]. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat, 2017,13:2011-2020.
[9] Bersani FS, Minichino A, Fojanesi M, et al. Cingulate Cortex in Schizophrenia: its relation with negative symptoms and psychotic onset. A review study[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2014,18(22):3354-3367.
Figures
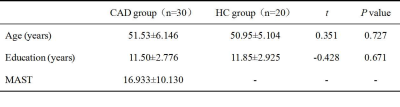
Table 1. Demographic and substance use characteristics(Mean±SD).
CAD, chronic alcohol dependence; HC, healthy control; MAST, Michigan alcoholism screening test.
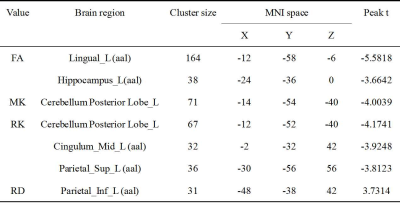
Table 2. The difference of DKI parameter values between chronic alcohol dependence group and healthy control group (p<0.001, cluster size>30).
FA, fractional anisotropy; MK, mean kurtosis; RK, radial kurtosis; RD, radial diffusivity; MNI, Montreal neurological institute.