1667
Application of DTI on hyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO) with Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy (DON) or diplopia patient after intravenous methylprednisolone strategy.1department of radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, wu han, China
Synopsis
The pathogenesis of DON and diplopia is totally different. This study use the MRI-DTI on DON and diplopia patients with good therapeutic efficacy, the multiple DTI parameters of optic nerve were calculated and assessed. The final results furtherly confirmed this difference. And the statistical difference of DTI parameter changes in DON patients validate the DTI can exactly, objectively and reliably detect the microstructure and functional repair of optic nerve after iv MP therapy.
Introduction & Purpose:
Dysthyroid optic neuropathy (DON) and diplopia are the common visual dysfunctions with thyroid-associated ophthalmopathy (TAO). But the pathogenesis of them is completely different. Diplopia is the major manifestation of extraocular muscle involvemen, while, two most widely accepted explanations for DON are the mechanical compression of the optic nerve at the orbital apex by the enlarged extraocular muscles1and the ischemic mechanism2. This study aims to observe the changes of DTI multi-parameters value in patients with TAO and DON in comparison with patients with TAO and diplopia after the administration of intravenous methylprednisolone. Additionally, investigate the role of MRI-DTI in pathogenic mechanism and neural functional recovery of DON after pulse methylprednisolone therapy.Methods:
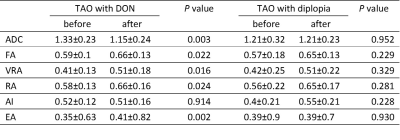
MRI-DTI images were prospectively viewed in 38 patients with TAO and diplopia, 15 patients with TAO and DON ,all the patients had a good effect on the treatment of intravenous methylprednisolone(iv MP) according to overall ophthalmic assessment. All the subjects underwent MRI-DTI examination before and after the therapy plan. The raw DTI images were reconstructed using FUNCTOOL on GE-AW4.6 workstation. Multiple scalar measurements of optic nerve, including fractional anisotropy (FA), apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), volume ratio anisotropy (VRA), relative anisotropy (RA) anisotropy index (AI) and exponential attenuation (EA) were calculated and analyzed by appropriate statistical methods.Results:
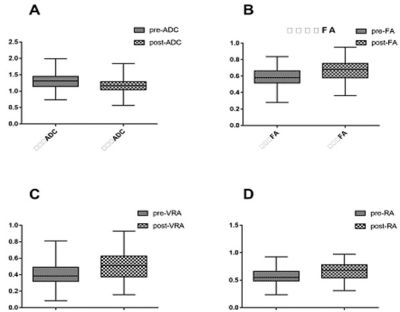
In patients with TAO and DON, after the intravenous methylprednisolone treatment, the DTI parameters of optic nerve changed (Fig.1), the ADC decreased statistically (p=0.003) and FA, VRA, RA and EA increased significantly (p=0.022, p=0.016, p=0.024, p=0.002, respectively) (Table 1). No significant difference of ADC, FA, VRA, RA, AI, EA were observed in patients with TAO and diplopia (p=0.952, p=0.229, p=0.329, p=0.281, p=0.228, p=0.930, respectively).Discussion:
Diffusion-tensor imaging provides useful information regarding the axonal state and myelin degradation of the optic nerve in visual pathway diseases3. The multiple parameters of DTI have become the primary tools of valuable clinical applications. The FA is thought to reflect fiber density, axonal diameter, and myelination in the white matter. Previous study has demonstrated that increased FA of the optic nerve can differentiate thyroid eye disease (TED) from normal controls, but also the active and inactive stages of TED4. In our study, the iv MP treatment can control and alleviate ocular inflammation, thus, the microstructure of damaged optic nerve changed, axonal integrity of the optic nerve and neural functional recovered partially, the increased FA well validate this change. The ADC reflects the average diffusivity of water molecules. The higher ADC value reflect the degeneration and demyelination of nerve fiber, a good therapeutic effect appeared as a decreased ADC on MRI-DTI. In diplopia patients with TAO, impaired visual function has nothing to do with optic nerve, even if achieve a good therapeutic effect, the optic nerve DTI parameters had no significant difference.Conclusion:
MRI-DTI can noninvasively differentiate the pathogenic mechanism of DON and diplopia in TAO patients partially. The DTI parameters can objectively and directively reflect the functional and structural recovery of optic nerves after iv MP stratagem.Acknowledgements
This study has received funding by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81301192 and No.81771793)References
1. Feldon SE, Muramatsu S, Weiner JM. Clinical classification of Graves' ophthalmopathy. Identification of risk factors for optic neuropathy. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984;102(10):1469-72.
2. Dosso A, Safran AB, Sunaric G, Burger A. Anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in Graves' disease. J Neuroophthalmol. 1994;14(3):170-4.
3.Engelhorn T, Michelson G, Waerntges S, et al. Changes of radial diffusivity and fractional anisotropy in the optic nerve and optic radiation of glaucoma patients. TheScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:849632.
4.Lee H, Lee YH, Suh SI,et al. Characterizing Intraorbital Optic Nerve Changes on Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Thyroid Eye Disease Before Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy. Journal of computer assisted tomography. 2017.
Figures