1608
Comparison between readout segmented diffusion weighted imaging and single shot echo planar imaging for differential diagnosis of prostate cancerChuangbo YANG1, Qi YANG1, Nan YU1, Hui TAN1, Wei WEI1, Guangming MA1, Shaoyu WANG1, and Shenglin LI2
1Departments of Diagnostic Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang,China, China, 2Shaanxi University of Chinese Medicine, Xianyang,China, China
Synopsis
Readout segmented diffusion weighted imaging (Rs-EPI) with ultra-high b value ( 1000、2000、3000s/mm2) have high sensitivity , specificity, PPV and NPV in the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer than single shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) does.
Objective
To compare the efficacy of readout segmented diffusion weighted imaging (Rs-EPI) and single shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) with ultra-high b value for prostate cancer differential diagnosis.Methods
37 pathologically confirmed patients after surgery or biopsy, readout segmented diffusion weighted imaging (Rs-EPI) and single shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) with ultra-high b value were obtained. The b values were 1000、2000、3000s/mm2. The patients were identified with either prostate cancer (15 cases) or prostate hyperplasia (22 cases) according to pathological results. All the images were analyzed by two experienced radiologists blinded to the final result. The efficacy of parameters for differentiation of prostate cancer were investigated by comparing the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) between Rs-EPI and SS-EPI.Results
The sensitivity specificity, PPV and NPV of RS-EPI were higher than those in the SS-EPI for all b values ( 1000、2000、3000s/mm2). These values obtained from RS-EPI with 3000s/mm2 presented more significantly higher. (table 1,2)Conclusion
Both Rs-EPI and SS-EPI with ultra-high b value (1000、2000、3000s/mm2) can be used for identification of prostate cancer and benign prostatic hyperplasia. However, RS-EPI with higher sensitivity specificity, PPV and NPV may provide more information in the differential diagnosis of prostate cancer than SS-EPI does.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
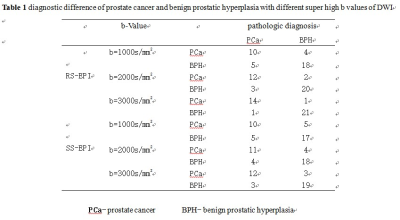
Table 1
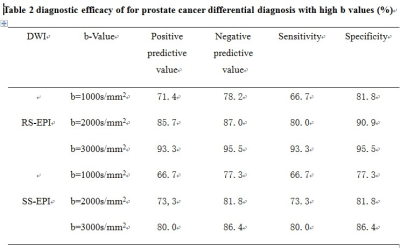
Table 2
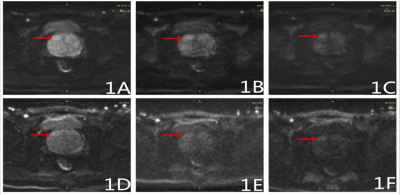
Figure 1, A-F Male, 68 years old,
with abnormal signal on the right side of the prostate was diagnosed as
prostatic hyperplasia. Images obtained from Rs-EPI with b=1000s/mm2(1A)
, b=2000s/mm2(1B) , b=3000s/mm2(1C) shown a
lesion obviously with a clear border and mild diffusion limitation; while
images obtained from SS-EPI with b=1000s/mm2 (1D) ,b=2000s/mm2(1E), b=3000s/mm2 (1F) shown a unclear lesion with blurred border.
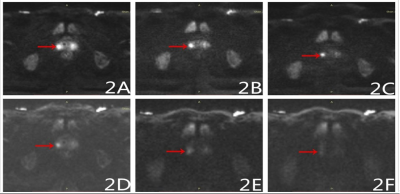
Figure 2A-F, Male, 65 years old,
with abnormal signal on the central gland of the prostate was diagnosed as
prostatic cancer. Images obtained from Rs-EPI with b=1000s/mm2 (2A), b=2000s/mm2(2B), b=3000s/mm2(2C) shown a
lesion obviously with a clear border and obviously contrast between the lesions
and normal liver tissue; while images obtained from SS-EPI with b=1000s/mm2
(2D), b=2000s/mm2(2E), b=3000s/mm2 (2F) shown a unclear lesion with blurred border.