1606
Application value of DKI in grading of pancreatic cancer1Department of Radiology, Jiangxi Cancer Hospital, Nanchang, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Beijing, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Tumor cells and the complex micro-environment would lead to restricted the water molecules diffusion, in the form of non-Gaussian distribution at space, and diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI)(1) describes the degree of non-Gaussian distribution, and it has shown to reflect more sensitive diffusion information comparing with regular diffusion weighted image(DWI)(2). It was reported that DKI helped to classify tumors like astrocytomas (3). However, there is challenges on the DKI application mostly due to low SNR in pancreas diffusion images and motion artifacts. pancreatic cancer is a malignant pancreatic tumor,and the recent prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer is determined by the histopathological grade of tumor. Herein, we reported the investigation on applying DKI to differentiate the histological grade of pancreatic cancer.,by assessing DKI parameters.
Purpose
DKI(1) provides quantitative informations about how water diffusion deviates from a normally distributed diffusion and reflect the inhomogeneity of the organization .Therefore,the purpose of the study was to investigate DKI parameters in different histological grades of pancreatic cancer and to explore the preliminary application of DKI the classification value of the pancreatic cancer.Methods
This Institutional Review Board (IRB)-approved, a total of 6 patients (2 males and 4 females) with pancreatic cancer confirmed were recruited, and all the subjects gave written informed consent. Demographic and physiological information for participants were acquired before MR scanning.4 patients with no specific pancreatic cancer histological grade or large necrotic area of pancreatic lesions were excluded from the study. MRI exams were performed on 3.0T MR Scanner (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare,Best,the Netherlands).DKI was obtained with following parameters:TE=96ms, TR=3500ms,FOV=370mmx322mmx180mm,Thick 4.5mm,NSA=3. Repletion is high (2, 4, 6, 6, 8) for DKI with b-values at 0, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500 s/mm2, to recover lost SNR in DWI images at higher diffusion weightings. Respiratory-triggered acquisition was applied to weaken the impact of respiratory motion.
Images with multiple diffusion weightings were analyzed by in-house configured kurtosis analysis algorithm. The mean kurtosis (MK) and mean diffusion (MD) values were measured for pancreas for DKI model. Ellipsoid ROIs of approximately 10-15 pixels were placed inside and outside the pancreatic cancer.
Results
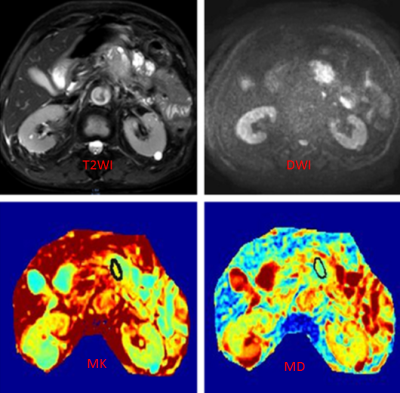
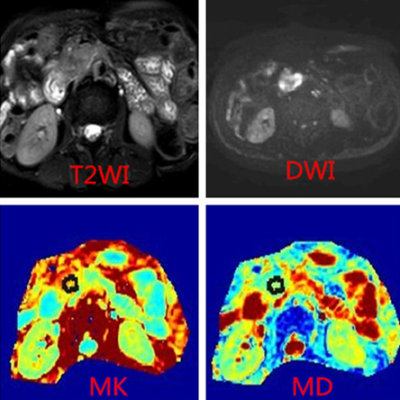
In this study, we found MK values are correlated with the histological grade of pancreatic cancer,however, there was no significant difference in MD values at different histological grades of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Figure 1 shows that the MK value of the well differentiated adenocarcinoma is 0.473 and MD value is 1.92×10-3mm2/s; Figure 2 shows that the MK value of the poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma is 0.62 and MD value is 1.95×10-3mm2/s.Conclusion and Discussion
Compared to well differentiated adenocarcinoma, MK value of the poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma is higher. it indicated that MK values increase with tumor grade.Pancreatic cancer cells proliferate actively and form tumor-like tubular or adenoid structures,and tumor cells are large and close, which are the pathological basis for the restricted diffusion of water molecules(4).The tumor structures of the poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma are more complex. Proliferation, necrosis, degeneration of the tumor cells lead to the more obvious heterogeneity , and the proportion of fibrosis and tumor-like structures increase , which make the water molecules diffusion much slower(5)and the deviation from the Gaussian distribution larger. This difference can be reflected by the difference of DKI parameters. MK values of our results indicate that the previous report of MK values application in the grading of other tumors could also borrowed into the grading pancreatic cancer. For example, Raab(6) found, with DKI technology on II, III, IV astrocytoma, that MK values increased and MD values decreased, with the increase of malignancy. However, in our study, there was no significant difference in MD values for different histological grades of pancreatic cancer, which may be due to the small number of cases.
DKI use quantitative, noninvasive methods to show tissue microstructure changes. In this study, we found that MK may be related to the pathological grade of pancreatic cancer. We are studying more clinical cases to analyze the significance of DKI in different pathological grades of pancreatic cancer to help preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic cancer pathology.
Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1.Jensen JH, Helpern JA. Ramani A, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaing : the quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med, 2005,53(6): 1432–1440.
2.Van Cauter S ,Veraart J ,Sijbers J,et al.Gliomas:Diffusion kurtosis MR imaging in grading[J]. Radiology,2012,263(2):492-501.
3.Delgado AF, Fahlström M et al.Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging of Gliomas Grades II and III - A Study of Perilesional Tumor Infiltration, Tumor Grades and Subtypes at Clinical Presentation.Radiol Oncol. 2017 Feb 15;51(2):121-129.
4.Matsuki M,Inada Y,Nakai G,et al.Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of pancreatic carcinoma[J] . Abdom Imaging.2007.32(4):480-484.
5. Klauss M, Gaida MM, Lemke A, Grünberg K, Simon D, Wente MN, Delorme S, Kauczor HU, Grenacher L, Stieltjes B. Fibrosis and pancreatic lesions: counterintuitive behavior of the diffusion imaging-derived structural diffusion coefficient d. Invest Radiol. 2013;48:129–133.
6. Raab P, Hattingen E, Franz K, et al. Cerebral gliomas:diffusional kurtosis imaging analysis of microstructural differences. Radiology,2010, 254(3): 876–881.