1602
The diagnostic values of DTI and DKI techniques in degeneration of corpus callosum of chronic alcoholism1Imaging Center, the 251st Hospital of PLA, Zhangjiakou, China, 2The Graduate School of HeBei North University, Zhangjiakou, China, 3GE Healthcare, China, Beijing, China
Synopsis
Chronic alcoholism is a common disease, and many patients are often associated with corpus callosal degeneration. In this study, the values of fractional anisotropy (FA) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and the mean kurtosis (MK) values in diffusion kurtosis imaging (DKI) were used to analyze chronic alcoholism with corpus callus (MBD) patients, to explore the diagnostic value of these three parameters in MBD patients. Receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC)analysis of the parameters of the diagnosis of the disease. The results showed that FA is better than ADC and MK, and the sensitivity and specificity are better.
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to find early abnormal changes of corpus callosum in patients with MBD, to provide the basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment. The changes of the corpus callosum in MBD patients were observed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) DTI and DKI. The diagnostic efficacy of each parameter was evaluated by ROC curve.Material and Methods
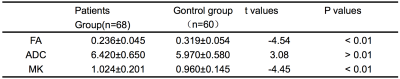
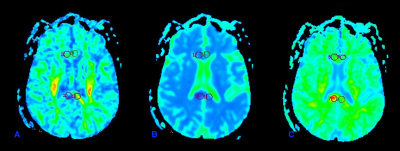
68 patients with chronic alcoholism who were admitted to the 251st Hospital of PLA from July 2015 to February 2017 were collected, with an average of 48 ± 1.2 years old and 60 healthy middle-aged volunteers with an average age of 53 ± 3.1 years. MRI examination using GE signa HDxt1.5T superconducting magnetic resonance scanner, 8-channel phased-wave head coil, the subjects were routine MR scan, using DTI and DKI to generate the relevant parameters (FA, ADC, MK), to assess the measurement value of the diagnosis of corpus callosum degeneration。 DTI uses a single-shot spin echo planar imaging (SE-EPI) sequence with scan parameters of TR 8000 ms, TE 85.5 ms, matrix 256 × 256, field of view 230 mm × 230 mm, diffusion-sensitive gradient direction number 15, b = 1000 s / mm2, scanning layer thickness 5 mm, layer spacing 0 mm, excitation number 2. DKI scan with double spin echo sequence, TR2400 ms, TE 108 ms, FOV 256 mm × 256 mm, matrix 128 × 128, layer thickness 4 mm, diffusion-sensitive gradient field applied in the direction of 20. The ADW 4.5 workstation was used to analyze and process the data, and the region of interest (ROI) was placed on the DTI parameter map and the DKI parameter map in three consecutive levels of the corpus callosum, corpus callosum and corpus callosum (Figure.1). Experimental Data Statistics Application SPSS software for processing, measurement data to x ± s said two samples paired t test for comparison between groups; the use of ROC curve to assess the diagnostic efficacy of each parameter, P < 0.01was used to indicate statistical difference.Results and Discussions
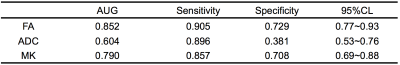
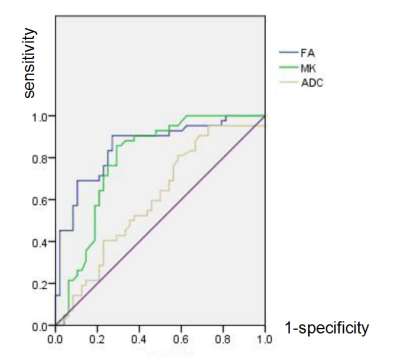
There were significant differences in FA and MK between the two groups (P <0.01). ADC values were similar in the two groups; the difference was not statistically significant (Table 1,Figure.2). Through the ROC curve comparison analysis in Table 2: According to the Youdon index maximum cut-off point for the critical value, determine the MBD patients with ADC threshold of 5.55, the sensitivity was 89.6%, the specificity was 38.1%, AUG was 0.603, 0.5 to 0.7, MBD diagnostic performance comparison it is good. FA refers to the anisotropic fraction. According to the Youdon index maximum cut-off point for the critical value, determine the MBD patients with FA threshold of 0.274, the sensitivity was 90.5%, specificity was 72.9%, AUG was 0.852, in 0.7 to 0.9, MBD diagnosis of high performance. MK refers to the average of all kinks in gradient direction. According to the maximum cut point of Youdon index as the critical value, the critical value of MK for MBD patients was determined to be 0.874, with a sensitivity of 85.7%, specificity of 70.8% and AUG of 0.790, 0.7 to 0.9, indicating higher diagnostic MBD performance. in the diagnosis of MBD patients in the three parameters, FA is superior to ADC and MK, and the sensitivity and specificity is ideal in the diagnosis of MBD corpus callosum degeneration has a high diagnostic value, the study the results show that DKI technology in the diagnosis of chronic alcoholism caused by changes in the corpus callosum no obvious advantages.Conclusion
The results of this study show that DTI technology has a high diagnostic value for MBD. Among the three parameters in the diagnosis of MBD, FA is superior to ADC and MK, and its sensitivity and specificity are ideal. Early diagnosis of degeneration of corpus callosum has a high diagnostic value, which is conducive to clinical decision-making.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1]Konrad A, Vucurevic G, Lorscheider M, et al. Broad disruption of brain white matter microstructure and relationship with neuropsychological performance in male patients with severe alcohol dependence[J]. Alcohol and Alcoholism, 2012; 47(2): 118-126.
[2]Little DM; Kraus MF; Joseph J; Geary EK; Susmaras T; Zhou XJ; Pliskin N; Gorelick PB. Thalamic integrity underlies executive dysfunction in traumatic brain injury[J]. Neurology, 2010, 74(7):558-64.
[3]Kesav P, Modi M, Singla V, et al. Kaleidoscopic presentation of neurobrucellosis[J]. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 2013, 331(1-2):165.
Figures