1579
Clinical assessment of simultaneous diffusion tensor imaging and T2 relaxometry of lumbar nerve roots in patients with low back pain1Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Tougane, Japan, 2Division of Health Sciences, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 3Philips Japan, Tokyo, Japan, 4Faculty of Health Sciences, Institute of Medical, Pharmaceutical and Health Sciences, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan, 5Orthopaedic Surgery, Eastern Chiba Medical Center, Tougane, Japan, 6Chiba University Graduate School of Medicine, Chiba, Japan, 7Philips Healthcare Korea, Seoul, Korea, Democratic People's Republic of
Synopsis
We developed a single-shot dual-echo EPI-DTI sequence (Diffusion-Relaxation Matrix: DRM) that can simultaneously provide the diffusion tensor parameters and T2 values. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical feasibility of DRM for the lumbar nerve roots in patients with low back pain. FA values were negatively correlated with each quantitative value. Prolongation of T2 values were observed in case of abnormally enlarged nerve roots. Therefore,simultaneous acquisition of diffusion tensor imaging and T2 map by using DRM technique might be able to evaluate the extent of nerve disorders more accurately.
PURPOSE
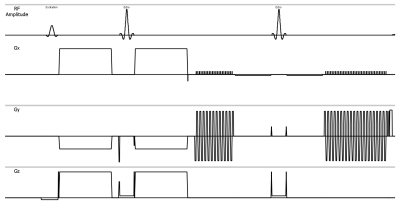
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) based on single-shot Echo Planner Imaging sequence (EPI-DTI) is promising method to evaluate lumbar nerve roots for assessment of low back pain1 using quantitative parameters such as fractional anisotropy (FA) value,mean diffusivity, radial diffusivity, and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values2,3. Alternatively, T2 value, which obtained by multi-echo EPI sequence with multiple-acquisition, has also been reported4 for evaluation of lumbar nerve roots. In this study, we developed a single-shot dual-echo EPI-DTI sequence (Diffusion-Relaxation Matrix: DRM) that can simultaneously provide the diffusion tensor parameters and T2 values. The purpose of this study was to investigate the clinical feasibility of DRM for the lumbar nerve roots in patients with low back pain.METHODS
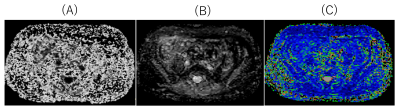
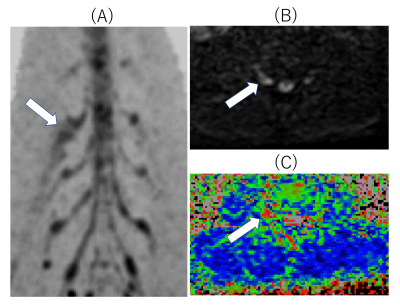
All subjects were examined with 1.5T whole-body clinical system (Ingenia, Philips Healthcare). Fifty-five low back pain patients with unilateral neurological symptom (median age, 58.2 years; range, 24–72 years), underwent DRM sequence. To assess the diffusion parameters and T2 values quantitatively, regions of interests (ROIs) were placed both proximally and distally to the lumbar foraminal zone at the levels responsible for symptoms. Quantitative values obtained from DRM including FA value, ADC value, and T2 value (Fig.2) were compared between symptomatic and asymptomatic side. Imaging parameters were; Axial, voxel size=3.33× 2.21× 3.50mm3, FOV=320×253mm2, 50 slices, b-value=0,800s/mm2, MPG=15 directions, TR=10900ms, TE=54, 120ms, and total acquisition time=6m00s.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
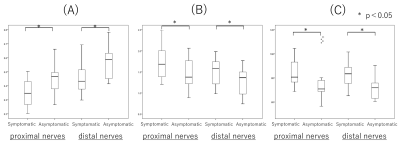
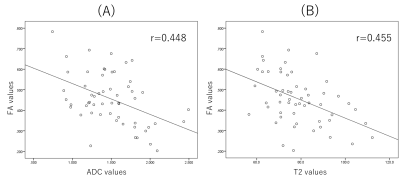
Average FA values of symptomatic side were significantly lower than those of asymptomatic side (p<0.05). Also, average ADC values and T2 values of symptomatic side were significantly higher than those of asymptomatic side (p<0.05) (Fig.3). FA values were negatively correlated with each quantitative value (correlation coefficient of FA values and ADC values was 0.448. correlation coefficient of FA values and T2 values was 0.448.) (Fig.4). Prolongation of T2 values were observed in case of abnormally enlarged nerve roots (Fig.5). Therefore, addition of T2 evaluation might be able to further assess the condition of edema in the nerve roots.CONCLUSION
Simultaneous acquisition of diffusion tensor imaging and T2 map by using DRM technique might be able to evaluate the extent of nerve disorders more accurately.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1 Eguchi Y, et al. Quantitative evaluation and visualization of lumbar foraminal nerve root entrapment by using diffusion tensor imaging: preliminary results. Am J Neuroradiol 2011;32(10):1824–9.
2 BalbiV, et al. Tractography of lumbar nerve roots: initial results. Eur Radiol 2011;21(6):1153–9.
3 Olmarker K, et al. Edema formation in spinal nerve roots induced by experimental, graded compression. An experimental study on the pig cauda equina with special reference to differences in effects between rapid and slow onset of compression. Spine. 1989 Jun;14(6):569-73.
4 Karampinos DC, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging and T2 relaxometry of bilateral lumbar nerve roots: feasibility of in-plane imaging. NMR Biomed. 2013 Jun;26(6):630-7.
Figures