1575
Optimal b-value selection for IVIM-DWI: identification of pancreastic lesions based on entire-tumor1Tongji Hospital, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Synopsis
The purpose of this paper is to explore the successful b-value combination of IVIM-DWI that maximizes the diagnostic efficiency of parameters in differenting pancreatic cancer and normal tissues. IVIM parameters were measured by different b value combinations, and then the diagnostic performance of each significant parameter in identificating tumors and normal tissues was calculated and compared between different combinations. The results show that in different b value combinations, the diagnostic efficiency of the parameters are also different. The final conclusion is that b value combination of 0-1700 may be the best selection in clinical practice.
Introduction:
IVIM-DWI can be used to evaluate the tissue diffusion and perfusion information through the use of a series of b values, which can provide more microstructure information and have been widely used in abdominal organs. However, the results of previous studies are not entirely consistent, which shows that IVIM-DWI still has some limitations .For instance, stability and accuracy of parameters are vulnerable to different b values 1 .In addition, the scan protocol has not yet reached a consistent optimization parameters . Therefore, this article attempts to explore the most suitable combination of b values,when using IVIM-DWI to identify pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from normal tissue .Methods:
This study has obtained the approvement from the Institutional Review Board of our institute .Twenty patients with histopathologically confirmed pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma were underwent preoperative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ,including multi-b value DWI (0,50,80,100,150,200,300,500,800,1000,1300,1700,2000 s/mm2) ,using a 3.0T system . True diffusion coefficient (Dt), pseudodiffusion coefficient (Dp), perfusion fraction (f) were obtained based on the entire tumor and distal pancreas using different b-value combination(0—1000,0—1300,0—1700,0—2000s/mm2). All parameters were compared using the paired T test or the Mann–Whitney U-test. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was used for statistical evaluations.Results:
In all b-value combinations (0—1000,0—1300,0—1700,0—2000s/mm2), the differences of mean Dt between PDAC group and NP group were not significant(P=0.23,0.33,0.12,0.53).However ,mean f values of PDAC were significantly lower than normal pancreas for all b-value combinations (p=0.00), and the highest AUC(0.90) was obtained in 0-1700 combination compared with other combinations(0.875,0.895,0.815 ). For mean Dp values , PDAC group had significantly lower values for all b-value combinations except 0—2000 s/mm2 (P = 0.065 for 0—2000 s/mm2, P = 0.00 for other b values combinations ),and the comparsion of diagnostic performance was successful at b values of 0—1700 (AUC were 0.78,0.79,0.82 and 0.705 respectively, for b0—1000,0—1300,0—1700,0—2000s/mm2).Discussion:
There are many factors that affect I VIM parameters and this study only explored the impact of b values. IVIM-DWI imaging requires multiple b values (containing both high and low b values),then data fitting will be performed to obtain IVIM parameters (Dt, f and Dp) after multi-b DW-Imaging. It is generally believed that the signal attenuation of high b value is mainly related to diffusion, while the signal attenuation of low b value is mainly related to perfusion factors2. This study maintained the sufficient low b values unchanged in the scanning parameters , but only the highest b value was gradually increased. However, the results showed that the Dt value was decreased gradually, the values of f and dp was statistically gradually increased, and the AUC was also increased. This shows that high b value may also affect perfusion-related parameters . One possible explanation was that the capillary state3 of tumor tissue and normal tissue is fairly different, so they are affected in a different degree by the b value strength, thereby increasing the difference of identification between tumor tissue and normal tissues. However, the AUC appears to decrease at a maximum b value of 2000s/mm2, perhaps because which lead to image distortion and artifacts and unsuitable for calculating parameter values.Conclusion:
The use of multi b(0-1700s/mm2) of IVIM-DWI for differentiating pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas from normal pancreas may improve the diagnostic performance in clinical practice. Morever, f value may be the most helpful parameter .Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Pang Y, Turkbey B, Bernardo M, Kruecker J, et al. Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging for prostate cancer: an evaluation of perfusion fraction and diffusion coefficient derived from different b-value combinations. Magn Reson Med 69 (2): 553-62, 2013.
2. Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168 (2): 497-505, 1988.
3. Melstrom LG, Salazar MD, Diamond DJ, et al. The pancreatic cancer microenvironment: A true double agent. J Surg Oncol 116 (1): 7-15, 2017.
Figures
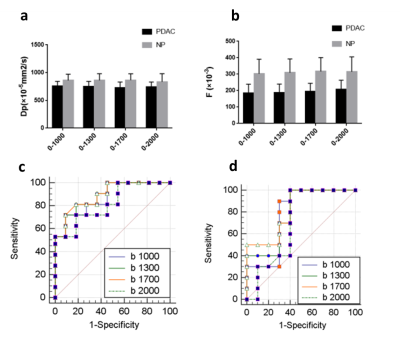
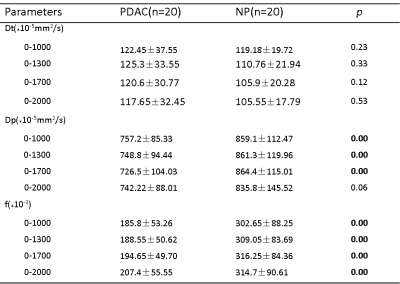
TABLE 1. IVIM-DWI Parameters of different b values combinations in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas and normal tissues
*Data are means ± standard deviations. Significant differences are in bold.