1563
A preliminary application of the diffusion tensor imaging in estimating the functional and structural recovery of the visual pathway in Dysthyroid Optic Neuropathy patients after intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy.1department of radiology, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, wu han, China
Synopsis
The management of DON (dysfunction optic neuropathy) is complex, an effective method to reflect the response of treatment is indispensable. We use the MRI-DTI combine d with DtiStudio software to assess the visual pathway changes in DON patients pre and post intravenous methylprednisolone pulse therapy. The results did demonstrate the improvement of visual pathway. The DTI can be regarded as a reliable tool to assess and follow up DON patients during therapy.
Introduction & Purpose:
According to NOSPECS severity classification of eye disease, thyroid dysfunction optic neuropathy (DON) is the most feared complication of thyroid associated ophthalmopathy (TAO)1. DON can result in optic atrophy and permanent and irreversible visual loss. Appropriate treatment will delay the progression of the illness and avoid unnecessary surgical decompression.Direct optic nerve function test may yield misleading results and incorrectly assess the functional and structural changes of the visual pathway in DON patients after therapy. The visual pathway include the optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract and optic radiation, the conventional imaging method just reflect the anterior visual pathway (optic nerve, optic chiasm). Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) is a noninvasive MRI modality, which is sensitive to the microscopic motion of the water molecules in nerve fibers. It has been widely used in glaucoma to assess the whole visual pathway2. We postulate the DTI may help to find the functional changes of the whole visual pathway on patient ,who have response to intravenous methylprednisolone pulse (iv MP) therapy in early stage. Our purpose in this study is to assess whether the characteristic changes of DTI parameters can predict the prognosis of DON patient after iv MP therapy.Methods:
We retrospectively reviewed 27 patients diagnosed with DON in our Ophthalmology Department between February 2016 and March 2017. Finally, six bilateral and symmetrical DON patients were included according to inclusion and exclusion criteria. All of the six patients obtain a good therapeutic effect after iv MP treatment. In addition, these patients successfully finished MRI-DTI scan pre and post treatment. All the DTI data processing was performed using DtiStudio (www.MriStudio.org)3. Multiple scalar measurements, including fractional anisotropy (FA), axial diffusivity (λ1), mean diffusivity (MD), radial diffusivity (RD) and voxel numbers of 12 visual pathway datasets were recorded and analyzed by using proper statistical method.Results:
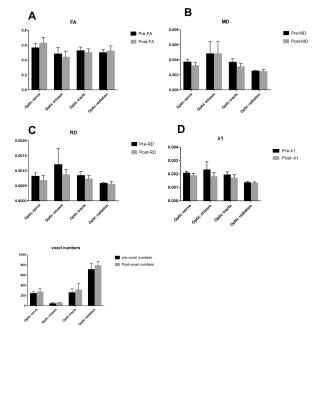
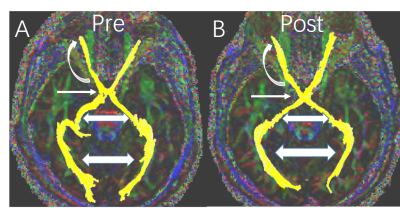
The Fig 1 showed the changes of DTI parameters before and after treatment. For optic nerve, most parameters improved after therapy, although the optic nerve morphology alteration can be seen on color map after treatment (Fig2), voxel numbers reflecting the morphology alteration was no statistical difference. This study got a statistical increase of FA value (p=0.002) and significant decrease of λ1, RD and MD (p=0.012, p=0.004, p=0.006, respectively). All the DTI parameters of optic chiasm had no statistical significance before and after treatment. As for optic tract, except for the voxel number, all the remnant scalars have statistical decrease (Table 1). Only the increase of voxel numbers of optic radiation can be seen after therapy (p=0.041).Discussion:
The pathophysiology behind DON is not well understand.Mechanical compression, vascular and inflammatory components were commonly accepted pathogenesis,but it is definite that the decline of visual function is associated with damage to the visual pathway. Timely diagnose and intervention can avoid unnecessary surgery and permanent visual loss. A direct and reliable method to assess the functional and structural repair is indispensable. DTI is an ideal way to reflect the microscopic changes of nerve fiber bundles. DTI Studio is a deterministic tractography based on ROI.FA reflect the myelination, axon diameter, axon density, and ultrastructure of nerve fibers. In present study, after the iv MP stratagem, the increased FA value means the optic nerve damage is reversed. MD represents the water molecular movement, affected by integrity of tissue, it is also a parameter of demyelination4, the significant decrease of MD in optic nerve may be due to the role of methylprednisolone, which reduce inflammation and speed up healing of nerve fibers. Radial diffusivities (RD) reflect myelin pathologies. Axial (λ1) and radial diffusivities reflect axon and myelin pathologies, respectively, the decrease of them imply the recovery of axon and myelin.Conclusion:
DTI can evaluate the functional and structural changes of whole visual pathway in DON patients, it can be used to evaluate the response to iv MP and follow-up the DON patients during therapy.Acknowledgements
This study has received funding by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81301192 and No.81771793).References
1.Parmar H, Ibrahim M. Extrathyroidal manifestations of thyroid disease: thyroid ophthalmopathy. Neuroimaging clinics of North America. 2008;18(3):527-36, viii-ix.
2.Engelhorn T, Michelson G, Waerntges S, et al. Changes of radial diffusivity and fractional anisotropy in the optic nerve and optic radiation of glaucoma patients. TheScientificWorldJournal. 2012;2012:849632.
3.Jiang H, van Zijl PC, Kim J, et al. DtiStudio: resource program for diffusion tensor computation and fiber bundle tracking. Computer methods and programs in biomedicine. 2006;81(2):106-16.
4. Song SK, Sun SW, Ju WK, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging detects and differentiates axon and myelin degeneration in mouse optic nerve after retinal ischemia. NeuroImage. 2003;20(3):1714-22.
Figures