1562
Angular versus spatial resolution in tractography for deep brain stimulation in psychiatry1Dept. of Psychiatry, Academic Medical Center - University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2Amsterdam Neuroscience, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 3Netherlands Institute for Neuroscience, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 4Dept. of Radiology, Academic Medical Center - University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, Netherlands, 5Spinoza Centre for Neuroimaging, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Synopsis
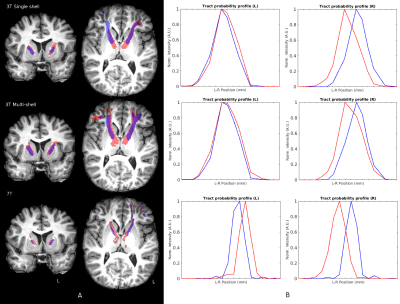
Deep brain stimulation of the ventral part of the anterior limb of the internal capsule (vALIC) could potentially benefit from tractography-guided targeting, since it contains two major fiber bundles. In order to develop a diffusion-weighted sequence that has the greatest bundle specificity within the vALIC, we compared tractography results from a single-shell 3T sequence with multi-shell 3T and high-resolution 7T sequences. Although the multi-shell sequence showed superior SNR, it did not allow increased bundle discernibility in the vALIC. The high-resolution sequence showed more anatomical detail, with more radially constrained tractography, and proved superior for separating the two bundles.
Introduction
There is ongoing debate on finding a trade-off between angular and spatial resolution in tractography of the human brain. In a study into the corticospinal tract, arcuate fasciculus and corpus callosum, a spatial resolution of 2.0 mm proved to be sufficient, and angular resolution was more critical[1]. In animal imaging at high field it was found that a balanced consideration of both spatial resolution and diffusion sampling was necessary[2].In this work, we are focusing on the ventral part of the anterior limb of the internal capsule (vALIC), that is a target for deep brain stimulation (DBS) in treatment-refractory psychiatric disorders[3]. The vALIC contains two major fiber bundles: the anterior thalamic radiation (ATR) and medial forebrain bundle (MFB)[4]. Tractography-assisted surgical planning for vALIC DBS may improve treatment outcomes by specifically targeting one bundle over the other. Optimizing bundle localizations is governed by the dimensions of DBS electrodes, which have a diameter of approximately 1.5 mm. This work aims to establish whether it is better to acquire data at a higher spatial or angular resolution to ensure greatest bundle specificity in surgical planning.Methods
Data of a single consenting volunteer was acquired on 3T and 7T scanners (Philips, The Netherlands), both equipped with 32-channel phased-array head coils.
3T single-shell: FOV=224x224x135mm, matrix 96x96, isotropic voxel size 2.3mm$$$^3$$$, SENSE 1.5, multiband 2, 32 gradient directions at b=1000s/mm$$$^2$$$, TR/TE=5363/99ms, Half-scan 0.7, SPIR fat suppression, total scan time 3m7s.
3T multi-shell: Additional 20 directions at b=600 s/mm2, 48 directions at b=1700 s/mm$$$^2$$$, total scan time 9m44s.
7T: isotropic voxel size 1.4mm$$$^3$$$, FOV=140x179x51mm, matrix 100x127, SENSE 2.7, 32 gradient directions at b=1000 s/mm2, spatial presaturation in two slabs of half the FOV perpendicular to the imaging plane to prevent folding,TR/TE=3038/71ms, Half-scan 0.7, 3 NSA, total scan time 10m13s.
For all diffusion acquisitions an identical b=0-volume with opposite phase-encoding was acquired to correct for distortions. Additionally, a structural scan with a resolution of 1 mm isotropic was acquired at 3T as a reference.
The diffusion data were distortion, motion and eddy current corrected with FSL’s topup and eddy tools, and noise filtered using an adaptive LMMSE noise-filter was applied.Voxel-wise diffusion orientations were estimated with FSL’s bedpostx algorithm. Tractography seeds were placed in the anterior thalamic nucleus and ventral tegmental area for the ATR and MFB, respectively, along with waypoints in the vALIC. FSL’s probtrackx was used for probabilistic tractography with default parameters.
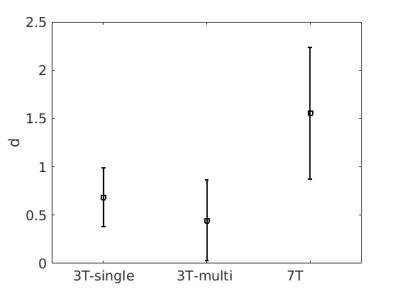
Tracking results were affinely transformed to structural space with FSL’s Flirt for comparison within the vALIC. Possible DBS stimulation sites were identified on the structural scan and local tract probabilities were extracted for further analysis. Tract probability profiles were analyzed in the left-right direction along 5 adjacent positions. Line tract probabilities were normalized, before calculating standard deviations and peak-to-peak distances. Cohen’s d was calculated per line as a measure of tract discernibility, which was finally averaged over multiple lines and both hemispheres.
Results
The 3T multi-shell and 7T acquisition FA-maps show improvements in SNR and resolution respectively over the baseline 3T sequence (Figure 1). Tractography at 7T showed more radially constrained tractography trajectories (Figure 2A). Left-right tracking probability profiles indicate that there is a clearer distinction between the ATR and MFB in the 7T data (Figure 2B). It seems that the peaks in the intensity profiles are shifted medially in the 7T tracking by approximately 2 mm. Finally, Cohen’s d calculated for an average of 10 lines showed a stronger discernibility of the ATR and MFB in the 7T data (Figure 3).Discussion/Conclusion
The increased spatial resolution at 7T seems superior for vALIC DBS planning because of its improved bundle discernibility with respect to the 3T, even at higher angular resolution. We attribute this to the decrease in partial voluming that appears to be the most prominent effect. The displacement of the peaks of the 7T tracking probability with respect to the 3T acquisitions is striking, given the fact that a shift of 2 mm could possibly have a significant effect on surgical planning. This should be elucidated in a further study on a larger population and eventually be histologically validated.Acknowledgements
We thank Frans Vos for his involvement in data acquisition.References
[1] Vos SB, Aksoy M, Han Z, Holdsworth SJ, Maclaren J, Viergever MA, Leemans A, Bammer R. Trade-off between angular and spatial resolutions in in vivo fiber tractography. Neuroimage 2016;129:117–132.
[2] Calabrese E, Badea A, Coe CL, Lubach GR, Styner MA, Johnson GA. Investigating the tradeoffs between spatial resolution and diffusion sampling for brain mapping with diffusion tractography: Time well spent? Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014;35:5667–5685. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22578.
[3] Munckhof P, Bosch DA, Mantione MHM, Figee M, Denys DAJP, Schuurman PR. Active Stimulation Site of Nucleus Accumbens Deep Brain Stimulation in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder Is Localized in the Ventral Internal Capsule. In: Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. Vol 117. Vienna: Springer Vienna; 2013:53-59. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-1482-7_9.
[4] Coenen VA, Panksepp J, Hurwitz TA, Urbach H, Mädler B. Human medial forebrain bundle (MFB) and anterior thalamic radiation (ATR): imaging of two major subcortical pathways and the dynamic balance of opposite affects in understanding depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012;24(2):223-236. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.11080180.
Figures