1538
Assessment of Tumor Hypoxia Using Tissue Oxygen Level Dependent in a Rabbit VX2 Liver Tumor model1Department of Radiology, Zhujiang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, 2Philips Healthcare, Guangzhou, China
Synopsis
There is attractive focus in developing non-invasive methods that assess tumor hypoxia. We applied tissue oxygen level dependent (TOLD) MRI to explore tumor oxygenation using VX2 liver tumor xenografts in a rabbit model. In this study,we demonstrated alteration in tumor oxygen inhalation and correlation in different hypoxia levels.
Introduction
Hypoxia is a common feature of most solid malignancies and associated with tumor progression and metastatic potential, resulting in resistance to radiotherapy and chemotherapy1-4. Thus non-invasive measurements of tumor hypoxia would be particularly attractive for tumor progression evaluation and treatment planning2,5,6. TOLD-MRI is an emerging technique that can quantify tumor oxygen delivery, as longitudinal relaxation rate (R1=1/T1; units s-1) sensitively detects the changes in the level of molecular oxygen (O2) dissolved in plasma or interstitial tissue fluid6. The aim of this study was to explore the feasibility of TOLD MRI in assessment of tumor hypoxia in rabbit VX2 liver tumors.Material and Method
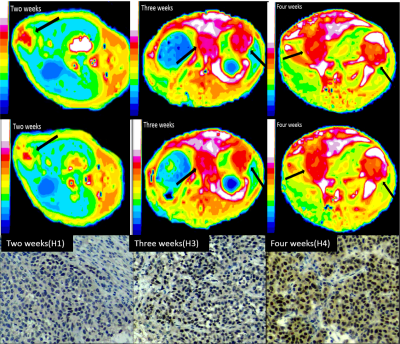
Sixteen VX2 tumors were implanted in the livers of eight New Zealand white rabbits, which were incubated for two weeks, three weeks and four weeks. TOLD was performed on a 3.0T MRI scanner (Ingenia, Philips, Netherlands) before and after 30 min oxygen inhalation, using an animal coil. T1 mapping sequence was implemented using Look-Locker with 51 inversion delay time points varying from 56ms to 4500ms. The parameters were as follows: TR/TE= 5ms/1.7ms, FOV= 120mm×120mm, matrix= 80×64, flip angle= 7°, slice thickness= 4mm, acceleration factor = 2. T1 maps were generated with MRmap software V1.4. R1 difference of VX2 liver tumor were measured for whole lesion (ΔR1whole) and non- necrotic area (ΔR1nonnecrotic), and the corresponding relative change ΔR1%whole and ΔR1%nonnecrotic were calculated. Immunohistochemical analysis of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α(HIF-1α)expression of rabbit VX2 liver tumor was performed on a high-powered microscope(H0-H4). Spearman correlation test was used to evaluate the correlation between measured values and the expression of HIF-1α. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was used to determine diagnostic accuracy.Results
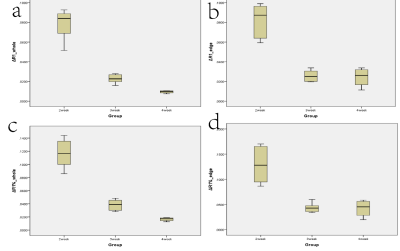
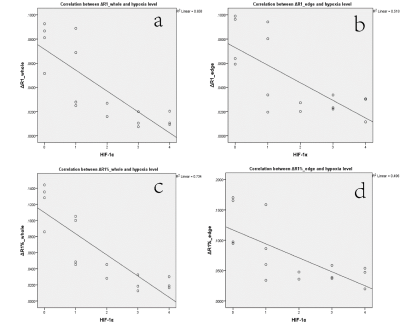
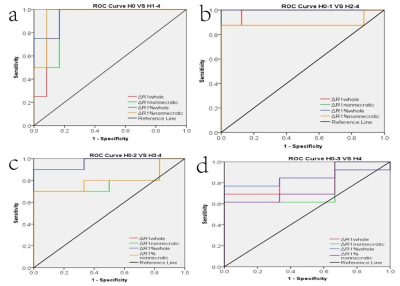
TOLD maps of VX2 liver tumor after incubation for two weeks, three weeks and four weeks, and corresponding expression of HIF-1α are shown in Figure 1.One-way analysis show statistical differences of ΔR1whole, ΔR1nonnecrotic, ΔR1%whole among the different time points.(Figure 2). Significant differences (P< 0.01) were detected in ΔR1whole, ΔR1nonnecrotic, ΔR1%whole and ΔR1%nonnecrotic of different hypoxia level (H0-2 vs. H3-4),especially ΔR1%whole. Hypoxia level was inversely correlated with ΔR1whole, ΔR1nonnecrotic, ΔR1%whole, ΔR1%nonnecrotic (r=-0.811, r=-0.720, r=-0.857, r=-0.707, respectively) (Figure3). Area under ROC curve(AUC) of ΔR1whole, ΔR1nonnecrotic, ΔR1%whole and ΔR1%nonnecrotic in differentiating hypoxia levels were as follows: H0 VS H1-4(0.917, 0.917, 0.958, 0.958); H0-1 VS H2-4 (0.984, 0.891, 1.00, 0.891) H0-2 VS H3-4(0.936, 0.783, 0.967, 0.800); H0-3 VS H4 (0.821, 0.744, 0.846, 0.769) (Firgure 4).
Discussion
In this study , well-oxygenated tissues showed significant ΔR1 whereas the regions of tumor hypoxia show little change on ΔR1 when hyperoxic gas is inhaled, as ΔR1 changes with different concentration of molecular oxygen dissolved in plasma or interstitial tissue fluid6. A strong correlation was observed between the fraction of tumor which failed to respond to oxygen breathing challenge and hypoxic fraction identified by using HIF-1α immunohistochemistry.Conclusion
Our study shows that ΔR1 has a high diagnostic efficacy for noninvasive measurement of tumor hypoxia of VX2 liver tumor, suggesting the potential of TOLD as a non-invasive technique for the assessment of tumor hypoxia level.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Dewhirst MW, Birer SR. Oxygen-Enhanced MRI Is a Major Advance in Tumor Hypoxia Imaging. Cancer Res. 2016;76:769-772.
[2] Zhou H, Zhang Z, Denney R, et al. Tumor physiological changes during hypofractionated stereotactic body radiation therapy assessed using multi-parametric magnetic resonance imaging. Oncotarget. 2017;8:37464-37477.
[3] White DA, Zhang Z, Li L, et al. Developing oxygen-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as a prognostic biomarker of radiation response. Cancer Lett. 2016;380:69-77.
[4] O'Connor JP, Naish JH, Parker GJ, et al. Preliminary study of oxygen-enhanced longitudinal relaxation in MRI: a potential novel biomarker of oxygenation changes in solid tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;75:1209-1215.
[5] Milosevic M, Warde P, Menard C, et al. Tumor hypoxia predicts biochemical failure following radiotherapy for clinically localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:2108-2114.
[6] O'Connor JPB, Boult JKR, Jamin Y, et al. Oxygen-Enhanced MRI Accurately Identifies, Quantifies, and Maps Tumor Hypoxia in Preclinical Cancer Models. Cancer Res. 2016;76:787-795.
Figures