1514
DKI can early detect radio-insensitive human nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenograft in nude mice1Fujian Provincial Cancer Hospital, Fuzhou, China
Synopsis
In order to evaluate feasibility of DKI sequence in early differentiating radio-insensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts, Seventy-two nude mice were implanted with CNE-1(low radiosensitivity) and CNE-2(high radiosensitivity) and the xenografts were obtained. MRI scanning was performed after fractional irradiation. There are differences of the changes of DKI parameters (both D and K) between CNE-1 and CNE-2 before tumor volumes changed. Therefore, Both D and K can early (before volumes changed) distinguish radio-insensitive NPC xenografts from others.
OBJECTIVE
To explore the feasibility of DKI sequence in early differentiating radio-insensitivity of nasopharyngeal carcinoma xenografts in nude mice.MATERIALS AND METHODS
Seventy-two nude mice were implanted with CNE-1(low radiosensitivity) and CNE-2(high radiosensitivity) nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells, and the xenografts were obtained. Then, the mice were underwent fraction irradiation separately. Nude mice of each cell line were randomly divided into non-irradiated group (G0), 10Gy group (G1), 20Gy group (G2), 30Gy group (G3) and 3 and 5 days after the whole dose irradiation group (G4, G5). DKI sequence was performed on each group. Volumes, parameter D and K were measured by two experienced radiologists double blindly. Student t test and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were included in our study. Significant level α was be chosen as 0.05.RESULTS
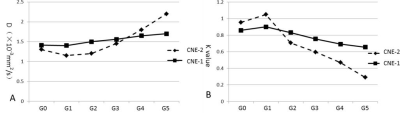
The difference of volumes’ shrink rate between CNE-1&2 were firstly find in G2, with the shrink rate of 5.954% and 27.716% (p=0.032). D value decreased first (DG1, p=0.001) and then increased, K value increased first (KG1, p=0.001) and then decreased after irradiation in CNE-2, but not in CNE-1 xenografts (p>0.05). The AUC of DG1 and KG1 were 0.875 and 0.917, with sensitivity of 0.667 and 0.833, specificity of 1.000 and 1.000 respectively in the cutoff values 1.27×10-3mm2/s of parameter D and 0.88 of parameter K.CONCLUSION
Both D and K can early (before volumes changed) distinguish radio-insensitive NPC xenografts from others. DG1 and KG1 may be the most useful parameters.Key Words
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma, Diffusion kurtosis imaging, XenograftAcknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Lee, A. W., W. T. Ng, L. L. Chan, W. M. Hung, C. C. Chan, H. C. Sze, O. S. Chan, A. T. Chang and R. M. Yeung. Evolution of treatment for nasopharyngeal cancer--success and setback in theintensity-modulated radiotherapy era. Radiother Oncol,2014. 110(3): 377-384.
2.Chen YB, Liao J, Xie R, et al. Discrimination of metastatic from hyperplastic pelvic lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Imaging 2011; 36(1):102-109.
3. Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, Lu HZ, Kaczynski K. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: The quantification of non-Gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reso Med 2005; 53(6): 1432-1440.
4.Jensen JH, Helpern JA, Ramani A, et al. Diffusional kurtosis imaging: the quantification of non-gaussian water diffusion by means of magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 2005; 53(6):1432–1440.
5.Lu H, Jensen JH, Ramani A, Helpern JA. Three-dimensional characterization of nongaussian water diffusion in humans using diffusion kurtosis imaging. NMR Biomed 2006, 19(2):236–247.
6.Basser PJ. Inferring microstructural features and the physiological state of tissues from diffusion-weighted images. NMR Biomed 1995; 8(7-8):333-344.
7. Jimmy Lätt, PhD, Markus Nilsson, PhD, Ronnie Wirestam, PhD, et al. Regional Values of diffusional Kurtosis Estimates in the Healthy Brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013; 37:610–618.
8.Falangola MF, Jensen JH, Babb JS, et al. Age relatednon Gaussian diffusion patterns in the prefrontable brain. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008; 28(6):1345-1350.
9. Josehp A. Helpern, PhD, et al. Preliminary Evidengce of Altered Gray and White Matter Microstructural Development in the Frontal Lobe of Adolescents With Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Study. J Magn Reson Imaging 2011; 33:17-23.
10. Raab P,Hattingen E,Franz K,et al.Cerebral Gliomas: Diffusional Kurtosis Imaging Analysis of Microstructural Differences.Radiology 2010, 254: 876-881.
11.Jansen JF, Stambuk HE, Koutcher JA, et al. Non Gaussian analysis of diffusion weighted MR imaging in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a feasibility study. AJNR, 2010, 31(4): 741-748.
12. Chen YB, Ren W, Zheng DC, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging predicts neoadjuvant chemotherapy responses within 4 days in advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Nov;42(5):1354-61.