1410
Effects of PDE5A inhibition on skeletal muscle 1H2O T2 following an acute bout of downhill running and endurance training in dystrophic mice1University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, United States, 2University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States
Synopsis
This study examined the effects of phosphodiesterase 5A inhibition with sildenafil citrate on skeletal muscle 1H2O T2 in dystrophic mice (
Introduction
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is characterized by the absence of dystrophin, which is accompanied by lack of sarcolemma localized neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). This lack of nNOS impairs the ability to blunt sympathetic vasoconstriction, reduces local blood flow, and increases susceptibility to damage in dystrophic muscle(1, 2). To compensate for lack of nNOS, treatments that inhibit phosphodiesterase-5A (PDE5A) have been proposed(3). In this study, we utilized transverse relaxation time constant (T2) of 1H2O, an in vivo marker of skeletal muscle damage(4), to test the hypothesis that a PDE5A inhibitor (sildenafil citrate) will reduce muscle damage following an acute bout of downhill running and during four weeks of progressive low-intensity endurance training in dystrophic (mdx) mice.Methods
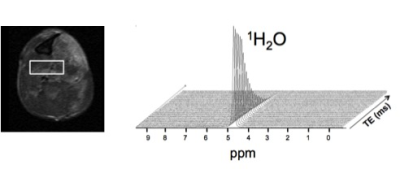
Single voxel 1H-MRS data were acquired using stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM; TR 9 s, 10-128 TE’s exponentially spaced: 5-288 ms, 4 phase cycles) with a 4.7 T Varian/Agilent MR system to evaluate 1H2O T2 of skeletal muscle in mdx and wild-type mice (Figure 1). Mice treated with sildenafil citrate (mdx-sil: n=14) were compared to untreated mice (mdx: n=14; wild-type: n=5) before and 24 hours after downhill running and in a subset of mice (5-10/group) were compared weekly during four weeks of horizontal treadmill running (5 days/week). Data were acquired from the deep medial compartment (MC) in the lower hindlimbs; this region has previously been established to be consistently susceptible to muscle damage following downhill running in mdx mice(4). Downhill treadmill running was performed for 30-60 minutes at 6-12 m/min with a 14% grade. Also, a low-intensity treadmill running program was performed five days/week for four weeks with weekly increases in intensity and volume (8-12m/min; 25-60min;0o incline). Spectra were fit with principal component analysis and 1H2O T2 was calculated using a monoexponential model.Results
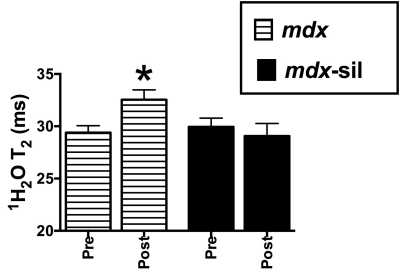
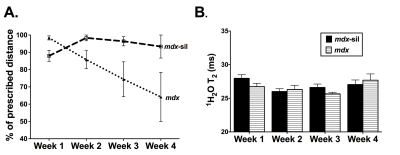
At baseline, 1H2O T2 was greater (p<0.05) in treated and untreated mdx than wild-type mice (Con: 25.5±0.8ms; mdx: 29.4±0.7ms; mdx-sil: 30.4±1.6ms). Following downhill running, T2 increased (p<0.05) by, on average, 11% in the MC of untreated mdx mice compared to baseline, whereas in the treated mdx mice, there was no increase in T2 of the MC (Figure 2). Also, wild-type mice did not show an increase in T2 following this downhill running protocol. During four weeks of treadmill training, T2 did not increase from baseline during training in wild-type, mdx, or mdx treated with sildenafil; however, the prescribed distance completed during training was greater in sildenafil treated mdx mice (98%) and wild-type (100%) than untreated mdx mice (60%) (Figure 3).Conclusions
Overall, sildenafil citrate diminished the increase in T2 of skeletal muscles 24 hours after an acute bout of downhill running in mdx mice, suggesting reduced muscle damage, possibly by enhancing local blood flow following exercise. Furthermore, sildenafil citrate resulted in an increase in exercise performance during treadmill training without an associated increase in muscle T2. Collectively, these results support the use of sildenafil citrate when combined with acute and chronic bouts of exercise as a potential therapeutic intervention in DMD.Acknowledgements
This research study was supported by the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases of the National Institutes of Health (R01AR070101), Muscular Dystrophy Association development grant, and the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory.
References
1. Thomas GD, Sander M, Lau KS, Huang PL, Stull JT, Victor RG. Impaired metabolic modulation of alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction in dystrophin-deficient skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(25):15090-5.
2. Kobayashi YM, Rader EP, Crawford RW, Iyengar NK, Thedens DR, Faulkner JA, Parikh SV, Weiss RM, Chamberlain JS, Moore SA, Campbell KP. Sarcolemma-localized nNOS is required to maintain activity after mild exercise. Nature. 2008;27(456(7221)):511-5.
3. Victor RG, Sweeney HL, Finkel R, McDonald CM, Byrne B, Eagle M, Goemans N, Vandenborne K, Dubrovsky AL, Topaloglu H, Miceli MC, Furlong P, Landry J, Elashoff R, Cox D, Group. TDS. A phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial of tadalafil for Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology. 2017;89(17):1811-20.
4. Mathur S, Vohra RS, Germain SA, Forbes S, Bryant ND, Vandenborne K, Walter GA. Changes in muscle T2 and tissue damage after downhill running in mdx Mice. Muscle Nerve. 2011;43(6):878-86.
Figures