0358
Improved 2D cardiac Cine MRI with retrospective gating using Golden-angle Radial acquisition and Angle-Based echo-Sharing (GRABS)1UIH America, Inc., Houston, TX, United States, 2United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China
Synopsis
Cardiac Cine MRI with retrospective gating using Golden-angle Radial acquisition and Angle-Based echo-Sharing is a promising technique permitting retrospective gating, arbitrary temporal resolution, and arrhythmia data rejection. It is an easy-to-implement and effective technique that features improved image quality by reducing streaking artifacts.
Introduction
Cine imaging using golden-angle (111.25°) radial acquisition is desirable in that it achieves relatively uniform angular distribution of radial spokes, therefore permits arbitrary choice of temporal resolution. Yet this property is compromised during a retrospective ECG-gated cardiac Cine, where interleaved subsets of a continuous golden-angle acquisition were grouped for image reconstruction. Extremely non-uniform angular distribution may result and ‘clustering’ of spokes were linked to streaking artifacts rendering images non-diagnostic1,2. A recent attempt to address this problem acquired radial spokes at modified golden angles, and the k-space was segmented into sub-regions each filled during a particular RR period3. However such approach is incompatible with arrhythmia rejection because it cannot afford discarding data retrospectively. To mitigate streaking artifacts and allow arrhythmia rejection, in this work a technique for 2D cardiac Cine MRI with retrospective gating using Golden-angle Radial acquisition and Angle-Based echo-Sharing (GRABS) is proposed.Methods
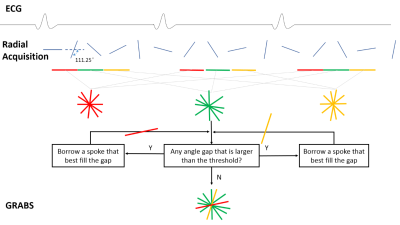
A modified 2D radial bSSFP sequence with spoke angles incremented by the golden-angle was used for cardiac Cine (Figure 1). The timestamp from the previous ECG R-wave was recorded for each readout. R-R durations were first normalized and timestamps were corrected accordingly. Based on the user-selected number of retrospective cardiac phases, all spokes were sorted into corresponding bins. Given that very non-uniform k-space spoke distribution contributes mostly to the streaking artifacts seen, an angle-based echo-sharing (ABS) approach was adopted. First, regions with large angle gaps were identified. Second, spokes from the two neighboring phases that best fill the gaps were included. Third, based on the updated distribution the largest gap was compared to a gap threshold, in our case set to 1.2 times the average angle gap based on experience. If smaller than the threshold then iterations stop, otherwise continue. This ABS approach is different from sliding-window reconstruction commonly used in other MR applications in that only spokes that effectively mitigates artifacts were included, rather than based on temporal closeness.
The proposed GRABS technique and the conventional radial retro-gating were implemented on a clinical 3.0T scanner (uMR770, United Imaging Healthcare, Shanghai, China). Imaging parameters were: TE/TR =1.3/2.6 ms, bandwidth = 1500 Hz, spatial resolution = 1.88*1.88 mm2, FOV = 360*360 mm2, slice thickness = 6 mm, flip angle =40°, reconstructed cardiac phase=20. A fixed number of 6000 spokes were acquired regardless of the heart rate. Reconstruction was done offline using regridding with Kaiser-Bessel kernel and density compensation considering angle non-uniformity.
Cine images of 11 healthy volunteers acquired using conventional technique and GRABS were reviewed by an experienced radiologist blinded to the imaging strategy for the appearance of streaking artifacts, on a scale of 1-5: 1 being non-diagnostic image quality due to streaking artifacts and 5 being no obvious image degradation. Subjective image quality scores were compared with Wilcoxon signed-rank test. P < 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
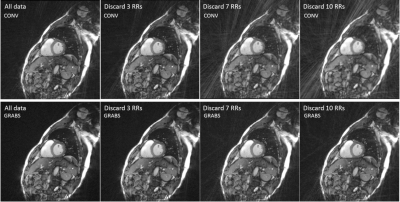
To further verify GRABS’ feasibility for retrospective arrhythmia rejection, in one volunteer the data acquired during random heart beats were discarded to mimic arrhythmia rejection, and images were reconstructed for quality evaluation.
Results
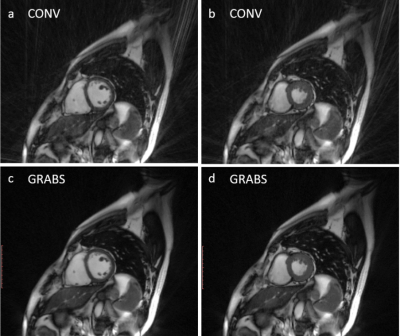
Typical Cine images were shown in Figure 2. Conventional images (top row) demonstrate streaking artifacts of various degrees of severity, while GRABS (bottom row) show much alleviated artifacts. The image quality score of the proposed GRABS technique was significantly higher than that of the conventional method (3.27±0.90 vs. 1.55±0.52, p<0.001) based on 11 volunteers. GRABS’s support for arrhythmia rejection is shown in Figure 3. Although images with varying degrees of data rejection show increased artifacts, GRABS image (bottom row) remains diagnostic in contrary to the conventional method whose image (top row) quality was heavily degraded.Conclusion and Discussions
GRABS is a promising cardiac Cine technique permitting retrospective gating, arbitrary temporal resolution, and arrhythmia data rejection. It is an easy-to-implement and effective technique that features improved image quality by reducing streaking artifacts. Future work should focus on optimizing the gap threshold and evaluating its influence on temporal dynamics.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Kawaji et al. PLoS One 2015;10(2):e0112020
2. Krämer et al. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014; 40:413–422.
3. Han et al. J. Cardio. Magn Reson 2015, 17(Suppl 1):Q124
Figures