0349
Benefits and Challenges of Spiral MRI in Routine Clinical Brain Imaging: Early Results1Philips Healthcare, Gainesville, FL, United States, 2Barrow Neurological Institute, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 3Phoenix Children’s Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, United States, 4Philips Innovation Campus, Bangalore, India, 5Philips Healthcare, Best, Netherlands, 6Philips Healthcare, Tokyo, Japan, 7Philips Healthcare, Gurgaon, India, 8Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, OH, United States, 9University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States, 10Kyushu University Hospital, Fukuoka, Japan, 11University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, United States, 12Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, MA, United States, 13Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon, India, 14University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States, 15Dent Neurologic Institute, Amherst, NY, United States
Synopsis
Spiral MRI possesses several advantages vs. Cartesian MRI, due to differences in their k-space trajectories and underlying MR physics, which can be leveraged for added value in routine clinical imaging. A Spiral Neuroimaging Cooperative, consisting of nine clinical sites, was formed for the multi-center evaluation of spiral MRI as an alternative to Cartesian MRI in routine clinical imaging. Post-contrast brain spiral 2DT1SE were compared with Cartesian 2DT1SE or TSE. Spirals demonstrated faster scanning with consistent flow artifact reduction vs. both Cartesian options, and superior overall image quality (T1 contrast, lesion visualization) vs. TSE.
Introduction
Spiral MRI (1,2) provides several advantages vs. Cartesian MRI. Spiral MRI is faster, because of longer readout durations (τ), which enable a concurrent decrease in scan time while simultaneously increasing image SNR (3). Spirals are also more robust to artifacts – such as flow, motion, aliasing, and geometric distortions – due to reduced gradient moments (4), a non-dedicated phase-encode direction, and incoherent dispersion of unwanted signal changes between spiral arms. Despite these benefits, spiral MRI has not gained widespread adoption in the clinic due to its greater demand on system fidelity (e.g. B0, gradient accuracy/precision), and recon complexity. The current work investigates the feasibility of spiral MRI as an added value alternative to Cartesian MRI in routine clinical imaging.
Post-contrast brain applications were selected for early clinical evaluation. Routine protocols utilize Cartesian 2DT1 spin-echo (Cart-SE), although it is slow, and often corrupted by flow artifacts due to the hyper-intense flow signal. Alternately, Cartesian 2DT1 turbo spin-echo (Cart-TSE) is used, enabling faster scans, but at the cost of T1 contrast and image sharpness. In these cases, we evaluate the diagnostic benefit of spiral 2DT1 spin-echo (spiral-SE) as an alternative to the routine standard-of-care Cart-SE/TSE.
Methods
A Spiral Neuroimaging Cooperative was formed for the multi-center clinical evaluation of spiral vs. routine Cartesian, which is the first of its scale and kind. Nine participating sites – covering North America, India, and Japan – acquired 135 patient cases with spiral-SE and matching Cart-SE or Cart-TSE, depending on each site’s routine or generic protocol database. Images were used for early clinical comparison and joint technical development. The study was performed on Philips 3.0T/1.5T Ingenia scanners with standard hardware configuration.
The spiral-SE is a conventional 90°-180° spin-echo followed by a fully sampled spiral-out readout (5) with τ ~ 10 ms (3.0T) or 20 ms (1.5T). Adjustable crusher gradients are positioned around the 180° RF-pulse to control black blood contrast and flow signal suppression (6). Reconstruction was performed online using a conjugate-gradient algorithm for joint off-resonance deblurring and Dixon-based water/fat separation (7), which is intrinsic to the spiral implementation. Current reconstruction times are ~ 1 sec/slice. A B0 prescan (~ 30 s) was acquired prior to the spiral scan for use in reconstruction. Spiral-SE were geometry-matched to the Cart-SE/TSE, and performed after the Cart-SE/TSE as per each site’s routine.
Results
Patient images highlight neuroradiologists’ feedback where spiral-SE demonstrates consistent benefits (Figures 1-4), or remaining artifacts (Figure 5), vs. Cart-SE/TSE. All spiral-SE images shown are water-only.
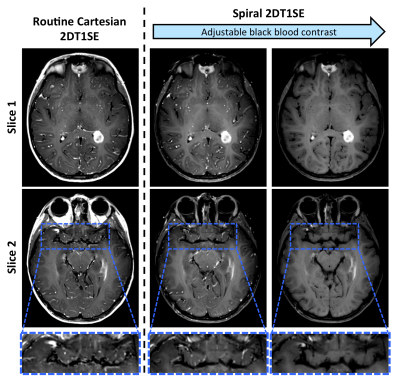
Figure 1 illustrates the typical post-contrast image quality, as well as the spiral-SE adjustable crusher gradients and their effect on black blood contrast, which can be controlled according to neuroradiologist’s preference.
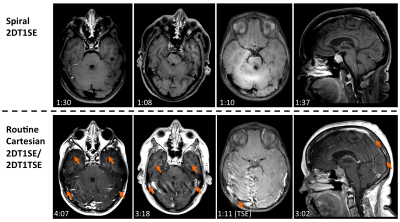
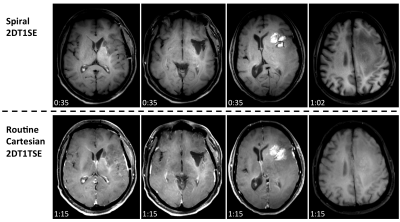
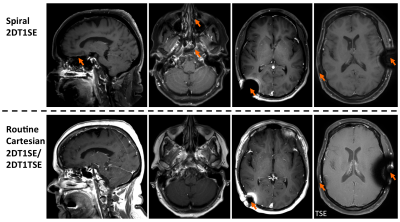
Figures 2-4 denote scan times (mm:ss) in the bottom-left corner of each image, showing that spiral-SE is as much as 2-3 times faster than Cart-SE/TSE, depending on the protocol. Figure 2 illustrates the consistent and significant flow artifact reduction in spiral-SE vs. Cart-SE/TSE. Figure 3 compares spiral-SE vs. Cart-TSE, where overall image quality (T1 contrast, lesion visualization, flow artifact reduction) from neuroradiologist’s feedback was clearly in favor of spirals. Figure 4 highlights the advantage of spiral-SE with built-in Dixon, where water-only images are beneficial for delineating pathologies in/around fat tissue.
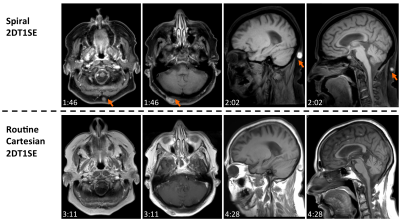
Figure 5 summarizes some remaining challenges of spiral MRI around areas of naturally/artificially occurring magnetic susceptibility, which can manifest as signal loss and residual blurring.
Discussion & Conclusion
Spiral MRI is an enabling technology for a new family of applications. The full range of possibilities is on par with, and provides an alternative to, Cartesian MRI that is the current clinical workhorse. Spiral-SE demonstrates faster scanning with consistent flow artifact reduction vs. both Cart-SE and Cart-TSE, and superior overall image quality (T1 contrast, lesion visualization) vs. Cart-TSE. These early clinical results suggest the potential for spiral MRI to be leveraged across a range of clinical applications in order to demonstrate a compelling diagnostic benefit.
Technical challenges for robust routine spiral MRI exist in areas where the B0 map is not well defined, due to the increased sensitivity of the relatively longer spiral readout τ. Areas of large magnetic susceptibility can induce signal voids, which can be reduced by shortening τ at the cost of scan efficiency. Residual blurring can also occur in areas where the B0 prescan deviates from the nominal value (e.g. over time). These challenges can be mitigated with advanced B0 mapping and self-navigated techniques. Other artifacts observed during this clinical study have been addressed in a separate abstract submission. Remaining challenges, together with other applications of clinical feasibility, will be avenues of future investigation.
Acknowledgements
Thanks also to our clinical research collaborators for their support of this study: Ivan Pedrosa, Ananth Madhuranthakam, Sebastian Flacke, Michael McGranor, Sudarshan Ragunathan, Quin Lu, Jan Groen, and Miha Fuderer.References
1. Ahn CB, Kim JH, Cho ZH. High-speed spiral-scan echo planar NMR imaging-I. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 1986;5(1):2-7.
2. Meyer CH, Hu BS, Nishimura DG, Macovski A. Fast spiral coronary artery imaging. Magn Reson Med 1992;28(2):202-213.
3. Pipe JG, Robison RK. Simplified Signal Equations for Spoiled Gradient Echo MRI. Proceedings of the 18th Annual Meeting of ISMRM. Stockholm, Sweden2010. p 3114.
4. Nishimura DG, Irarrazabal P, Meyer CH. A velocity k-space analysis of flow effects in echo-planar and spiral imaging. Magn Reson Med 1995;33(4):549-556.
5. Pipe JG, Zwart NR. Spiral trajectory design: a flexible numerical algorithm and base analytical equations. Magn Reson Med 2014;71(1):278-285.
6. Li Z, Hu HH, Miller JH, Karis JP, Cornejo P, Wang D, Pipe JG. A Spiral Spin-Echo MR Imaging Technique for Improved Flow Artifact Suppression in T1-Weighted Postcontrast Brain Imaging: A Comparison with Cartesian Turbo Spin-Echo. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015.
7. Wang D, Zwart NR, Pipe JG. Joint water-fat separation and deblurring for spiral imaging. Magn Reson Med 2017.
Figures