0291
Intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging: Evaluation of myocardial microcirculation in diabetes patientsli shi lan 1, li xin2, li zhi yong2, song qing wei1, and liu ai lian2
1Radiology, Dalian medical university, Dalian, China, 2Dalian medical university, Dalian, China
Synopsis
Because of 80% type 2 diabetic patients died of cardiovascular complications, diabetic microangiopathy in the diabetic cardiomyopathy couldn’t be ignored. At present, we lack simple and accurate methods for assessment of myocardial microcirculation. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) technology is a new noninvasive method that can be used for quantitatively assessing myocardial microcirculation status.
Backgrounds
Because of 80% type 2 diabetic patients died of cardiovascular complications, diabetic microangiopathy in the diabetic cardiomyopathy couldn’t be ignored. At present, we lack simple and accurate methods for assessment of myocardial microcirculation. Intravoxel incoherent motion (IVIM) technology is a new noninvasive method that can be used for quantitatively assessing myocardial microcirculation status. The aim of this study is a preliminary study of diabetic myocardial microcirculation using IVIM technology, compared with normal people.Material and methods
Thirty-four healthy volunteers (21male, mean age, 35.65±16.18, BMI 22.38±3.23) and fourteen diabetes (7male, mean age,55.00±12.10, BMI 25.9±5.49) were enrolled in this study between May 2015 to January 2017. All of them performed CMR-IVIM on GE 3.0T magnetic resonance on the apex, middle, base of left ventricular short axis respectively using multi b values (0, 20, 50, 80, 100, 120, 200, 300, 500s/mm2). IVIM parameters including ADCslow, ADCfast, fraction was measured by Function 9.4.05a(GE)software, The region of interest (ROI) is received through the manual delineation of endocardial and epicardial. All data was analyzed by SPSS 22.0 software, conforming to the normal distribution of the data using independent sample t-test, P<0.05 was defined as statistical significance.Result
The imaging success rates of healthy volunteers group (84.31%) were higher than the diabetic group (69.04%). ADCfast values in the diabetic group were lower than healthy volunteers group (0.09+0.02 vs0.12+0.02 , P=0.02), while, the f values in the diabetic group were higher than healthy volunteers group (0.47 + 0.08 vs0.38 + 0.05 , P=0.04). ADCslow values had no any statistical difference between both groups (3.84 + 0.68 vs 3.77 + 0.82, P>0.05).Discussion
IVIM could be used to evaluate the myocardial microcirculation, but the imaging success rate is not high, because the image affected by heart rate, respiratory, etc. In this result, the success rate of healthy volunteers was higher than diabetic group. Secondly, ADCfast values in the diabetic groups were lower than that in healthy volunteers, we thought it may be due to decreased microcirculation in diabetic groups.Conclusion:
IVIM can noninvasively detect myocardial microcirculation perfusion, ADCfast value could be a quantitative parameter for assessment of myocardial microcirculation perfusion changes in patients with diabetes.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
No reference found.Figures
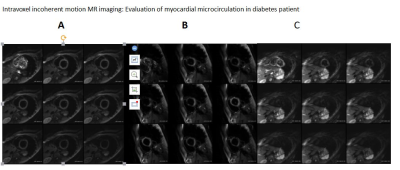
Image evaluation criteria: Thirty-four normal volunteers (apex, middle, base, 102 slices, 86/102), fourteen diabetes (42 slices, 29/42).II, III images were defined as successful, I was not successful. A (III, myocardial opacification and clear outline, images have no artifacts),B (II, myocardium edge is blur and ventricular myocardium loss of signal, but the measurement of data has no effection. C (I, myocardial signal is severely loss, it is unable to measure the parameter ).
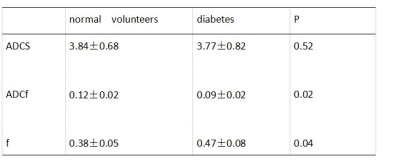
ADCfast values in the diabetic group were lower than healthy volunteers group (P=0.02), while, the f values in the diabetic group werehigher than healthy volunteers group (P=0.04). ADCslow values had no any statistical difference between both groups ( P>0.05).