0059
High Contrast and Resolution Simultaneous T1 and T2 MPRAGE at 7T1MRRC, Dept. of Radiology, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA, United States
Synopsis
T2W MRI is useful for lesion detection in neurological disorders. At 7T, while SNR can be excellent for high-resolution imaging, T2W imaging is known to be difficult due to problems with B1 amplitude and homogeneity, as well as low T2 contrast between WM vs. GM. To address these, we developed new simultaneous T1W/T2W MP2RAGE sequence. We simulated the new sequence to optimize brain contrast and implemented on 7T combined with B1-shimmed pTx multi-transceiver and high-order B0 shim. The results show homogeneous contrast of WM vs. GM over whole brain with excellent SAR efficiency, giving high resolution detection of hippocampal sub-structures.
Introduction
T2 weighted (T2W) MRI at 7T1 is difficult due to known limitations in B1 amplitude and homogeneity, as well as the small difference in T2 values between white and gray matter (WM, GM). With conventional turbo-spin echo methods, the limited B1 problem results in an image acquisition that is comparatively slow. While adiabatic pulses improve transmit B1 homogeneity, the necessary power can still be difficult for high SAR, particularly in multi-slice 2D MRI. Furthermore, the 10-15ms difference in T2 values of WM vs. GM at 7T result in relatively poor tissue contrast, resulting in 7T T2W images that appear less informative in comparison with equivalent 3T images. In this report we describe a SAR efficient T2 and T1 weighted MRI sequence that provides high contrast whole brain imaging at 7T. This performed using a T2 preparation module {90°(x) – 180° – 180° – 90°(-x)} that is integrated with a modified MP2RAGE inversion recovery (IR) sequence to simultaneously generate T1W and T2W images, achieving sub-millimeter resolution in ~11min.Theory
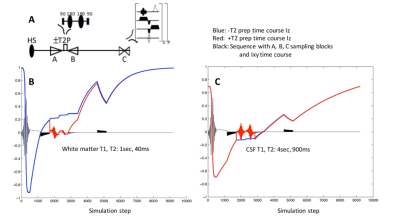
As built on a modified MP2RAGE IR sequence in which two imaging blocks (A, C in Fig. 1A) are acquired that generate the high contrast T1W, an additional T2W imaging block B is applied as shown in Fig. 1A. With this added imaging block B, the difference between the block A and B generates weighting that is a function of T1, T2, TE and B1+. With block B applied immediately after block A and relatively early in the recovery period, the resulting A and B block images differ with additional T2 weighting. The spatial phase encoding of blocks A and B are applied in centric-down and -up respectively in order to maximize only T2 contrast. Simulation of the proposed sequence with and without T2 preparation shows the anticipated signal recovery for WM and CSF (Fig. 1B,C). Adopting the receptivity and B0 self-correcting image reconstruction approach 2, the difference image (imaging block B – A) is referenced to imaging block C to provide a fixed maximum dynamic range of [-0.5, 0.5]. Notably, in this approach if the T2 weighting is large (as with WM) such that the B signal intensity approaches zero, the resulting B – A image is identical to –A such that conj(B – A)*C/(A*A+ C*C) [Eq.1] has a signal amplitude in the negative half of the [-0.5,0.5] range. With very long T2 values as with CSF, the B signal differs from A only in terms of T1 recovery such that the reconstructed pixels have signal amplitude in the positive half of the [-0.5, 0.5] range.Methods
A Siemens 7T whole body pTX system equipped with 40mT/m, 200mT/m/s gradient coil, 1st-4th degree shim insert and 8×2 transceiver coil (Resonance Research Inc., MA) was used. Operating in multiple transmit mode, RF shimming was performed for a homogeneous B1 distribution, and a 3rd–4th degree shim insert used for B0 shimming as previously described 3,4. As implemented in a 3D modified MP2RAGE (TR/TE=7s/1.63ms, TI1/TI2/TI3=901/1350/2760ms, resolution=0.6×0.6×1.5mm3, acceleration factor of 3 in PE) with an adiabatic refocusing pulse pair (hyperbolic secant with mu=10, 4 cycles) in the T2 preparation, the total acquisition time was ≤11min. With the adiabatic pulses operating at 360° flip angle for both inversion and T2 preparation two refocusing RF pulses, the global SAR remained well below FDA limits 4W/kg per 6min.Results
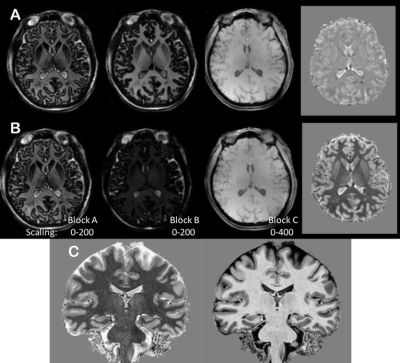
To separately identify the effect of the T2 preparation contrast, Fig. 2A and B shows lower resolution data from the three blocks acquired without and with the T2 preparation module. As expected, the CSF signal in the +T2 preparation (Fig. 2B) block B image is bright while there is less contrast between white and gray matter. Also shown for each set are the calculated images (far right). Fig. 2C shows high resolution coronal images from a control subject and shows excellent resolution of the hippocampal sub-structures.Conclusions
We have implemented a T2 and T1 weighted MRI sequence at 7T that generates T2 contrast assisted with T1 contrast to improve separation between WM, GM and CSF. As performed with an inversion recovery, a matched T1W MP2RAGE contrast image is simultaneously generated. The sequence was implemented with a pTx 8×2 transceiver with excellent SAR efficiency.Acknowledgements
The study is supported by NIH EB011639, EB009871, NS090417, NS081772.References
1. Visser et al., MRM,64:p194-202, 2010.
2. Marques JP et al, Neuroimage,49:p1271-1281, 2010.
3. Hetherington HP et al, MRM,63(1):p9-19, 2010.
4. Pan JW et al, MRM,68:p1007-1017, 2012.
Figures