MR Angiography
1Depts. of Medical Physics & Radiology, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, United States
Synopsis
Traditional clinical MR Angiography (MRA) provides volumetric datasets to characterize the vessel lumen. These MRA techniques can be generally separated into two categories: contrast-enhanced MRA, which requires the venous injection of a paramagnetic contrast agent in form of a Gadolinium (Gd) chelate and non-contrast-enhanced MRA (NCE MRA), which relies on signal properties of the blood or the motion of the blood to create signal differences between the blood pool and the surrounding tissues. The underlying contrast mechanisms of contrast-enhanced (CE MRA), time-of-flight, phase-contrast, and balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP) MRA will be discussed including recent developments in accelerated dynamic contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA), the use of iron-based contrast agents, and velocity-encoded MRI.
Highlights
- MR Angiography relies on endogenous contrast generated by moving spins or blood signal, or exogenous contrast from agents such as Gadolinium or Ferrumoxytol.
- Advances in MR Hardware as well as Acquisition and Reconstruction Methodology have enabled dynamic Contrast-Enhanced MRA at high frames rates.
- 2D PC and 4D Flow MRI adds functional analysis in from of hemodynamic assessment to MRA.
Target Audience
Those with interest in methodology and clinical applications of MR Angiography including physicians and scientists. No basic knowledge of MRA is needed, but basic knowledge of MRI in general is advised.Objectives
- Understand the various origins of MRA contrast mechanisms with and without a contrast agent.
- Understand the issues related to MRA imaging including sequence design, acquisition strategies, and image processing.
- Understand the benefits, pitfalls, and future potentials of these approaches.
- Guide users into tailoring MRA exams to specific clinical questions.
Purpose
Traditional clinical MR Angiography (MRA) provides volumetric datasets to characterize the vessel lumen. These MRA techniques can be generally separated into two categories:
- contrast-enhanced MRA, which requires the venous injection of a paramagnetic contrast agent in form of a Gadolinium (Gd) chelate and
- non-contrast-enhanced MRA (NCE MRA), which relies on signal properties of the blood or the motion of the blood to create signal differences between the blood pool and the surrounding tissues.
These concepts will be reviewed and recent developments in accelerated dynamic contrast-enhanced MRA (CE-MRA), the use of iron-based contrast agents, and velocity-encoded MRI will be discussed.
Methods
Time-of-Flight (TOF) [1] and Phase-Contrast (PC) [2] imaging have been developed as NCE Angiography techniques in the early days of MR imaging. However, widespread clinical adaptation of MRA did not occur until the introduction of CE-MRA [3] in the mid-1990’s with significantly improved robustness from venously injected Gd chelates that result in T1 shortening of the blood pool.
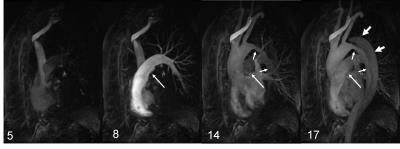
CE-MRA acquisitions either target a single volume at peak enhancement with high spatial resolution or a time-resolved acquisition that compromises spatial and/or temporal resolution for the benefits of a dynamic acquisition similar to x-ray digital subtraction angiography (DSA) as shown in Figure 1. Ferumoxytol is an iron-based contrast agent that is used as an alternative for Gadolinium agents, particularly for patients with renal failure [4].
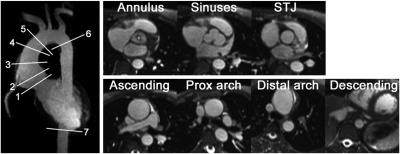
Recent developments have renewed the interest in imaging approaches that do not rely on any external contrast agents [5, 6]. Advances in hardware, especially gradient amplifiers and multi-channel coil technology, have reduced imaging times, improved the signal-to-noise ratio, and reduced artefacts so that NCE MRA has become competitive again. For example, the short repetion times (TR) allow for imaging with the balanced SSFP sequence with or without cardiac gating (see Figure 2). These approaches provide viable alternatives in patients that are at risk for nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) and should not receive a Gd-based contrast agent.
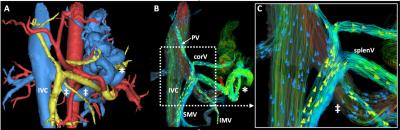
Some MRA approaches provide insights in functional information beyond the standard luminography. For example, arterial spin labeling (ASL) imaging can be used as a 'pseudo arterial injection' by labeling blood in targeted volumes and tracking its distribution over time. Novel '4D Flow MRI' imaging [7] is an extension of traditional PC MRA to capture volumetric velocity vector fields throughout the cardiac cycle, thereby allowing for direct measures of hemdodynamic parameters such as pressure gradient, wall shear stress, pulse wave velocity, kinetic energy, and more [8] (see Figure 3).
Conclusions
This lecture will provide an overview of CE MRA and NCE MRA approaches currently used in clinical practice. The underlying contrast mechanisms of CE MRA, time-of-flight, phase-contrast, and balanced steady state free precession (bSSFP) MRA will be discussed in the context of tailoring MRA exams to specific clinical questions. Current and potential future roles of these approaches in clinical imaging will also be discussed.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] F. W. Wehrli, A. Shimakawa, G. T. Gullberg, and J. R. MacFall, “Time-of-flight MR flow imaging: selective saturation recovery with gradient refocusing,” Radiology, vol. 160, no. 3, pp. 781-5, Sep, 1986. [2] G. L. Nayler, D. N. Firmin, and D. B. Longmore, “Blood flow imaging by cine magnetic resonance,” J Comput Assist Tomogr, vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 715-22, Sep-Oct, 1986.
[3] M. R. Prince, “Gadolinium-enhanced MR aortography,” Radiology, vol. 191, pp. 155-164, 1993.
[4] M. D. Hope, T. A. Hope, C. Zhu, F. Faraji, H. Haraldsson, K. G. Ordovas, and D. Saloner, “Vascular Imaging With Ferumoxytol as a Contrast Agent,” AJR Am J Roentgenol, vol. 205, no. 3, pp. W366-73, Sep, 2015.
[5] A. J. Wheaton, and M. Miyazaki, “Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: physical principles,” J Magn Reson Imaging, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 286-304, Aug, 2012.
[6] M. Miyazaki, and M. Akahane, “Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: established techniques,” J Magn Reson Imaging, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 1-19, Jan, 2012.
[7] L. Wigstrom, L. Sjoqvist, and B. Wranne, “Temporally resolved 3D phase-contrast imaging,” Magn Reson Med, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 800-3, Nov, 1996. [8] M. Markl, A. Frydrychowicz, S. Kozerke, M. Hope, and O. Wieben, “4D flow MRI,” J Magn Reson Imaging, vol. 36, no. 5, pp. 1015-36, Nov, 2012.
Figures