5622
A 35Cl ToRo Resonator System for Preclinical MRI/MRS at 9.4T1Computer Assisted Clinical Medicine,Medical Faculty Mannheim, Heidelberg University, Mannheim, Germany
Synopsis
Chloride (Cl-) is next to the cations Na+ and K+ the most abundant non-organic anion in the mammals. Assessment of chlorine’s (35Cl) concentration in tissue could provide further insights into tissue viability in addition to tissue sodium concentration. Yet, low Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) is challenging for the RF hardware components. To overcome these challenges, a Transmit-only-Receive-only (ToRo) system for 35Cl MRI/MRS at 9.4T was developed comprised of an actively-decoupled linearly-driven 16 leg low-pass Birdcage transmitter coil combined with two different receiver coils. Substantial SNR gain was reached using receive-only elements compared to the Birdcage coil in TxRx mode.
Purpose
Chloride (Cl-) is next to the cations Na+ and K+ the most abundant non-organic anion in the mammals1. Assessment of chlorine’s (35Cl) concentration in tissue could provide further insights into tissue viability in addition to tissue sodium concentration. Furthermore, information regarding physiological processes that involve diverse chlorine channels can be found by evaluating the 35Cl signal of cells in a controlled living environment2. Yet, low Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) is challenging for the RF hardware components. For example, special imaging/spectroscopy techniques, such as Triple-Quantum-Filtering3, require homogenous transmission and high receiver sensitivity. To overcome these challenges, a Transmit-only-Receive-only (ToRo) system for 35Cl MRI/MRS at 9.4T was developed and evaluated in simulations and measurements.Methods
The 35Cl ToRo resonator system is comprised of a
transmission (Tx) coil and two different reception (Rx) configurations. EM
fields of the coils were calculated using FEM simulations (CST AG, Darmstadt,
Germany). Measurements were performed at a 9.4T preclinical MR scanner (Bruker
BioSpec 94/20, Ettlingen, Germany).
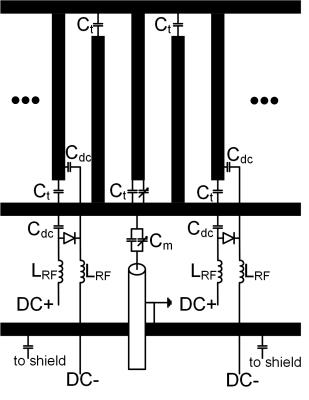
Tx coil: A linearly driven 16 rung low-pass birdcage (BC) coil was
developed to excite the 35Cl nucleus. The BC was tuned to 39.2 MHz (35Cl
resonance frequency at 9.4T) with tuning capacitors arranged alternately to
increase B1+-field homogeneity. Balancing of the coil was
done using a separated ground ring4. Active decoupling was implemented by
shortening 4 rung capacitors of the BC (Figure 1 and 2a). The BC was shielded
using a “Swiss roll” configuration made of copper foil and an FR4 dielectric. B1+-field
homogeneity was evaluated in simulation and measurement using a spherical
phantom (diameter=48mm) filled with 18% saline solution.
Measurement sequence:
2D UTE, TE/TR/FA=0.33ms/100ms/80°, matrix=80x80, FoV=60x60mm², slice=20mm,
Projections=252, TRA=4ms, Avg=4 and TA=1:40min. Simulation and
measurement results were compared using a calibration factor5.
Rx coils: Two different
configurations of Rx only coils (denominated Rx Loop and Rx Loop+BF) were
developed for measurement and in simulation. Rx Loop was made using a doubled
winded silver conductor (diameter=27mm, thickness=2mm) (Figure 2b). Rx Loop+BF consisted
of a doubled winded loop and a butterfly coil made of copper tape
(width=3mm)(Figure2c-e). All Rx coils were equipped with a cable trap, a low
noise preamplifier and actively decoupling unit. Simulation and measurements
were performed using two vials(length=28mm, diameter=6mm) filled with 0.9%
saline solution.
Measurement sequence: 2D UTE, TE/TR/FA =0.62ms/30ms/72°,
matrix=80x80, FoV=80x80mm², slice=8mm, Projections=252, TRA=4ms,
Avg=64, TA=8min.
Results
Tx coil:
A decoupling of 40dB was achieved by shortening 4 tuning capacitors using PIN
diodes. The results of the homogeneity simulations and measurements are
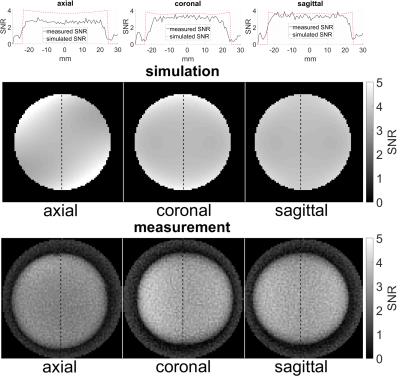
depicted in Figure 3. Simulated and measured SNR show resemblance. Yet, the simulated
SNR was overestimated. Good homogeneity was accomplished in axial, coronal and
sagittal plane over the whole sensitivity volume.
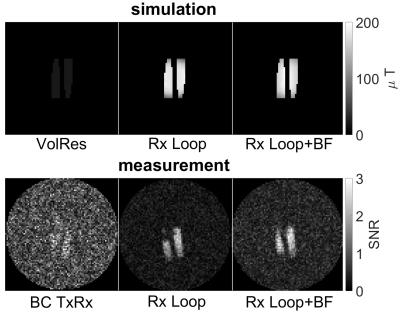
Rx coils: The simulation and measurement results of the BC coil in TxRx mode and the BC coil combined with the different Rx coils are shown in Figure 4. B1--fields increased using the Rx coils for signal reception instead of the volume resonator as expected. The respective SNR measurements revealed the same SNR gain of the Rx coils compared to the BC. The two vials can be well separated using the Rx only coils whereas the vials can hardly be seen using the BC coil in TxRx mode. The noise level of the Rx Loop+BF coil is higher compared to the Rx Loop coil, probably due to coil coupling.
Discussion
By using a BC coil for excitation of the 35Cl nucleus good homogeneity was achieved over a large volume. The extension of the BC coil with Rx only elements increased the SNR performance dramatically. No significant SNR gain was achieved using two receiver channels. The improvement of the Rx coils will be in the scope of future works.Conclusion
SNR gain using a ToRo setup for 35Cl MRI at 9.4T was achieved. Using this RF resonator system it is now possible to design studies with animals and cells in a controlled living environment.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
[1] Baier S, Krämer P, Grudzenski S, et al. Chlorine and sodium chemical shift imaging during acute stroke in a rat model at 9.4 Tesla. Magn Reson Mater Phy.2014;27(1):71-79.[2] Neubauer A, Ruttorf M, Kalaycian R, et al. 23Na Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI) on a High-Density 3d-cell culture on chip (3D-KITChip). ISMRM.2014;22:1278
[3] Gottwald E, Neubauer A, Schad LR. Tracking Cellular Functions by Exploiting the Paramagnetic Properties of X-Nuclei, Assessment of Cellular and Organ Function and Dysfunction using Direct and Derived MRI Methodologies, Dr. Christakis Constantinides (Ed.), InTech,2016.
[4] Streif JU, Lanz T, Griswold M, et al. A coil combination for magnetic resonance perfusion imaging of mice in vivo at 7 T. Rev Sci Instrum.2003:74(5):2843-2848.
[5] Stumpf C, Rehner R, Martius S, et al. Calibration of electromagnetic field simulations of MR coil arrays for accurate quantitative comparison with the measured image SNR. ISMRM.2012.20:2684.
Figures