5574
Gadolinium Calculator for Safe Dosing of Gadolinium Based Contrast Agents1Radiology, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, United States, 2Medical Physics, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI, 3Department of Computer Science, University of California, Santa Cruz
Synopsis
In this work, we describe the design, implementation, and utilization of an online and smartphone gadolinium calculator used to calculate gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA) dose. By providing a readily available, reliable, and rapid means of calculating the volume of a GBCA, we aim to ensure accurate dosing so as to avoid accidental over- or under-dosing. Utilization tracking demonstrated progressively increasing use of the online gadolinium calculator with a total of 22,074 page visits from 68 countries, logged during a 9-month tracking period.
Introduction
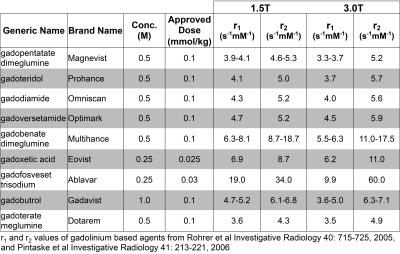
The introduction of gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCAs) in 1987 ushered in a new era of diagnostic capabilities for MRI. Table 1 contains a list of currently approved GBCAs, listed in the order of FDA approval in the United States [1,2]. The first five approved GBCAs had identical formulation (0.5M) and approved dose (0.1mmol/kg). This uniform formulation and dose led to the unfortunate and widespread terminology “single dose”, “double dose”, etc, which can lead to potential dosing errors and confusion [3]. The introduction of gadoxetic acid (0.25M, 0.025mmol/kg), gadofosvesset trisodium (0.25M, 0.03mmol/kg), and gadobutrol (1.0M ,0.1mmol/kg) created real opportunities for dosing errors, due to variability in formulation and approved doses between the various approved agents.
Motivated by several “near-miss” dosing errors in our practice, we created an online and mobile app gadolinium calculator to assist clinical and research professionals in calculating appropriate doses of approved GBCAs. The purpose of this work is to describe the design, implementation, and utilization of an online and mobile gadolinium calculator to calculate accurate and appropriate doses of GBCAs.
Materials and Methods
The following equation is used to calculate the volume, V (ml) of a GBCA to be injected into a subject:
\[V=\frac{D \times W}{C}\]
where D is the dose of gadolinium (mmol/kg), W is the patient weight (kg), and C is the agent concentration (M). Despite the simplicity of this equation, it is our experience that MRI technologists / radiographers in a busy clinical or research environment do not utilize this formula. Use of this formula also requires lookup tables that contain GBCA doses and formulations. For this reason, we developed an online gadolinium calculator to calculate the appropriate GBCA dose without the need for such tables.
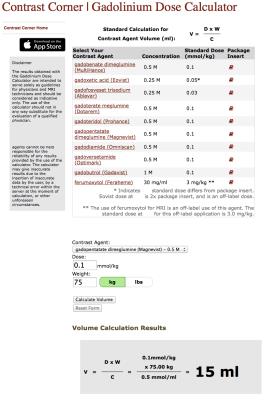
Online Gadolinium Calculator: Working with our information technology (IT) team, we first developed an online gadolinium calculator. The calculator included the formulations for all available FDA approved GBCA agents, as well as links to up-to-date package inserts for each agent. Figure 1 contains screenshots of the website, which is available at www.radiology.wisc.edu/contrastCorner/GadCalc.php. For excessive patient weight or patient dose, a pop-up warning is provided, to ensure that the user has entered the correct dose and/or patient weight.
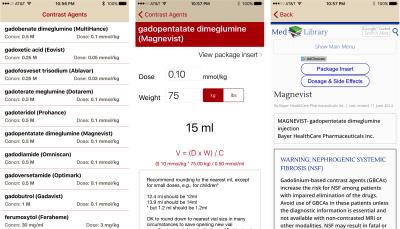
Mobile App: The online gadolinium calculator gained immediate traction and was widely adopted by all technologists in our practice. To expand the functionality of this calculator, a free mobile app (iPhone) was developed, based on the website design. Figure 2 contains screenshots of the mobile gadolinium calculator app. The gadolinium calculator app can be downloaded from iTunes from the following link https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/gadcalc/id1051070769?mt=8&ign-mpt=uo%3D4.
Utilization: In order to determine utilization of the online
gadolinium calculator, utilization was tracked using Google Analytics. This
report contains the total number of page visits and unique page visits, and
origin of these visits. The number of iPhone downloads from iTunes was also
recorded.
Results
Qualitatively, the gadolinium calculator has been widely adopted at all inpatient and outpatient sites at our home institution and is used uniformly by our clinical and research MRI technologists. Workstations with internet connectivity are located adjacent to all MRI scanners facilitating its use. Further, many outreach sites served by our institution have also adopted the use of the online gadolinium calculator.
The online gadolinium calculator was first implemented on February 10, 2014, but was tracked using Google Analytics starting on February 1, 2016. A total of 22,074 page visits and 9,841 unique page visits occurred during this time. Unique page visits were logged from 68 countries, although 92.9% of unique visits originated from the US, and 76.2% from our home state, suggesting that the majority of visits may originate from our institution or outreach sites. Figure 4 plots the number of unique page visits between February 1, 2016 and October 31, 2016. A progressive increase in utilization of the on-line gadolinium calculator was observed.
The iPhone gadolinium calculator app was
released on iTunes on November 24, 2015. Since its release there have been 239
unique installations from five countries, 55% from within the United States.
Discussion
In this work we report the design, implementation, and utilization of an online and mobile gadolinium calculator, aimed at providing an easy, reliable, and accurate method of calculating GBCA dose. The calculator has been widely adopted in our own practice, and we have successfully avoided GBCA dosing errors since the adoption of this technology. It is our aim that free and widely available tools such as the gadolinium calculator will ensure safe and appropriate dosing of GBCAs. Future work will develop an Android-based mobile app.Acknowledgements
The University of Wisconsin wishes to thank GE Healthcare and Bracco Diagnostics for their research support.References
[1] Rohrer M, Bauer H, Mintorovitch J, Requardt M, Weinmann HJ, “Comparison of magnetic properties of MRI contrast media solutions at different magnetic field strengths.” Invest Radiol 2005 40(11): 715-24.
[2] Pintaske J, Martirosian P, Graf H, Erb G, Lodemann KP, Claussen CD, Schick F, “Relaxivity of Gadopentetate Dimeglumine (Magnevist), Gadobutrol (Gadovist), and Gadobenate Dimeglumine (MultiHance) in human blood plasma at 0.2, 1.5, and 3 Tesla.” Invest Radiol 2006 41(3): 213-21.
[3] Reeder SB, “Gadolinium-based contrast agents: what does "single-dose" mean anymore?” J Magn Reson Imaging 2014 39(6): 1343-5.
Figures