5565
SKIN ENHANCEMENT WITH GADOLINIUM BASED CONTRAST AGENTS1Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine, Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto, Japan, 2Human Brain Research Center, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan
Synopsis
Skin tissue showed enhancement after GBCA administration. This phenomenon was confirmed by profile curve analysis. Subtraction image between pre-post contrast was calculated after image registration. This subtraction image showed distinct contrast effect of the skin tissue and may be helpful for the clinical diagnosis.
BACKGROUND and PURPOSE
In contrast MRI examination of the brain, the image obtained by subtracting the image before contrast from the post-contrast image, were useful for the detection of lesions showing enhancing effect by gadolinium based contrast agent (GBCA), such as metastatic brain tumor. Viewing this subtraction MR image in the maximum intensity projection (MIP) method, signal enhancement was observed in the skin tissue. Skin tissue appears to show contrast with GBCA. The purpose of this study was, first, whether the signal enhancement of skin tissue after GBCA administration is observed, and verified using profile curve analysis method. Then, the subtraction MR image using the MIP method was evaluated to examine the clinical usefulness of a characteristic MRI imaging findings indicated by the skin tissues other than the brain.
METHODS
This study was carried out as a
retrospective study. MRI used in this study was as follows. 3-T or
1.5-T MAGNETOM TRIO, SKYRA, PRISMA and AVANTO (Siemens Healthcare GmbH,
Germany). Dedicated head coil was used in each MR examination. The
subject patient using MRI, imaging of the head region was performed, including
brain tissue and the surrounding skin tissue. Three-dimensional T1-weighted
image (MPRAGE or VIBE) were taken before and after GBCA administration.
Sagittal image was obtained in the same FOV size and position. Spatial resolution
was 0.9mm isotropic. Before creating the subtraction image, image registration
processing of the before and after contrast image was performed. GBCA in
this retrospective study the following five types were used. Gd-DTPA,
Gd-DTPA-BMA, Gd-HP-DO3A, a Gd-BT-DO3A and Gd-DOTA. GBCA of the standard dose in
Japan was used. Per body weight 1kg, it was 0.1mmol or 0.05mmol. For displaying
subtraction image, AquariusNet software (TeraRecon, Inc., USA) was used. Displaying
the entire head in the MIP image, then, changing the slab thickness to 5mm from
10mm, the whole head in the three directions of view was used. Evaluation of
subtraction images were performed by a radiologist with 20 years of experience.
The MRI images were evaluated for the following. Blood vessels of the brain
tissue, in particular deep vein and choroid plexus, of the organization of the
contrast effect, neoplastic lesions such as metastatic brain tumor, dura mater
tissue of the skull inner surface and of the entire head skin. Especially for
evaluation of the contrast effect of the skin, it was confirmed by performing a
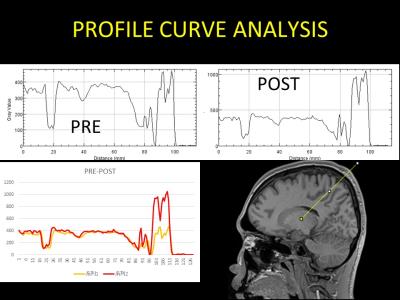
profile curve analysis whether the signal increase in the skin area was
observed. Further, using the MIP image of a thin slab thickness, investigated
clinical utility with the head skin contrast effect.
RESULTS
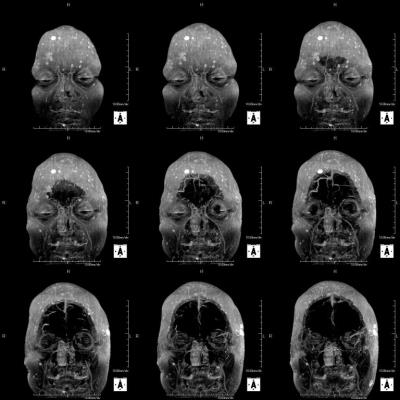
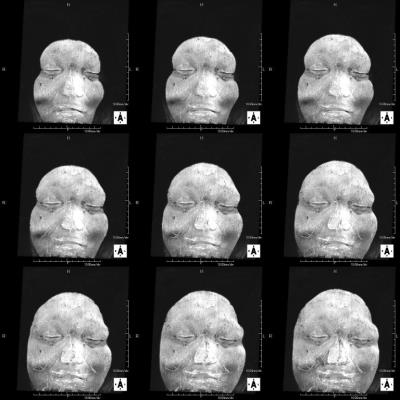
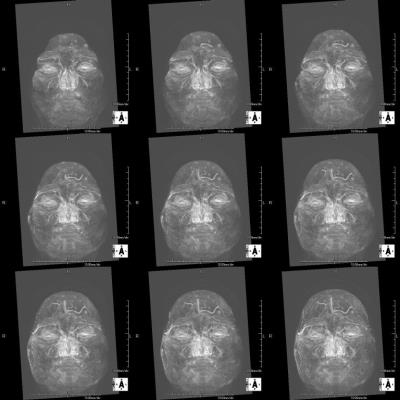
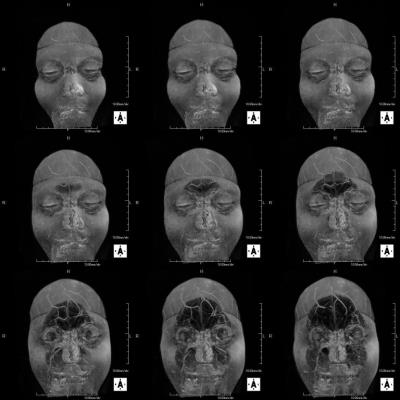
In the 3-D T1-weighted image after contrast, signal enhancing effect of the head skin was observed. In the subtraction image after image registration process, contrast effect was not observed in the brain tissue. In contrast, blood vessels, showed a clear contrast effect, especially deep vein and the choroid plexus. Also in all the static magnetic field strength and with all receiving coils, contrast enhancement of the head skin was recognized. Contrast enhancement of the skin in all five GBCA was observed. Strong contrast effect was observed in the tumor marginal part in metastatic brain tumor. In dura mater tissue of the skull inner surface, uniform thick contrast effect was observed. Head skin showed a strong contrast effect in the MIP image. In the profile curve analysis, a strong enhancing effect on the head skin dermis area was recognized (Figure 5). In some cases, a multiple small point-like defects area were observed in the head skin contrast effect (Figure 2). In contrast, in another cases, regions exhibiting multiple strong contrast effect spots on the head skin were observed (Figure 1,3,4).DISCUSSION
After GBCA administration, a strong contrast effect on the skin was observed. Contrast effect of the skin was not uniform, and cases showing defects or strong contrast effect. In the literature reports of biodistribution after GBCA administration, kidney, or other solid organs such as the spleen and liver, intestinal tract and heart has been reported. Among them, GBCA distribution to the skin has also been reported. So far, the literature were missing the evaluation of this skin contrast effect on the subtraction image. In this study, characteristic findings of the head skin contrast effect was observed. This point may suggest the possibility of skin contrast effect has clinical utility. By superimposing a further study in the future, there may be a possibility that the skin-contrast effect indicates a diagnostic utility.CONCLUSION
In conclusion, after GBCA administration strong enhancing effect on the skin was seen. Skin contrast effect was considered as potentially exhibiting clinical utility.Acknowledgements
No acknowledgement found.References
1. Abraham JL, Thakral C. Tissue distribution and kinetics of gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. European journal of radiology. 2008 May;66(2):200-7. PubMed PMID: 18374532. Epub 2008/04/01. Eng.
2. Aime S, Caravan P. Biodistribution of gadolinium-based contrast agents, including gadolinium deposition. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI. 2009 Dec;30(6):1259-67. PubMed PMID: 19938038. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2822463.
3. Barral JK, Bangerter NK, Hu BS, Nishimura DG. In vivo high-resolution magnetic resonance skin imaging at 1.5 T and 3 T. Magnetic resonance in medicine. 2010 Mar;63(3):790-6. PubMed PMID: 20146351. Pubmed Central PMCID: 2832104.
4. Bellin MF, Van Der Molen AJ. Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: an overview. European journal of radiology. 2008 May;66(2):160-7. PubMed PMID: 18358659.
5. Bittoun J, Querleux B, Darrasse L. Advances in MR imaging of the skin. NMR in biomedicine. 2006 Nov;19(7):723-30. PubMed PMID: 17075954.
Figures